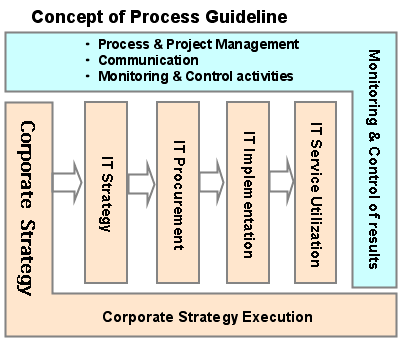
>Top Glossary:
- 0.6 Power Law
- 5E and 2A
- 6C of Community
- 7P of Marketing
- ABC = Activity Based Costing
- AC = Actual Cost
- ACWP = Actual Cost of Work Performed
- AD = Activity Description
- ADM = Arrow Diagramming Method
- AF = Actual Finish Date
- Active Listening
- AOA = Activity-On-Arrow
- AON = Activity-On-Node
- APQC = American Productivity & Quality Center
- AS = Actual Start Date
- Assumptions analysis
- BAC = Budget At Completion
- Backward Pass
- Baseline
- BCWP = Budgeted Cost of Work Performed
- BCWS = Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled
- BSC = Balanced ScoreCard
- Calendar Unit
- CAP = Control Account Plan
- CCB = Change Control Board
- Chart of Accounts
- Chaos
- CMMI = Capacity Maturity Model Integrated (= ISO/IEC 15504)
- COBIT = Control Objectives for Information
and related Technologies
- COBIT Maturity Model
- Communication
- Context
- Contingency Planning
- Contingency Reserve
- >Top
Contract
- Control
- Control Chart
- Core Competence
- COSO = Committee of Sponsoring Organization of the Treadway Commission
- Cost of Quality
- CPFF = Cost Plus Fixed Fee
- CPI = Cost Performance Index
- CPIF = Cost Plus Incentive Fee
- CPM = Critical Path Method
- CPO = Chief Project Officer
- CSF = Critical Success Factor
- CSO = Chief Strategic Officer
- CV = Cost Variance
- DD = Data Date
- Crashing
- Debt Equity Ratio
- Decision Tree Analysis
- Deliverable
- Domain
- DU = Duration
- Dummy Activity
- EAC = Estimate At Completion
- EF = Early Finish Date
- Effort
- EPC =Engineering , Procurement & Construction
- ES = Early Start Date
- ETC = Estimate to Complete
- EV = Earned Value
- EVM = Earned Value Management
- Exception Report
- Exit
- Expected Monetary Value
- Fast Tracking
- >Top
FF = Finish-to -Finish
- FFP = Firm Fixed Price
- FFIF = Fixed Price Incentive Fee
- Float
- FMEA = Failure Mode & Effects Analysis
- Forward Pass
- Front End Planning
- FS = Finish-to-Start
- FTA = Fault Tree Analysis
- Function Points Method
- GERT = Graphical Evaluation & Review
- Grade
- Hammock
- Hanger
- IDEF
- IFB = Invitation For Bid
- ID = Influence Diagram
- Initiation
- IRR = Internal Rate of Return
- ITIL = IT Infrastructure Library
- IT Maturity
- KGI = Key Goal Indicator
- KPI = Key Performance Indicator
- Lag
- Lead
- Lessons Learned
- LFD = Late Finish Date
- LOE = Level of Effort
- Logical Relationship
- Loop
- Lot Factor
- LSD = Late Start Date
- MECE = Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive
- Milestone Schedule
- Missing links of IT failure
- Mission (6W1H)
- Monte Carlo Analysis
- >Top
Monitoring
- Moral Hazard
- MPM = Modern Project Management
- Node
- OBS = Organizational Breakdown Structure
- Organizational Planning
- Parametric Estimating
- Pareto Diagram
- Pass Convergence
- Payback Period
- PC = Percent Complete
- Performing Organization
- Phased Termination Review
- PM Theory
- Predecessor Activity
- PDM = Precedence Diagramming Method
- PERT = Program Evaluation and Review Technique
- PFD = Planned Finish Date
- PFI = Private Finance Initiative
- PMP = Project Management Professional
- PPM = Product Portfolio Management
- Probability and Impact Matrix
- Project Charter
- PSD = Planned Start Date
- PV = Planned Value
- QA = Quality Assurance
- RAM = Responsibility Assignment Matrix
- RDU =Remaining Duration
- Real Option
- Residual Risk
- Resource Leveling
- >Top
Resource-Limited Schedule
- Retainage
- Rework
- RFP = Request For Proposal
- RFQ =Request For Quotation
- Risk
- Risk Database
- Risk Event
- Risk Management Plan
- Risk Mitigation
- Risk Transference
- SBU = Strategic Business Unit
- Scenario
- Scope Planning
- S-Curve
- SECI = Socialization, Externalization, Combination, Internalization
- Sensitivity Analysis
- SF = Start-to-Finish
- Should-Cost Estimate
- Six Sigma
- SMART = Specific, Measurable, Agreeable, Realistic, Time bound
- Solicitation
- SPA = Software Process Assessment
- SPI = Schedule Performance Index
- SPDLI = Strategy, Plan, Do, Learning, Innovation
- SS = Start-to-Start
- Stake
- Structured Walk-through
- SV = Schedule Variance
- SWOT = Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat
- Task
- T&M = Time and Material contracts
- TCD = Target Completion Date
- TFD = Target Finish Date
- TQM = Total Quality Management
- Trigger
- TSD = Target Start Date
- Value Proposition
- >Top
VE = Value Engineering
- WBS = Work Breakdown Structure
- Workaround
- Work Item
- Work Package
|
*Source:
mostly from PMBOK guide (2000 version) ,
P2M guide book (2001) , COBIT, ITC Process Guideline, Wikipedia,etc.
- 0.6乗則:一般的に生産設備など生産プロセスが変わらない場合、建設コストはベキ乗比例に依って変動する。n=0.6を適用する生産設備が多い。
- 5E + 2A for Assessment: Efficiency, Effectiveness, Earned Value,
Ethics, Ecology, and Accountability, Acceptability
- 6C:Communityの人間・情報・文化的な属性には、Context (全体に共有する意義), Creativity, Collaboration,
Communication, Contents, Concentrationがある。
- マーケティングの7P:Product (製品), Price (価格), Place (チャネル), Promotion (販売促進),
Promise (顧客の信頼), Provider (サポート), Performance (顧客満足度)
- 活動基準原価計算:Robert S. Kaplan & Robin Cooperによるコスト計算法の一つ。活動が資源を消費し、製品が活動を消費するという二段階の配賦を行う。多品種少量生産時代の間接費配賦を正確化した。Activityに応じてCost
driverを決めて活動の間接費を計測する (例:営業訪問回数)。Cf: ABM (Activity Based Management)
- 実コスト (Total costs budgeted within the planned value and earned
value)
- 作業完了実コスト、実績コスト (= now replaced with the term Actual Cost)
- アクティビティ記述 (The activity description normally describes the scope
of work of the activity.)00
- アロー・ダイヤグラム法 (The tail of the arrow represents the start, and the
head represents the finish of the activity. The length of the arrows
does not represent the expected duration of the activity. Activities
are connected at points called nodes to illustrate the sequence
in which the activities are expected to be performed.)
- 実終了日
- アクティブ・リスニング (傾聴)
- アクティビティ・オン・アロー
- アクティブティ・オン・ノード
- 米国生産性品質センターの標準的なビジネスプロセスモデル:7つの基幹業務プロセス (顧客・戦略策定・設計・販売・生産出荷・サービス・代金回収)と6つの支援業務プロセス
(人材・情報・財務・環境・生涯・改革)から成る。
- 実開始日
- 前提条件の分析 (explores the assumptions' accuracy and identifies risks
to the project from inaccuracy, inconsistency, or incompleteness
of assumptions.)
- 完成時総予算
- 復路時間計算 (The calculation of late finish dates and late start dates
for the uncompleted portions of all network activities. Determined
by working backwards through the network logic from the project's
end date.)
- ベースライン (The original approved plane for a project, a work package,
or an activity)
- 完了作業予算コスト、出来高 (Now called EV)
- 予定作業予算コスト
- バランススコアカード (introduced by Robert
Kaplan & David Norton in 1992. It balances a financial perspective
with customer, internal process, and learning & growth perspectives.)):財務、顧客、業務
(内部プロセス)、人材 (学習と成長)の4つの視点からバランスよく評価する。過去 (財務)、現在 (顧客・内部プロセス)、未来
(学習と成長)
- カレンダー単位 (The smallest unit of time used in scheduling the project;
hours, days, or weeks, or even in minutes.)
- コントロール・アカウント・プラン (Previously called a Cost Account Plan. A management
control point where the integration of scope, budget and schedule
takes place, and where the measurement of performance will happen.)
- 変更管理委員会 (A formally constituted group of stakeholders responsible
for approving or rejecting changes to the project baselines.)
- 勘定科目表 (Any numbering system used to monitor project costs by category;
e.g. labor, supplies, materials, and equipment.)
- カオス:周期性を持たず、一見、不規則かつ乱雑な挙動を示す軌道をもつ系をいう。
- ソフトウェア能力成熟度モデル:プロセス改善の国際標準でベンダーの成熟度を示す。CMMの後継。CMM V1.0は1987~1997、CMM
V1.1は2002に、CMM V1.2は2006.8にリリース。CMMIはSEI (Software Engineering Institute)が策定した総合的指標。
- ITガバナンス実践規範 (COBIT):ISACA (Information
Systems & Audit Association)が決めたITを管理するためのオープンスタンダード。CSF, KGI,
KPIを定めている。 34のITガバナンス領域について6段階の成熟度で評価する。PO=Plan & Organize,
AI= Acquire & Implement, DS=Delivery & Support, ME=Monitor
& Evaluate
- COBITの6つの成熟度モデル:Level-0: Non-existent 存在しない, Level-1: Initial
初歩的, Level-2: Repeatable 反復可能, Level-3: Defined 定義された, Level-4:
Managed 管理された, Level-5: Optimized 最適化された
- コミュニケーション:1) 他者を理解し、理解されようとする過程の動き、2) 言語シンボルを通じて反応を引き出す過程、3) 記号を選択し、創出、伝達することで、伝達者が意図した意味を受け手が近くできるにする過程。
- コンテキスト:コミュニケーションに影響する物理的、社会的、心理的、時間的な環境を指す。
- コンティンジェンシー計画 (特定リスク事象の場合でもプロジェクトを成功させる代替戦略)
- コンティンジンシー予備 (リスクに対応するプロジェクト上乗せ金額や時間)
- 契約:調達には、定額請負契約 (一括請負)、実費償還契約、単価契約のいずれか、またはこれらの組合せの契約形態がある。
- コントロール (Process of comparing actual performance with planned performance,
analyzing variances, evaluation possible alternatives, and taking
appropriate corrective action as needed)
- 管理図 (A graphic display of the results, over time and against established
control limits, of a process. it is used to determine if the process
is in control or in need of adjustment.)
- コア・コンピタンス戦略:Garyt Hamel, C.K. Prahaladが定義。既存のCC × 既存市場=レバレッジ戦略、既存CC
× 新規市場=空白エリア、新規CC × 既存市場=プレミアムプラス10、新規CC × 新規市場=巨大なビジネスチャンス
- 米国トレッドウェイ委員会内部統制フレームワーク
- 品質コスト (The cost incurred to ensure quality. )
- コスト・プラス固定費 (The buyer reimburses the seller for the seller's allowable
costs, and the seller earns its profit if it meets defined performance
criteria.)
- コスト効率指数 (実コストに対比したEVのコスト効率; CPI = EV / AC)
- コスト・プラス・インセンティブフィー (Allowable cost + Incentive)
- クリティカルパス法 (to predict project duration
by analyzing which sequence of activities has the least amount of
scheduling flexibility. Early dates are calculated by means of a
forward pass, using a specified start date. Late dates are calculated
by means of a backward pass, starting from a specified completion
date.)
- 重要成功要因:COBIT定義のITプロセスを成熟度レベル毎に適正に実行するための成功要因。
- チーフ・プロジェクト・オフィサー、プロジェクト総括責任者
- 経営戦略責任者:IT戦略を統轄し、経営を支援する責任者。日本ではまだ少ない。
- コスト差異 (CV = EV - AC)
- データ日付 (The date at which, or up to which, the project's reporting
system has provided actual status and accomplishments. Also called
as-of date.)
- クラッシング(最小コストで、最大の所要時間短縮)
- 債務資本比率:負債の自己資本に対する比率。この比率が高いとレバレッジ度は高くなり、財務内容が不安定化する。
- デシジョンツリー分析 (incorporates probabilities or risks that the costs
or rewards of each logical path of events and future decisions.)
- 要素成果物 (Any measurable, tangible, verifiable outcome, result, or
item that must be produced to complete a project.)
- ドメイン:Derek.F. Abelの定義:ドメインには顧客の軸 (市場)、技術の軸、機能の軸3つの決定要因がある。どのような顧客に対し(whom)、どのような技術をもって(how)、どのような利便性・満足(what)を提供していくのかCustomer,
Technology, Functionを定義。それぞれの軸に対し、特化戦略 (少数セグメント対象 Niche player)、差別化戦略
(事業内の差別化 Challenger)、非差別化戦略 (広範囲に事業展開 Leader)、さらに経済性・模倣戦略(Follower)
- 所要時間
- ダミー・アクティビティ (An activity of zero duration, which is used when
logical relationships cannot be completely or correctly described
with regular activity arrows.)
- 完成時総コスト見積
- 最早終了日
- 作業工数 (人・時、人・日など) (The number of labor
units required to complete an activity.)
- ターンキー契約。プラント契約などで、設計、調達、据付工事までの一括請負契約という。
- 最早開始日
- 残作業コスト見積、今後必要コスト
- アーンド・バリュー (The physical work accomplished, per the authorized
budget for this work. The sum of the approved cost estimates for
activities. Previously called the budged cost of work performed,
BCWP)
- アーンド・バリュー・マネジメント (It compares the amount of work that was planned
with what was actually earned and with what was actually spent to
determine if cost and schedule performance are as planned.)
- 例外報告書 (Document that includes only
major variations from plan, rather than all variations.)
- 退出:プロジェクトの終了(Close Out)をプロジェクト主体の立場からExitと呼ぶ。任意の時点でExitできることを意味する。
- 期待金額値 (発生確率×損失額)
- ファスト・トラッキング (Compressing the project schedule by overlapping activities
that would normally be done in sequence, such as design and construction.
CFM: concurrent engineering)
- 終了ー終了関係
- 完全定額
- 定額インセンティブフィー
- フロート (The amount of time that an activity may be delayed from
its early start without delaying the project finish date. CFM. Slack)
アクティビティまたはパスが所要期間から遅延した場合に、他に影響を及ぼさない余裕のこと。全体フロート (全体の余裕) と自由フロート
(個々の余裕) とがある。
- 故障モード影響解析:設計の不完全性や潜在的欠点を見出すために構成要素の故障モードとその上位アイテムへの影響をボトムアップ的に解析する技法
- フォワード・パス (往路時間計算) (the calculation of the early start and early
finish dates for the uncompleted portion of all network activities.)
- フロントエンド・プラニング:プロジェクトは時間経過とともに消費される資源は幾何級数的に増大し、蓄積された情報量も成果物も増大する。後ほどインパクトが大きくなる。従って、プロジェクト初期段階で、人を含む、より綿密な計画を作成する手法
- 終了ー開始関係
- 好ましくない事象について、その発生の経過に遡って樹形図に展開し、発生経路、発生原因、発生確率をトップダウン的に原因を解析する技法
- ファンクション・ポイント法:ソフトウェアの規模はソースコードの行数ではなく、実現される機能の数を基に算出する方法。あるソフトウェアのFunction
Point(FP)は、FP = K × (Pi+Po+Pq+Pf+Pe) となる。Piは入力数、Poは出力数、Pqはユーザからの問い合わせ数、Pfはデータとして利用されるファイル数、Peは外部インターフェイス数。
- ガート (ネットワーク分析手法の一つ)
- 等級 (A category or rank used to distinguish items that have the
same functional use, but do not share the same requirements for
quality.)
- ハンモック (An aggregate or summary activity. A hammock may or may
not have an internal sequence.)
- ハンガー (An unintended break in a network path. Hangers are usually
caused by missing activities or missing logical relationships.)
- Integrated DEFinition: プロセスを相互作用するアクティビティの集合としてモデル化、関係を矢印で表現するシステムの分析手法
- 入札招請書 (Equivalent to Request for Proposal
- インフルエンス・ダイヤグラム:競争優位を出発点として、収益をもたらし、それが投資の要素となり、活動レベルと結びつくことで、競争優位が得られる。矢印の始点が原因であり、終点が結果となるPositive
feedbackとなる。
- 立ち上げ (Authorizing the project or
phase)
- 内部収益率:その投資が稼働する各年毎に収益の現在価値の合計と投下した資本の現在価値とが等しくなるような利益率を求めることで、プロジェクトの可否を判断する。
- ITインフラストラクチャ・ライブラリィ:英国OGC=Office of Government Commerce が索敵したコンピュータシステムの運用管理業務に関する体系的なガイドライン。サービスサポートとサービスデリバリの2つの領域から構成。
- IT成熟度:= IT governance × IT literacy × IT environment × IT service
utilization
- 重要目標達成指標:何を達成するかを示す尺度
- 重要成功業績評価指標:ITプロセスがどのように実行されるかを示す尺度
- ラグ (A modification of a logical relationship that directs a delay
in the successor task.)
- リード (A modification of a logical relationship that allows an acceleration
of the successor task.)
- 教訓 (プロジェクト記録の一つ)
- 最遅終了日
- 間接作業 (Support-type activity; e.g. vendor or customer liaison that
does not readily lend itself to measurement of discrete accomplishment.)
- 論理的順序関係 (A dependency between tow
project activities:
- FS (Finish-to-Start): The initiation of work of the successor
depends upon the completion of work of the predecessor.
- FF (Finish-to-Finish): The completion of the work of the successor
depends upon the completion of work of the predecessor.
- SS (Start-to-Start): The initiation of work of the successor
depends upon the initiation of the work of the predecessor.
- SF (Start-to-Finish): The completion of the successor depends
upon the initiation of the predecessor.
- ループ (A network path that passed the same node twice. Loops cannot
be analyzed using traditional network analysis techniques. loops
are allowed in graphical evaluation and review technique.)
- ロットファクター:製品調達で、多数個注文した方が安価になることをいう。
- 最遅終了日
- ミーシー:論旨思考のルール:相互に排他的で重複が無く、かつ全体が網羅されていること。
- マイルストーン・スケジュール (A summary-level schedule that identifies the major
milestones.)
- IT失敗のミッシング・リンク:1) 経営改革とIT活動の乖離、2) IT活動の各段階の分断、3) 利害関係者のdiscommunication
- ミッションの表現:Who (所有者), What (問題と解決), When (始まりと終わり), Why (意義), How
(エンジニアリング), Which (方向性・選択), Whom (ステークホルダ)
- モンテカルロ法 (to perform a project simulation many times to calculate
a distribution of likely results.)
- 監視 (Capture, analysis, and reporting of project performance, usually
as compared to plan)
- モラルハザード:貸し手と借り手の情報が非対称的である場合、借り手がその立場を利用して、金融貸借において有利な行動をとるリスクをいう。広義には倫理観の欠如。
- モダン・プロジェクトマネジメント (A term used to
distinguish the current broad range of project management; scope,
cost, time, quality, risk, etc.)
- ノード (A junction point joined to some or all of the other dependency
lines.)
- 組織ブレークダウン・ストラクチャ
- 組織計画 (プロジェクトでの役割、責任、報告関係を文書化)
- 係数見積 (実績データと変数との統計関係を用いた見積)
- パレート図 (A histogram, ordered by frequency of occurrence)
- パス収束 (The node in the schedule where parallel paths merge or join.
At that node, delays or elongation of any converging path can delay
the project.)
- 回収期間:プロジェクト投資の回収期間を、予想されるキャッシュフローの総和が初期投資に等しくなる期間を指す。その後のキャッシュフローや金の現在価値など考慮しないシンプルな投資回収算出法。
- 出来高パーセント
- 母体組織 (The enterprise whose employees are most directly involved
in doing the work of the project.)
- フェーズ終了時レビュー:下流のフェーズへの移行をスムーズに行うために、そのフェーズの成果物を対象に実施されるレビュー。
- PM理論:リーダーシップの類型化。集団機能は、P機能 (Performance、叱咤激励) とM機能 (Maintenance、ねぎらい)とから成る。生産性は、短期的にはPM>Pm>pM>pmだが、長期的にはPM>pM>Pm>pmと言われる。
- 先行アクティビティ (Activity that enters a node, or 'from' activity)
- プレシデンス・ダイヤグラム法 (Activities are linked by precedence relationships
to show the sequence in which the activities are to be performed.)
- パート (遂行評価図)
- 計画終了日
- PFI、公共施設の整備のための資金調達。完工後の運営も民間委託することで、財政負担を軽減する。PPP = Public &
Private Partnershipともいう。
- プロジェクト・マネジメント・プロフェッショナル
- プロダクト・ポートフォリオ・マネジメント:市場の成長率を縦軸に、市場シェアを横軸にとり、SBUをプロットする。1) 低成長シェア大:金のなる木
Cash cow、2) 低成長シェア小:負け犬 Dogs、3) 高成長シェア小: 問題児 Question mark、4) 高成長シェア大:花形製品
Star。負け犬は撤退し、金のなる木からの収益を問題児に投入し、花形に育てる投資戦略。
- 発生確率影響度マトリックス (to determine whether a risk is considered low,
moderate, or high by combining the two dimensions of a ris1k, its
probability of occurrence, and its impact on objectives if it occurs.)
- プロジェクト憲章 (A document issued by senior management that formally
authorizes the existence of a project.)
- 計画開始日
- 計画価値
- 品質保証
- 責任分担マトリックス
- 残余期間 (アクティビティの残余部分を完了するのに必要な時間)
- リアルオプション法:従来のNPV法が、投資案件を現在価値だけで捉え、過小評価しがちなのに対し、これは投資の延期、拡大縮小、撤退といった意思決定の柔軟性や選択権をも価値として捉え、投資案件全体の価値を評価する特徴がある。オプション行使による柔軟な対応:延期
(Postpone)、拡大 (Expand)、縮小 (Contract)、撤退 (Abandon)、段階 (Time to Build)、転用
(Transfer)、中断 (Shutdown & Restart)、解約 (Cancellation)
- 残余リスク (リスク対応策実施後も残存するリスク)
- 資源平準化 (スケジュールを資源管理を考慮して行うネットワーク分析の一つ)
- 制限制約型スケジュール
- 留保金 (A portion of contract payment that is held until contract
completion to ensure full performance of the contract terms.)
- 手直し (Action taken to bring a defective
or nonconforming item into compliance with requirements or specifications.)
- 提案依頼書
- 見積依頼書
- リスク:f(リスク事象 Risk event × 発生確率 Probability × インパクト Amount at stake)
- リスクデータベース (An output of the risk monitoring and control process.)
- リスク事象 (A discrete occurrence that may affect the project for better
or worse.)
- リスク・マネジメント計画書 (Documents how the risk management processes will
be carried out during the project. The output of risk management
planning.)
- リスク軽減 (to reduce the probability and/or impact of a risk to below
an acceptable threshold.)
- リスク転嫁 (to shift the impact of a risk to a third party together
with ownership of the response.)
- 戦略的事業単位:事業単位がマネジメントの観点からの組織単位に対し、同一の事業特性をもつ事業 (製品群)を基に全社的な戦略実現の観点から再設定した組織単位。Cf:
Product portfolio
- シナリオ:現状(As-is)からあるべき姿(To-be)へのストーリとして描く表現形式。問題設定
(Issue setting)、問題解決の教示 (Solution implication)、実現の道筋 (Roadmap)、方法論(Methodology)、その効果(Performance)
- スコープ計画 (プロジェクト作業を段階的に詳細化するプロセス)
- Sカーブ (Graphic display of cumulative costs, labor hours, percentage
of work, etc; flatter at he beginning and end, steeper in the middle)
Cf: Front End Planning
- SECIモデル:野中郁次郎理論:Socialization (共同化=暗黙知を獲得伝達), Externalization
(表出化=暗黙知を形式知化), Combination (連結化=形式知同士を組み合わせて新たな形式知を創造), Internalization
(内面化=利用可能な形式知を個人が実践し、暗黙知として体得)
- 感度分析:合理的な前提条件の下での経済性評価(Base Case)に対し、前提条件が変化した場合、Base Caseに対し、事業性やCash
flowへの影響を検討することをいう。
- 開始ー終了関係
- 査定見積 (応札額の妥当性評価) (An estimate to provide an assessment of the
reasonableness of a prospective contractor's proposed cost.)
- シックス・シグマ:欠陥率を従来の3σ、4σから6σに改善することで、収益性、能力を向上させる経営手法。
- 経営戦略のSMART:具体的 Specific、定量的 Measurable KGI, KPI、同意 Agreeable、現実的
Realistic、時間内 Time bound
- 引合 (Obtaining quotations, bids, offers, or proposals as appropriate.)
- ソフトウェア・プロセス・アセスメント:ベストプラクティスと現状との乖離を把握するためのギャップ分析のためのSoftware
Process Improvement (SEI)。5つのフェーズ(IDEALモデル) から成る。初期 (Initiating)、診断
(Diagnosing)、モデル構築 (Establishing)、改善実行 (Acting)、展開 (Learning)
- スケジュール効率指数 (SPI = EV/PV)
- SPDLIサイクル:PDCAとは異なり、構造変革を含むサイクル。Planは実行計画ではなく変革計画である。またCheckでは変化に対応できないので、Learningプロセスを入れ例外事項の予測、戦略変更にも対応。短期のPDCAを内包する長期的成功を支えるダブルループ。ビジョン(what)も実行(how)も同時に遂行する(whathow)。
- 開始ー開始関係
- ステイク:A piece of wood or metal >> Money or property risked
in a wager or gambling game; A share or an interest in an enterprise;
Personal interest or involvement.
- ストラクチャード・ウォークスルー:レビューの実施方法。成果物の担当者がプロジェクト関係者・有識者を集めて、その成果物の妥当性を評価するために実施される会議
- スケジュール差異
- SWOT分析:内部環境分析と外部環境の変化による
- タスク (WBSに含まれない最下位の間接作業)
- タイム・アンド・マテリアル契約 (実費精算契約)
- 目標完成日
- 目標終了日
- 総合品質管理:経営戦略から顧客満足向上、品質向上へとブレイクダウンしていくマネジメント手法
- トリガー (Risk symptoms or warning signs, indicators that a risk has
occurred or is about to occur.)
- 目標終了日
- バリュー・プロポジション:事業の独自性のこと。類型としては、1) 業務の卓越性 Operational excellence、2)
緊密な顧客関係 Customer intimacy、3) 製品の優位性 Product leadership
- 価値工学 (Life cycle costの最適化)
- ワーク・ブレークダウン・ストラクチャ (A deliverable-oriented grouping of project
elements that organizes and defines the total work scope of the
project. Each descending level represents an increasingly detailed
definition of the project work.)
- 迂回策 (リスクを避ける)
- 作業項目=Activity
- ワーク・パッケージ (A deliverable at the lowest level of the WBS.)
|