
IT Sales Process Management
for New Business Development
Cat: ECO
Pub: 2015
#1588b
Author, Ken Kawashima (川嶋 謙) translated by Kanzo Kobayashi (小林寛三)
up 15z31
Title
IT Process Management fro New Business Development
新規開拓のためのIT営業プロセスマネジメント
Index
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Original resume
Remarks
0. The day when a local small dealer starts consulting for a major company:
What is 'a good company'?:
Usually it is defined as the scale of sales, profit, and number of employees. But its financial statements describe more than that; it is the evidence document how the company is needed by the market.
- Asclab (Active Solution Consulting Laboratory) aims to be a large company; in the ways of having great influence and being expected by the market.
- If the market, which is equivalent to customers themselves, became to require your company, its sales could not grow. Conversely, the market expected your company to do something, which could grow sales and cause profits. This is the starting point of a good company we presume.
- Starting from a small local town with 200K inhabitants:
- Asclab has its headquarters in Tsuyama City, which is an old castle town with 200K inhabitants, located about 60km north of Okayama City in the west of Japan. In 1973, Kawashima Trading, the original name of Asclab, was founded as a PC dealer of NEC products starting from the scratch - literally with zero customers and zero sales. The company had continued IT system supply business until the time of several years ago.
- Now Asclab has changed its business to promoting various value-added services including consulting for business process improvement; has grown up to deal with larger companies of different order of scales.
- Asclab had suffered critical times in business; such adversity turned to be an opportunity of restructure. As one of the lessons we have aimed non-debt management; to realize this goal we have tried to minimize our inventory. To reduce it, we have even taken tough measures to reduce the space of storage itself, or to arrange older products in the front, while newer products in the back like the shelves of a supermarket.
- During the process of challenging non-debt management, we decided to pursue daily closing system of accounting; which does not mean to every day closing (which is actually impractical to check the figures from the management side), but becomes available at the following day. Until then, our financial closing had become available on 10th or 15th of the following month; but we aimed that it should be available on the following day after end of the financial period. This activity has lead us to awake the importance of improvement such as minimizing uselessness and pursuing effectiveness in every business behavior of our company.
- No subcontracting jobs:
- It is Asclab's basic policy since the inauguration of the company not to accept subcontracting jobs. When we established our company, then other companies in Okayama prefecture are more or less doing such subcontracted jobs dispatching their engineers to the client's sites based on consignment contract. Monthly income by this job gained about ¥700,000 -800,000 by dispatched engineer, against an engineer was then paid around ¥200,000 per month; so easy big profit could be guaranteed. But this process had no progress at all in raising the skills of the dispatched engineers, and we worried about seriously about the future of such engineers who became senior as much as 40 years old.
- My family business was a car dealer; even a fresh university-graduate staff could get monthly sales more than one million yen; but in IT industry it was difficult to get those level of figure.
- I considered that IT industry looked like a kind of hobby-based business model such as "I like PC", or "I'd develop software.", which could not be called a real systematic industry.
- Under such situation, if earnings by mostly by subcontractors, no further business knowledge could be acquired such as negotiation ability or marketing skills.
- Frankly speaking, the productivity of our company was much lower; at most ¥200,000 or 300,000 monthly; but the other hand we could learn the essence of business including flows of document, marketing troubles and solutions, etc., particularly for mid-sized or small and medium business (SMB).
- Our second foundation overcoming the initial deficit:
- Several years ago, at the managers meeting it became obvious that the financial result of the fiscal period would cause a big deficit since foundation of the company. Though Asclab did not depend on subcontracting jobs during this period, the business model of then Asclab was still like a building block; building an illusory budget, saying, 'How many orders can we expect then?', 'Whose IT system will lease out?', or 'Can we expect additional orders from them?'. Against these illusions, many staff declare, 'We'll do it in the guts,' or 'We'll do our very best,' and so on. If the management believed such resolutions, it would cause bad debts or serious troubles.
- Then, we tried to pursue different approach unlike other competitors; they proposed describing hardware and software only, never mentioning about cost per performance.
- If a certain deficit became unavoidable at the closing, if the top management would instruct the staff to improve the figure in utmost efforts. Then probably exaggerated budget would come out; which might cause bad debts or serious troubles in the future.
- Thus we looked for a different business approach. If we proposed similar offer like other competitors, the client only compare the offered prices, and only would respond to appreciate submission of the offer. The proposal of competitors never mentioned about 'the cost per performance'. We thought that top executives could not decide the proposal without considering cost per performance. In the economic boom, companies could easily decide the proposals considering, only to follow the general trend, to raise the corporate image, or simply to introduce the latest IT system. But these mean that there should be some other possibilities to improve description of proposals more attractive from different aspect.
- As we were a new comer in the IT industry; good clients and big users were already occupied by and supplied from other competitors. So we need to explore from different approach in challenging them.
- Cost burden of managerial class:
- Considering the above, we recognized the reason why we fell into deficit; which would be due to administrative costs added to the proposals. In our home town, Tsuyama City, clients have known well our cost structure through long business relationship in a local community. It is the present market situation that no easy price increase could be allowed due to price increase factor of administrative cost.
- Thus we have concluded that senior staff should be changed to contribute some additional incomes in proportion to their salary, having consulting capability, and etc. Concurrently younger staff are required to complete their jobs by even smaller human resources as well as to find out personal redundancy.
- We adopted the advisor function system as one of the solutions; reducing the time needed for control as the manager's role, which should be used instead for external activities. This trial might be an activity to prevent failure, not to say to surely succeed. After a while we could gain consulting jobs for improving business structure from several major listed companies. It became a proof that a senior staff more than 40 years old be able to function as an consultant.
- Challenge to changing corporate culture:
- On the other hand, it it true that there still exists a big gap of conception; managers recognize seriousness caused by the change of market, while the front-end staff don't. This causes very large internal friction between the management and the front-end staff.
- Furthermore, we raised the slogan, the senior staff more than 40 should have an consulting function; to realize this we accelerated to transfer our experiences and skills to younger staff. But this perceived notion caused to worsen internal atmosphere in the meetings between senior staff and junior staff. The more I as the president talked the more worsened the communication with the front-end staff.
- This is not only generation gap, but also function gap; whenever I talk with managers of technical division, who insist his views from technical viewpoint. It usually happens that even I could understand his opinion, but could not agree him from the company's ROI viewpoint, because of difference of mutual function.
- For example, the concepts of solution, proposal, or sales activity are different among persons; each has his or her own way of thinking or process. If these processes were united, better communication could be possible; it is s software of 'PRONavi' which we developed as an very effective supporting tool, describing details in this book hereinafter.
- Challenging a great change:
- This book describes the history of our company how has tackled various issues to reform our company by ourselves; such challenge is still going on.
- This challenge includes how;
- to advance from local market to national market,
- to realize originality of our own product,
- to get out of local system integrator depending on subcontracting business.
- There are not a few solution providers like us in the IT market. If we tried to challenge an issue of sales process management based on our own experiences and skill sets, we could perform a great change of business; which would surely be appreciated from the market. Let's challenge this issue together with us!
0. 地方の中小ディーラーが大企業をコンサルティングする日:
良い会社とはどんな企業か?
一般的には、売上高・利益・社員数といった規模の大きい会社。しかし決算者にはもっと様々な数値が記載されている。その結果は、いかに市場がその会社を必要としているかの証拠である。
- アスクラボは大企業を目指している。それは「大きなことを企てる会社」「大きな影響力を持つ会社」「市場から求められる会社」になりたい。
- 市場=顧客が、仕事を依頼しないようになると会社の売上は伸びない。市場が必要とする会社になれば、必然的に会社の仕事の依頼が増え、結果として売上・利益が伸びる。
- 市場がいかにその会社を必要としているか。決算書にどんな結果を残せるかが、我々の考える良い会社の原点である
- 人口20万の町でゼロからのスタート:
- アスクラボ株式会社が本社を置く岡山県津山市は、岡山市の北約60kmに位置し、人口約20万程度の小城下町である。1973年にカワシマ商事という社名でNECの製品を販売するパソコンショップとしてスタートした。最初はお客はゼロ、文字通りゼロからのスタートであった。数年前までは、情報システムの導入事業で会社を運営していた。
- 現在は、業務改善、仕組みの改善を支援するコンサルティングという付加価値サービスによって収益を改善し、売上高や企業規模で比較にならない程大きな会社とも取引できるようになった。
- 現在のサービスの糧になっているのは、これまでアスクラボが直面してきた経営の危機であり、それを何とか乗り越えるために考えた経験である。その一つに無借金経営があり、これまでそれを続けてきている。
- ではどうして借入ゼロを実現できたのか。それは「在庫を減らせば良い」というのがその答えである。在庫を減らすために、倉庫を小さくして在庫ができないようにするという強硬手段を採ったり、スーパー市場の陳列棚のように「古い商品を前に新しい商品を後に」並べた。
- 無借金化を機に、日時決算の導入を決めた。この日時決算は「毎日毎日決算する」という意味ではない。それでは見る方がついていけない。当時のアスクラボは月末に締めても翌月の10日や15日にならないと集計結果に基づく会議が開けなかった。そこで月末に閉めた、翌月1日には決算が見られることを一つの目標にした。社内で発生している無駄を最小限に留めようとしたした経験がアスクラボが仕組みの改善、システムの改善を重視する姿勢につながっている。
- 下請けは絶対にやらない。:
- さらに、アスクラボが設立当初から貫いてきたことは、下請けを行わなかったことである。設立当初は、岡山県下のソフトハウスの実情はメーカーの下請けか派遣がビジネスだった。景気の良い時代だったので、大足程度の年齢の人材を派遣すれば、月70〜80万円の収入になった。会社の給料は20万円前後だったので、絶対に儲かる。その時の利益は得られても、将来に向けてスキルアップはできず、社員が40歳を過ぎた何ができるが疑問を持った。
- 私の生家の家業は自動車の販売会社で、小さい頃から自動車販売の仕事を見てきた。そこでは半年から1年目の新入社員が車検を担当すると一人当たり100万円前後の売上を上げていた。ソフトウェア業界では、SEや営業担当者が100万円を稼ぐことがとても難しいことだった。
- このことは、IT市場のビジネスモデルが非常に付加価値の低いビジネスモデルで、人材をこれほど非生産的に使っている業種はないと考えた。当時のIT業界はPCがすきだから、ソフトの開発をしたいからというような個人の趣味の上に成り立ったビジネスであり、本当のビジネス体系になっていないとさえ思っていた。
- 下請けだけをやっていたら、業務知識も交渉能力も営業力も身につかない。将来を考えれば、今利益は少なくても、業界知識を身につければ営業もSEもコンサルタント的な価値を見いだせると思った。そのため、アスクラボのSEの生産性は、業務をこなしながら勉強しているので、さらに低く月20〜30万円だった。その代わり中堅・中小企業において伝票がどう流れているのか、どこで困っているのか、何を悩んでいるのかといった知識を残すことを選択した。
- 創業以来の赤字が第二の創業を促す。:
- 数年前、各部署から年度予算が上がってきたのを見ながら部長会を開いたとき、どう見ても創立以来の赤字が出るという問題に直面した。下請けこそしなかったものの、それまでのアスクラボのビジネスモデルは積み木式であった。即ち、「今期はいくら買ってもら得るか」「どこがリース切れになるか」「あそこに行けば買ってくれそうか」をやっていた。そこで無理やり「何が何でも獲ってこい」と言うと嘘の予算が上がってくる。嘘の予算を前提に「根性でやります」「頑張ります」となってもそれを信じて経営はできない。またそれを行うと不良債権やトラブルにつながる。
- そこで他社とは違う提案・やり方を模索した。他社の提案書を見ると、ほとんどがハードとソフトの見積しか記載されておらず「投資効果がどうなる」かが表現されていない。そのような提案書は、経営者は判断できないと感じた。好景気の時は、顧客はさほど投資効果を考えずに投資対効果を考えずにシステム導入してくれる。「他社が導入した」「企業イメージが高まる」「IT導入したいから」といった顧客の判断に助けられていた。しかしユーザ企業トップの視点で見ると、そこに「他社と異なる提案できる余地がある」と考えるようになった。
- アスクラボは後発がゆえに、他社をリプレースしないことには生計が成り立たない。既に「良いお客」「ビッグユーザ」は他社がシステムを導入しているからである。新規顧客は他社とは違った視点から攻め、開拓することが、当社の営業活動では当たり前だった。
- マネジメント層のコストが負担になっている。:
- 同時に「なぜ赤字になるか」に対する答えも見つかった。部長職以上の共通認識は「我々部長以上のコストが乗っているから」である。岡山県津山市の市場では、顧客との長年の付き合いで、当社のコスト構造などは既に知られているので、管理を理由に料金を値上げするのは、市場が認めてくれない時代になった。
- そこで我々は、給料の高い順にプロフィットを稼ぐように「年配になったらコンサルティング業を生業にする」ことを決めた。若手には「予算が立たない、あるいは仕事が少ないなら、少人数で対応あるいは余剰人数を明確にする」ことを求めた。
- そこで導入したのが、アドバイザー制である。マネジャーの役割から管理の側面を削り、その空いた時間でプロフィットを上げる。その経験を活かせば「必ず成功する支援」はできなくても「必ず失敗するやりかたを避ける支援」はできると考えた。結果、一部上場企業からも営業構造改革のコンサルティングを数社受注できた。40歳以上になったらコンサルタント的な業務を手掛けられるという事実を示すことにもなった。
- ビジネスモデルを変えるために風土改革に挑戦:
- 一方で別の大きな壁にもぶつかった。市場が大きく変化していることに経営陣は気づいていても現場が気づいていない。経営層と現場営業との間に非常の大きな摩擦が生じるようになってきた。
- さらに「40歳以上はコンサルタント」を可能にするために、我々の経験・スキルを若い営業担当に教えてやろう、文化を引き継ごうと思えば思うほど営業会議の雰囲気は悪くなり、私が話せば話すほど、若い営業担当者とのコミュニケーションができない状況に陥った。
- 若手に限らず、私のSEの責任者とでも色々な議論をしていると話がかみ合わない。彼は技術的にこうあるべき、こうすべきと主張するが、私から見ると、そのことは分かっていても会社の状況から見れば投資対効果があわない。今はそこにお金を掛けられないという答えしか出せないのである。これはお互いの役割の違いから当然あり得る。
- 例えば「ソリューション」という言葉、「提案書」という言葉、「営業」という言葉のいずれも、3人いれば3人とも違った意味で理解している。個人個人が独自にプロセス=考え方をもっているからである。逆に、この独自のプロセスを統一できれば、コミュニケーションは改善できるはずである。ここから生まれたのが、本書で紹介する営業プロセスマネジメントであり、そのために独自開発した「PRONavi」という仕組みである。
- 大きな変革に挑戦しよう:
- 本書で紹介する営業プロセスマネジメントは、アスクラボがこれまでに、どのような課題に直面し、それに対してどう対峙しどう変革してきたかの記録である。その記録は現在も進行中である。
- そこでの大きな変革は、1) 地方市場から全国市場への進出、2) 自社商品によるオリジナリティの追求」を実現し、3) 地域SIという請負型ビジネスから脱却することである。
- IT市場には、我々と同じような経験・スキルを持つソリューションプロバイダが少なくない。その経験・スキルをベースに、営業プロセスマネジメントに取り組めば、大きな変革に挑戦できる。そしてこれまで以上に市場から価値を認められる存在になれる。さあ一緒に始めよう。
>Top
1. Changing market requires skills of the front-end staff:
Solution providers propose solutions for a client company; if there were no problems to be solved, there would be no need of such proposals. But acutely almost all companies have some problems to be solved, and which are getting more difficult according to rapid and big change of the market.
- IT service is a kind of high value-added business, which means insufficient supply of services against lots of demand (needs), just like diamond or gold.
- Until now, when a solution provider visits a client; the client discloses its own needs and requirements, then the staff of a solution provider prepares a proposal for the client, and SE (system engineer) develops the system and support it for the client. This had functioned well as a value-added successful business model of a solution provider.
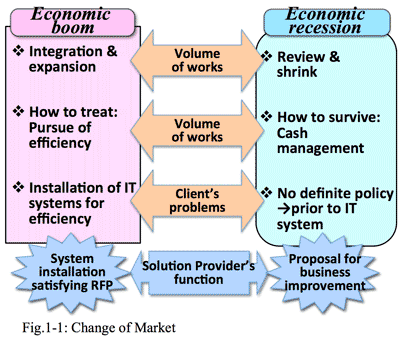
- But now, the market structure has drastically changed (Fig. 1-1), by which value of hitherto business model becomes out-of-date, accordingly both sales and profits have decreased.
- Quantitative gap in IT skills and knowledge has disappeared:
- Why the market has changed? The first reason is that there would be no difference in the volume of information and technical know-how between IT seller (=solution provider) and buyer (=customer or the market). Because users have used IT system so long time that they could understand almost all functions of sales and engineers as well as skills of installation and operation of IT systems of solution providers.
- At the initial stage of IT service industry, computer systems were unknown; users bought the system at the asked price without having inability of judgment whether the proposal were appropriate or not. But now users understood the buyer's all intentions; if the solution provider continued the same business model, which could be no more value-added services.
- The initial buyers had the knowledge of nether computer, software, nor operation of them; it was a typical seller's market. The front-end staff of the provider had no worried about the sales of systems which
- kind of joy that they were selling a dream to a customer.
- In 1990s, Japanese bubble economy collapsed, and economic downturn became obvious. At the same time, downsizing of computer systems (composed of client & server systems) appeared replacing so-called legacy system (mostly mainframe and office computer system installed with proprietary software). From around this time, sales staff tend to talk to customers with more technological jargons. Downsizing trend caused to grow PC's as terminal computers, and networks like
- were mostly developed and customized for the client. They even felt a LAN and WAN. Fashion of Computer language also changed from COBOL to C, or Visual Basic (VB) having favorable user friendly interface; using these languages the applications ordered and developed for the customers became an asset of the developer. (accumulated of business know-how of the clients as the templates which could be reusable later)
- The management of IT related companies recognized this change of languages as an advent of new computer age, encouraging younger generation to study these new languages. In reality, change of the languages were only expressive form, not drastic technological innovation of technology changing logic process itself. On the other hand SE who had business know-how could be explained neither necessity of learning new language nor preparing new role or function. In addition SE side themselves were so proud as engineers that they had missed to take the turning-point.
- In the current IT industry, there are many persons who have high skills and knowledge of latest technology. But there are very limited SE or sales staff who have knowledge of corporate management. This causes a mismatch, because clients require a process or mechanism to manage the corporation well. Thus it is needed for value-added solution providers to cultivate their SE or sales staff which could understand more about corporate management.
- Clients' need shifted from quantitative solutions to qualitative ones:
- The second reason is that clients' needs have changed from pursuance of efficiency to that of added value. In high economic growth period, it is important for customers to be how efficient to handle increasing jobs, having image of IT systems were always preferable and IT system division was regarded as a sanctuary. The management was influenced to dance the image of IT, who immediately instructed IT system division to introduce similar one if competitor introduced some IT system. But on the contrary when the steady economic growth could not be expected any more, clients must consider to review the scale of business according to reduce of transactions, and to maintain financial management to survive.
(Fig.1-2) And routine requirements from clients to solution providers became more carefully considered than before.
- Around that time, following winds for IT business blew a gale; the Internet became explosively popular and Y2K (Year 2000, or millennium bug) problem arose. IT system division is usually counterpart of the solution provider to introduce IT systems; who were getting more and more concerned about latest technology and efficiency; almost forgetting management point of view.
- Eventually, negotiation was focussed on sales of package software or that combined with hardware, which was a simple and easy transaction. Employee joined in IT industry in this period naturally thought this was a typical transaction.
- Then the mythology of IT system has collapsed; thus both the client system together with IT system division lost confidence from the top management. Under such situation IT solution providers have no reason to maintain same marketing style established in the economic boom period; the marketing style should be changed from only waiting the requirement from client but to taking more aggressive approach.
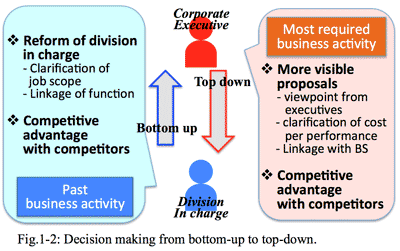
- Approving authority shifted to the director:
- The third reason is that decision-making authority of the client company shifted to the management executive which is upper status; for example, the approving authority of the general manager used to be up to ¥2 million, but it became up to half million due to decrease of corporate profit. The ¥200 million proposal must be authorized by the upper director. These changes reflect less credibility of IT system division, which could not introduce effective IT system from the director's point of view.
- At the time of economic boom, it is sufficient for sales staff of IT solution provider to contact with IT system division of the client company. But now it is needed to contact with upper status director(s).
- In addition the shift of authority to the upper directors means that they have less interest in IT technology itself such as function of hardware and software. They are mostly interested in business (=application) itself. It is natural that good communication should be focussed on the negotiation partner's interest, i.e., the issues related to the corporate management rather than IT technology. If sales staff or SE had no such knowledge, they could not communicate directors of the client company.
- The point is how to make a presentation more persuasive from the viewpoint of corporate management (Fig.1-3). The corporate management viewpoint consists of the principle of business, i.e., "profit should cover the cost, otherwise the company could not survive", which is the common and absolute principle applicable to any size of companies.
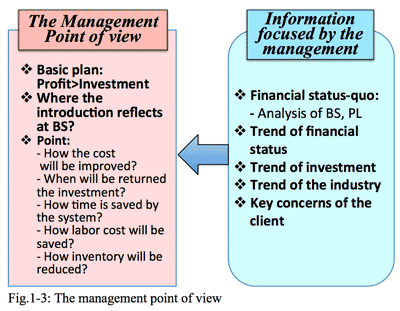
- Whenever the client company introduced IT system, directors would make decision considering its cost per performance from the proposals submitted by the solution vendors. But it looks strange that almost all proposals, I observed ever since, contain details of cost, lease fee, deprecation, etc. but no description about performance or effectiveness by introduction of this particular IT system.
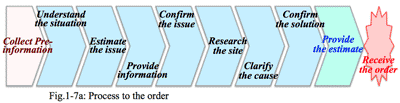
- New proposal to existing and new clients are atypical business solution:
- There are such types of sales of IT solution provider as; 1) Requirement-based sales to the existing client, 2) Proposal-based sales to the existing client, 3) Proposal-based sales to new client: (Fig 1-4)
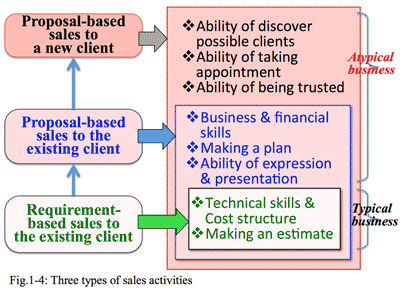
1) Requirement-based sales to the existing client:
- This is an order-taking sales visiting door-to-door. The existing client recognizes own problems to be solved, who knows the timing of introduction and rough range of budget. What is most interested thing for the client is to collect the cost and specification to submit for internal approval. To respond to such requirements, the skills required for a sales person are to prepare materials for technical evaluation and its cost structure; this is a typical routine sales.
- 2) Proposal-based sales to the existing client:
- This is a sales promotion showing a proposal from solution provider side which may applicable as a solution for the existing client. This proposal needs to include necessary factors to give a solution, including cost per performance which may be easily evaluated by the client. The proposal also needs to include a solution for the issue mentioned or suggested by the previous contacts with the client. The skills for this type of sales need to recognize necessary factors and rough cost for the solution, mentioning the effect is bigger than the cost in a way of understandable description. For this proposal-based sales, business and financial knowledge, planning ability, and persuasive expression in addition to the skills of the above 1) type of sales are needed.
- 3) Proposal-based sales to a new client:
- This is a challenge to a new client. The first step is to set up a goal to be approached; type of business and industry based on experience, technology, and features of the sales person. Once an appointment with a possible client is taken, then must prepare in advance; 1) what is the appealing point, 2) how to build trust, and 3) how to find out the opportunity of proposal. Other than the skills required on the above 1) and 2), more skills such as 1) to find an appropriate target, 2) to take an appointment, and 3) to build a trust relationship. This is atypical type of business.
- Typical type of sales visiting door-to-door is increasing:
- There are too many sales staff who visit the existing clients regularly asking their requirements; approaching to the same clients frequently causes less and less of sale volume per client. As the decision authority shifted to upper management, even regular contact to the person-in-charge or the manager could not maintain the usual level of sales due to decrease of the upper limit of decision authority.
- Now, sales staff also worries about it. The reason is they could not understand the meaning of sales. Request-based sale (regularly visiting sales) means customers disclose their issues, conditions, schedule, and plan, which is enough to submit the proposal according to this requirement shown by the client.
- On the contrary, proposed-based sales make the seller needs to infer the client's issues, conditions, schedule, and plan. The proposal may vary according to each client and trend of the age. But generally recent sales staff could not understand the essence of sales additivities are atypical business, or see the major portion of the living market. (Fig.1-5)
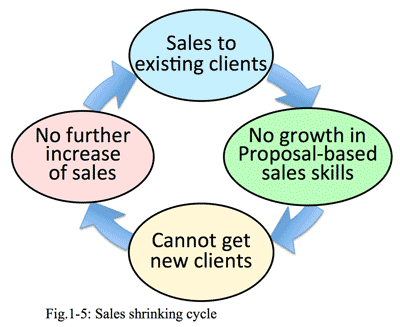
- Sales activities at the time of mainframe or office computer age are also patronized visiting sales; when sales staff receives a phone call from the client to come and hear the plan prepared by the client and reasons too. What the sales staff must do is to estimate the development of software or replacement of hardware and submit it; the order has been promised.
- But this activities are not a simple routine jobs. The sales staff have learned lots of knowledge; understanding the client business and application, or even attending sometimes at the same meeting with the client. Package software was then not enough in quality and in quantity; most of software was developed from the scratch. During these activities, both sales and technical staff could learn compulsorily lots of things.
- Once a proprietary system was developed and delivered, which could not be easily replaced by other competitors. In addition, the time span between change, addition, and replacement with new machines are relatively short, which forced to learn lots from one transaction with even one client. Compared this, the present sales staff seem learn less, who must consider that there still maintains lots of things to learn
- To cannot sell well means not to see the market well.
- Sales staff who could not sell well usually complains, 1) less opportunities of business negotiations, 2) less attractive products we have, 3) less opportunities to meet with clients, etc. All of these complaints shows the sales staff do not see the market well (Fig.1-6).
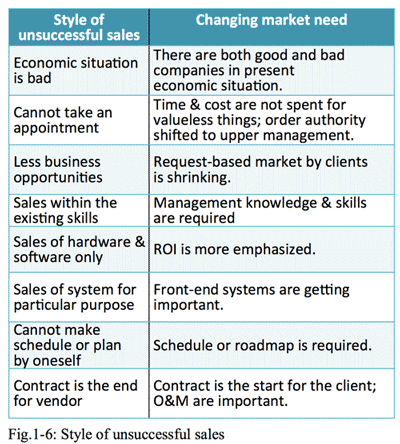
- <Economic situation is bad>
It is true there are bad companies due to bad economic conditions, but it is also true that there are good companies though bad economic conditions.
It is necessary to know such difference and plan to market. If you visit the existing clients only which seems easy to take an appointment, you may overlook good companies. If the existing clients are good companies under severe economic situation, whose criteria to decision-making are getting harder. Companies who have foresight show good financial result under severe economic environment, changing their organization or business model, and moreover, adopting severer criteria in investment.
- <less opportunities of business negotiations>
Actually requirements for clients decrease rather than less negotiations. Clients
feel difficult to find solutions for their business issues in such a rapidly changing environment. They could not visualize the image or establish a plan of introduction of a new system, though which were explained in details with usual catalogues or references. They could not decide at all with ambiguous explanations. The seller could not hear anymore what system the client would hope.
- In addition, the criterion itself of IT investment has changed. Because the decision authority shifter to the upper ranked director; it is useless to sell to the same positioned person. The company requires real ROI (Return on investment), but the front-end staff could not explain the meaning of ROI, who had no such an experience in the past marketing. It is just like anglers try to fish at the same place with same gimmick of fishing.
- <less attractive products>
There is a big difference of the product which the company want to sell between which the sales staff considers sellable.
The company always orders the sales staff to sell the products which remains unsold so many, while the sales staff consider those are no more products which are not sellable.
- But it is essential that such sellable difference caused by change of the market. Formally it was enough for the sales staff to explain the product, then the clients consider their issues, conditions, schedule, and so on. The sales staff need not to consider persuasive story to make the client recognize the necessity of the product. Excellent sales staff are always excellent story tellers.
- Now what the market requires is to know effectiveness of what portion of problems could be solved in preceding the business. It is also a major problem itself that the management and the sales staff discuss endlessly why and how the product could not be sold; which causes a mismatch with the market.
- <less opportunities to meet with clients>
Clients are conscious about not only money but also time; but the sales staff are not at all. Clients are eager to
find out added value in the sales talk, but the sales staff would not explain the added value for the client; or did not understand the value at all. It could not be possible to respond properly to the changing market as long as the sales staff stick to the former skills and experiences.
- To start from understanding the sales jobs and the market itself.
- It is essential that the sales staff must understand what is the market. To cultivate sales staff, the first step should start from knowing the client; including such information related to the kind of business, scale of the company, its organization, its financial situation. The sales staff should submit proposal considering the issues to be solved.
- But market of each industry to which the client belongs is different. Also problems to be solved among the corporate management and each division are not the same, or rather vary each other. Sales staff should know such differences.
- <Market for the top management>:
Many companies are under restructuring in such a severe economic environment. The leadership of the company is emphasized; in particular in selecting core IT systems, intention of the top management plays a critical role. Thus the sales team must approach to the top management of the client, otherwise getting the order will be hopeless. Also the sales team (both sales and technical staff) should understand intention of the top management of the client.
- <Market for the managers >
The approach to the manager
level of the concerned division is essential, who play the actual consideration as the end-users of the system, considering the basic intention of the top management. The managers are also keen in effectiveness of the investment. Both sales and technical staff should understand management of the particular industry.
- <Market for person-in-charge>
The business scale decided by staff of the client is reduced
according to severeness of the economic situation. So though big project opportunities are arisen, approaches to such staff only could not succeed in gaining the order.
- <Actual case>:
At some business party, we had an opportunity to talk with a president of
wood manufacturing company (A company), who said, "My company went into deficit as much as several hundred million yen. We could not yet locate cause the deficit." Then our company replied, "Could you give Asclab the opportunity to clarity such cause as a consultant?" The president of A-company agreed. Then we performed a field survey immediately of five locations of manufacturing sites in Japan. Later on we submitted the survey report concluding causes of the deficit, saying "We could identify the cause in two points; firstly, at several manufacturing sites, your sales staff sell the products without knowing the manufacturing costs, secondly, change of the exchange rate occurred during delivery of the raw wood from overseas by shipping was not properly reflected on your inventory." Other than these there were problems such as internal organization or mind of the workers, which we only mentioned "there are several other issues in your sites, but all are the matters of the president." Thereafter, Asclab could get the order of new replacement of IT system without completion, though A-company had introduced the IT system from other competitor.
- Business knowledge is the fundamentals to have viewpoint of the top management:
- Change of the market structure occurs not only in IT industry but other industries. Same approach to the same level of persons could not grow at all, because decisions are shifting to the more upper management. It is getting essential to have viewpoint of top management, and to propose with emphasizing investment effectiveness for the client company.
- Solution providers are usually pointed out to have more business knowledge, which should have corporate viewpoint and financial analytical knowledge. Now a few sales staff have become aware of the limit of former style of marking, but actual behavior has not changed at all, only repeating same old style of sales with neither proposal nor new client approach.
- It should be recognized that skill set and marketing process are totally different in the case of proposal-base sales and gaining new clients. Even sales staff who have the same old skills approach existing and new clients, the results would be fruitless.
- Approach to new clients are a kind of psychological warfare:
- There are various routes to take an appointment with a new client, by the way of direct approach or introduction of others. Then the mentality of the client is very passive, or reluctant to meet the new provider who made the appointment by introduction of others or frequent request to have a meeting.
- But after having meetings several times, the client may change and have an interest of the story or information given by the provider. And after a certain opportunity or happening, the client recognized value of the contact with the provider; then actual business relationship starts. (Fig.1-7)
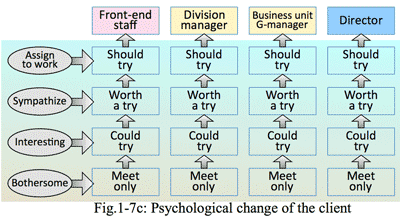
- It is necessary that similar changes of member of the client need to occur, including staff, manager, general manager, and director who are all the persons related to decision-making channel in the client company. Without these affirmative sentiment, the business negotiation with the client could not be possible.
- At the initial stage, the customer focusses personality of the provider; which is a kind of individual competition. But the case of existing client, who has already known both the staff and the company, having the meetings with sympathetic feelings. On the contrary the meeting with the new client is unusually short and superficial, leaving with clumsy and inconvenient feelings; which become rather tough mental barrier to the visitor, and tend to make higher threshold to visit again. This is a really occurred at the sales additivities. This could not expect organizational support from the company to which the provider belongs.
- The customer is also in the dark tunnel:
- The client and the staff of the provider have spent, worked, and worried in the same period. The client also in the dark tunnel, feeling difficulty in finding solution in these days. Therefore, one-sided proposal-based sales became ineffective to hear voices of the client.
- If the solution provider could talk solution literally, who could have affect the client to remove from the dark tunnel for a solution; by the way of recognition of changing environment as well as setting aside personal former pride and success stories. In particular the front-end sales staff must change themselves.
- Personal sentiment affects and sometimes becomes a so big barriers in communication in personal relations, division and corporation that may change in different color in tint or even meaning of words and corporate policy. Conversely if we could control sell this sentiment, we would proceed to the different direction.
- <Column>: Turning point of business model: Entry of Electronics retail store:
- When we established Kawashima Trading (now Asclab) in 1973, we could have orders whenever new PC was published so easily that we were too busy to write order sheet particularly at the weekend of bonus season.
- But we had felt that such an abnormal seller's market never continuing for a long time. NEC's PC was so popular that no marketing activities were needed; the PC was only selected and bought by clients.
- If competitors existed, sales activities were needed persuading clients regarding selection of the product with proper advice or enlightenment, etc. If the client selected easily the product without any persuasion of the sales staff, who might misunderstand that the order was attained by his sales ability.
- After a while, electronics mass retailers came into the market; because PC became literally consumer product. They prepared large display shelves with many part-time sales persons having a certain knowledge about the products. This means there existed no more business model as specialist' advice or support regarding PC needed.
- Many clients accumulated knowledge of PC and its usage from buying new product, and replacement and additional purchase. Conventional sales style retain specialists and visit to the client site by car and explain the feature of the product and system; the similar change of sales style has occurred regarding to the market of corporate IT systems.
1. 変化した市場構造が求める営業担当者のスキル:
ソリューションプロバイダは、顧客企業にソリューションを提案する。問題がなければ解決すべきことや提案すべきことは何もないが、ほとんどの企業が何らかの問題を抱えている。しかもその問題を正しく把握することが難しくなってきている。ソリューションプロバイダがターゲットにする市場構造が大きく変化してきたからである。
- ITサービス産業は高付加価値ビジネスである。高付加価値とは、ダイヤモンドや純金のように「需要はあるが供給が少ない」ことである。
- これまで、ソリューションプロバイダは顧客企業を訪問すれば、顧客自身がニーズを語り要求を出してくれた。そこでは、営業担当者は見積書を作成し、SEが開発・サポートをするというビジネスモデルが十分機能し、高付加価値だった。
- しかし今、市場構造は大きく変わってしまった。(図1-1) ソリューションプロバイダは、これまでのビジネスモデルの付加価値が低くなり、結果として売上や利益が下がってきた。
- ITのスキルや知識の量的格差が消えた:
- 市場構造が変わった理由はいくつかある。第1の理由は、ITの売り手(=ソリューションプロバイダ)と買い手である顧客(=市場)との間に、圧倒的な情報量と技術の差がなくなったことである。顧客が長年情報システムを使ってきたことで、ソリューションプロバイダのビジネスモデルの仕組みや、そこでの営業担当者や技術者らの役割、あるいは情報システムを構築・運用するためのスキルなどの全てを顧客が知るようになった。
- ITサービス産業が立ち上がった最初の頃は、一般にはコンピュータはまだ分からない製品だった。ITベンダの提案内容が適切かどうかを判断できず「言われるような費用が掛かるのだろう」と思うしかなかった。しかし顧客が売り手側の手の内の全てを把握した今、旧来と同じビジネスモデルを続けていては、ソリューションプロバイダとしての付加価値は低くなるだけである。
- 初期の顧客はコンピュータやソフトの知識、あるいは操作方法についての情報がほとんどなく、絶対的に売り手市場だった。システムに関しても開発案件が中心で、営業担当者が先行きを不安視する必要はなかった。むしろ顧客に夢を売っているという喜びすらあった。
- 1990年代に入り、日本はバブルが崩壊し、景気低迷が叫ばれるようになった。そしてメインフレームやオフコンといった独自システムに暗雲が垂れ込め、ダウンサイジングの掛け声と共にクライアントサーバー型のオープンシステムが台頭してきた。この頃から、営業担当者が、より技術的な方向に走る傾向が出てきた。ダウンサイジングの副産物として、専用端末のPC化や、LAN/WANなど新たな仕組みが登場したからである。開発言語もCOBOLからC言語やVisual Basicなどに変わり、ユーザーに優しいインターフェースが重要視されるようになった。同時に、顧客のアプリケーションが資産として受け継がれるようになった。
- IT関連会社の上層部は、「言語の交代=新しい時代の流れ」と捉え、新しい世代の人間に新しい言語を習得させた。実態は表現的な見掛けが変わっただけで、処理自体の中身が新しいテクノロジーで刷新された訳ではなかった。業務ノウハウを持っていたSEは、新たな技術を習得することの必要性を説明されず、新たな待遇も用意されなかった。同時にSE自身、技術者としてのプライドが転換時期を見誤らせたのも事実である。
- 今のIT業界には、技術スキルの高い人材、技術に詳しい人材が沢山いる。しかし企業のマネジメントを理解しているSEや営業担当者となると極端に少なくなる。顧客ニーズとのミスマッチが起こっている。顧客が今ソリューションプロバイダに求めるいるのはITそのものではなく、企業をマネジメントするための仕組みである。経営が分かるSEや営業担当者を育てられれば高付加価値のソリューションプロバイダになれる。
- 顧客ニーズが量的解決から質的解決に変化:
- 第2の理由は、顧客ニーズが効率追求から勝ち残るための付加価値追求に変化したことである。高度成長期の市場では、顧客にも数々の仕事が舞い込み、それに伴って業務もどんどん拡大し、それらの仕事をどう処理するかという量的価値を中心に考えてきた。ITに対するイメージも、当時はITや情報システムは聖域扱いだった。経営者もITという虚像に踊らされ、他社が導入すれば、「遅れてなるものか」と、自社の情報システム部門に劇を飛ばしていた。
- ところが、右肩上がりの成長が期待できなくなった今、顧客の仕事は減少し、業務の縮小と見直しを余儀なくされている。顧客は、どのように生き残るか、どうやって資金繰りをするかを考えるようになった。(図1-2)。景気が良い頃は、当たり前のようにソリューションプロバイダに出されていた要求も吟味されることなく出されることはまずない。
- ただ幸か不幸か、インターネットの爆発的な普及や2000年問題(Y2K)といった要因が重なり、顧客の側、特に情報システム導入を検討し稟議を上げる立場の情報システムも、技術と効率の問題意識しかなくなり、マネジメントの視点が抜けてしまった。
- 結果、これまで以上に単純に販売できパッケージソフトやハードを組合せた営業活動が主流になり、しかもそれが通用した。効率的な販売という甘い汁を吸ってしまったのかも知れない。この時期に、IT業界に入った人たちは、それが当たり前と思っても仕方がない。
- そして情報システム神話の崩壊である。顧客の情報システムや情報システム部門も経営者からの信頼を大きく損なってしまった。にもかかわらず、ソリューションプロバイダが好景気時と同じポジションで営業活動を展開していては良いはずがない。リクエストに応えるという待ちのポジションはなく、一歩踏み込んだ攻めのポジションに変わらなければならないのである。
- 決裁権限がより上位のマネジメント層に
- 第3の理由は、景気の後退に伴って、顧客企業内での決済権限が、段々と上位の役職に上がっていることである。例えば、これまで部長の決裁権限が200万円までだった会社は、利益減少と共に部長決済は50万円までに低下し、部長決済だった200万円は役員決裁となるなどである。これは、これまでに導入した情報システムが経営とマッチしていないため情報システム部門の信頼が薄れてきているを反映している。
- 好況時には、ソリューションプロバイダの営業担当者は、顧客企業の担当部門に営業活動すれば十分だった。しかし顧客の決裁権限が変化したことで、アプローチする対象は、担当部 長から、より上位の役職者や役員層に変えなければならなくなった。
- さらに決済権限が経営層に近くなるということは、ハードやソフトといったITの話には、ますます興味がなくなることを意味する。企業の上層部・経営層の大多数は、ハードやソフトにはほとんど関心がなく、興味があるのは業務(アプリケーション)だけである。ITに興味がない相手に営業し、コミュニケーションを図るには当然、相手の興味、すなわち業務に焦点を合わせられなければならない。必然的に、営業担当者やSEは、業務の話ができるだけの知識をもっていなければコミュニケーションができないということになる。
- これらの変化によって、今まで以上に重要になってきたのが、経営者の視点で提案ができているかどうかである(図1-3)。経営者の視点とは、企業を運営するという行為であるビジネスの原理、即ち、「収益が経費を上回っていない限り会社は継続できない」ということである。これは企業規模の大小を問わず、どの会社にも共通の原理である。
- 顧客企業がITを導入する際、顧客の経営者は必ず、経費に対する効果、つまり収益を考慮しながら判断を下す。ところがソリューションプロバイダが作成した数々の提案書をみるとそこには経費が掛かることが明記されているし、リース料がいくらで減価償却がいくらということも分かるが、導入効果について財務的などうんな収益が見込めるかを表現した提案はほとんど見たことがない。
- 提案型、新規顧客開拓の営業は"非定型業務":
- ソリューションプロバイダの営業スタイルは、大きく1) リクエストとに応じる営業、2) 提案型の営業、3) 新規開拓の営業の3つに分けられる(図1-4)
- 1) リクエストに応える営業:
既存顧客のリククエストに答えるいわゆる「御用聞き営業」である。既存顧客自らが、自社で解決しなければならない問題を把握している。導入時期についてもいつごろ導入すれば効果があるかを計り、そのための社内コンセンサスも取れている。顧客の関心はその計画を実行するため、あるいは社内稟議をあげるための費用の仕様にある。この段階のスキルは技術的なアセスメントと費用の算出という定型業務である。
- 2) 提案型の営業:
既存顧客に対し、ソリューションプロバイダがユーザが抱える課題を見つけ出し、その解決策を提案する営業である。解決策を実現するための必要な要素の拾い出しや、投資効果を考慮し顧客が理解判断できる形で提案する。この段階の営業担当者に必要なスキルは、顧客との商談の中で掴んだ情報を基に課題を見つけ、それを確認した上で解決方法を考える。その解決のためにどうのような要素が必要で、それを実行するには、どの程度の費用が発生し、その費用よりも効果の方が大ききこと、かつそのことを顧客が理解して判断できる資料を作らなければならない。御用聞き営業に必要とされるスキルに加え、業務や財務の知識、プラン作り、表現・説明能力などが必要となる非定型業務である。
- 3) 新規開拓の営業:
これまで取引のない企業を対象に、2)の提案型営業を仕掛ける営業である。自社がもつ経験・技術・特徴を基に、営業する業種や、具体的な訪問先を決めたり、面談時間を取ったりする所からが業務の対象となる。この段階の営業担当者は、どのような方法で具体的に訪問先を見つけるのか、どんな手段で会うのか、何をメリットして歌えるのか、さらに営業担当者や会社に対する信頼をどう築くか。そしてその過程の中で商談のキッカケをどう見つけるのかといったスキルが必要になる。上記の1), 2)に加えてアプローチ先を見つける、アポイントを取る、信用してもらう、といったスキルが必要になる。これも自分で考え行動する非定型業務である。
- 御用聞きで定型業務しかできない営業が増えている:
- まず、既存顧客ばかりを周り、相変わらず御用聞きだけをしている営業担当者が多いため、顧客1社から引き出せるIT投資額が小さくなり、売上が上がらず収益が非常に苦しくなっている。また同じ担当者、役職の相手ばかり攻撃していると、その役職に決済権限がある金額に下がっているために、ソリューションプロバイダの売上も上がらなくなってくる。
- ただ、営業担当者も今非常に悩んでいる。理由のほとんどは、本当の意味での営業を理解していないことによる。顧客ニーズを答えるだけのリクエスト営業 (御用聞き営業)では、顧客が課題や条件、スケジュール、プランを出してくれるので、営業担当者はそのプランに従って見積書を作成すれば十分だった。
- 提案型の営業担当者は、顧客が気づいていない課題を推論し、条件やスケジュール、プランを立てて提案しなければならない。そのやり方は顧客や時代によって千差万別の非定型業務である。本来、営業は非定型業務であることを理解していない営業担当者が増えたことから、実際に存在する市場の大部分を見ることができず悩んでいる。
- メインフレーム/オフコン時代の頃の営業担当者も、ある意味で御用聞き営業だった。顧客からの電話に応じて訪問すれば、すでに顧客が考え時期開発のプランがあり、そのための大義名分も揃っていた。営業担当者は、その仕様を基に開発やハードウェア拡張、あるいはリプレースの見積を作成し提出すれば、即契約となっていた。
- 但し、勘違いしてはならないのは、彼らは単なる御用聞きではなかった。種々の知識があったのだ。顧客の業務を理解し、顧客との打ち合わせに参加していたし、業務やアプリケーション、ハードに関する知識も習得していた。パッケージソフトが少なく、ほとんどが個別開発だったため、営業・SEともに必然的に業務知識が習得できた。
- しかもプロプライエタリなシステムは、一度導入すると簡単に他社が入り込めない。加えて顧客の仕様変更、仕様追加、新システムと言ったスパンが短く、既存ユーザ1社からも学べる部分が非常に多かった。過去の営業担当者は営業という言葉が示している範囲をフルメニューで体験してきたのに対し、今の営業担当者はただ話を聞いて知っているだけである。この経験の差において、今の営業担当者が学ばなければならない所が多いことは紛れもない事実である。
- 売れない営業の口癖は市場を見ていない証拠:
- 売れない営業担当者の口癖には、景気が悪い、商談が少ない、売れる玉がない、相手が会ってくれないなど、実にいろいろある。しかしそのいずれもが市場を見ていない証拠でもある(図1-6)。
- <景気が悪い>:
不景気の中、景気の悪い会社が多いのは事実だが、景気が良い会社があるのも事実である。この識別とプラン立てができていないし、プランの必要性を理解していない。既存顧客で、しかも自分たちが訪問しやすい顧客ばかり選んでいては、景気が良い会社を見落としていても不思議はない。もし既存顧客が、この景気が悪い時代においても、業績をのばしている良い会社であれば、その会社の発注姿勢は非常にシビアであるはずである。先見の明により組織や業態を時代に合わせて変化させているのだから、IT投資においても従来と同じはずはない。
- <商談が少ない>:
商談が少ないのではなく、従来から多数存在した既存顧客からのリクエストが少なくなっているだけである。市場が変化している中で、顧客も自らのビジネスにおける問題解決を見つけることが困難になっている。そこにおざなりのカタログや販促ツールの抜粋を元に説明されても顧客は具体的な導入イメージを描いたり、明確なプランを立てたりができない。漠然とした説明ではその価値を判断できないからである。結果これまでのように顧客からどんなシステムを作りたいかを聞けなくなった。
- 加えて、顧客のIT投資判断の基準そのものが変化した。例えば選択肢を選ぶ権限が上層部に移っているのに、同じポジションを攻めるワンパターンになっている。本当のROIが求められているのに、ROIの意味が分からない。いずれも過去にその部分を検証する経験がなかったのが原因である。現在の営業現場は、過去から知っている限られた市場に、誰もが同じ餌で釣り糸を垂れているのが実態である。
- <売れる玉がない>:
会社が思っている玉と、営業が思っている玉の間にはいつも大きな認識の違いが存在する。会社側が、これだけ玉があるのに、なんで売ってこないのかという命令を出すのに対し、営業担当者からは、玉とは売れる玉を言い、売れない玉は玉ではないという反論が噴出する。
- しかし、その本質は、ハード・ソフトを説明さえすれば売れていたはずの商品が最近は売れなくなってきたことになる。製品を説明すれば顧客が課題や条件、スケジュール、プランを考えてくれていたために、それらのことを顧客に気づかせるための効果的にストーリー作りや説明の仕方を磨いて来なかったからである。優秀な営業担当者は、商品にストーリーをつけることで売れる玉にしている。
- 今、市場が求めているのは、情報システム自体の機能や仕組みではなく、それを使うことで顧客のどの部分の問題が解決でき、どれだけ効果的に業務を進められるかといった効果である。いつまでも会社上層部や営業担当が売れない玉を論じていること自体が大きな問題で、市場とのミスマッチを起こす原因である。
- <相手が会ってくれない>:
お金だけでなく、時間も超すとであることを顧客が意識しているのに、営業が理解していないことの表れである。顧客は、話の内容から価値を見出そうとしているにも関わらず、機能の説明ばかりで、"価値"を証明しないし、そもそも理解していない。過去のスキルと経験だけで既に変化した市場に向かっているようでは、顧客の期待に答えられるはずがない。
- 営業の仕事や市場の理解から始まる:
- これからの営業担当者を育てるには、まず市場とは何かを理解させる必要がある。営業の第一歩が顧客を知ることであることは変わらない。顧客がどんな仕事をしているのか?企業規模は?組織は?経営状態は?などを知らずに問題の解決方法を提案出来る訳がない。
- しかし、顧客の中にもそれぞれ異なる市場がある。顧客のそれぞれのポジションでの悩みとその会社の経営層の悩みが一致するとは限らない。むしろ一致しないことの方が多い。ソリューションプロバイダの営業担当者は、企業内にある市場の違いを理解する必要がある。
- <企業トップ向けの市場>:
経済環境が非常に厳しい現在、多くの企業が事業再構築の最中にある。そこでは、企業トップのリーダーシップが強く求められており、結果、情報システム導入、特に中核システムに関しては、トップの意向が強く反映される。この企業トップ向けにアプローチできなければ、大きな商談を見出し受注することは非常に難しくなっている。対象が中堅・中小企業であればなおさらである。企業トップに向けた市場にアプローチするには、本当にマネジメントを理解した営業・SEがいなければ対応は不可能である。
- <管理者向けの市場>:
トップの判断であっても、実際に検討し具体的に動くのはこの管理者層の市場である。ここへのアプローチを欠かすことはできない。管理者層としても当然、企業の投資効果を判断するので、この市場のマネジメントを理解した営業・SEを必要とする。
- <担当者向けの市場>:
経済状況が厳しくなるにつれ、現場担当者に対するビジネスは縮小し、商談規模も小さくなっている。大規模商談があっても、この担当者層の市場のみへのアプローチでは受注チャンスは非常に小さくなる。
- <実例>: ある会合で木材製造業A社の社長と一緒になる機会があり、A社の社長が「当社は今期初めて数億円の赤字が出た。しかし赤字の原因がわからない」と行ってきた。そこで「アスクラボが調べましょうか?有料ですが。」と答えると「分かった」との返事。そしてA社の持つ全国5カ所の製造工場を現地調査しヒアリングすることになった。
- 結果として、アスクラボが出したのは、「赤字の原因は何か」だけ。A社の社長への報告書には、「当社がつかんだ原因は2点。1つは、幾つかの製造工場で営業担当者が製造原価を知らずに販売していること。もう1つは、海外から船便で輸入している原木が、輸送期間の間に為替変動が発生しているのに在庫金額に反映されていないこと」を明記した。もちろん、他にも内部の体制やマインドの問題などがあったが、「これは社長の問題」とだけ伝えた。その結果、A社は競合他社から情報システムを導入していたが、アスクラボは競争することなく、リプレース案件を受注できた。
- 業務知識は経営者の視点を持つための基礎:
- IT業界に限らず、市場構造が変わったにも関わらず、同じポジションに同じアプローチをしていては次の成長はない。IT投資の判断層がより上層部に移行しているだけに、経営者に効果やメリットが見える提案を行う必要がある。経営者の視点、投資効果の明確化が強調される背景には、こうした市場変化がある。
- ソリューションプロバイダに対しては、しばしば業務知識が不可欠だと指摘される。これも経営者の視点で考える必要があり、そのためには、財務知識を含めた業務知識が必要になる。もっとも誰もが御用聞き営業の限界を知り、提案型営業や新規顧客開拓の必要性には気づいているはずである。しかし実態は一向に実行されず、提案はできない、新規顧客も増えないという結果に終わっている。
- 提案や新規開拓が実行されない原因は、それぞれの段階で要求される営業のスキルとプロセスが御用聞き営業とはまったく異なるからである。見積書しか提出できない営業担当者が、そのスキルのままで、既存顧客への提案や新規顧客にアプローチしても、顧客に受け入れられないし通用もしない。
- 新規開拓は顧客との心理戦でもある:
- 新規顧客に対しては色々な方法でアポイントを取る。会うきっかけは、無理やりだったり、誰かの紹介だったりする。その時点の顧客の心境は、あの人の紹介だから断れない、たびたび来るから断れないというもので、本当は迷惑だ、面倒だといった気持ちが大半で、とりあえず会っているのが実情である。
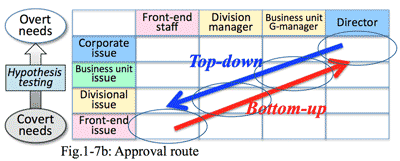
- しかし、実施に何回が訪問していると、顧客の側も訪問してくる人物や話に興味を持ち、営業やSEの話に対して、そうかも知れないという気持ちへ変化し、それがもう一歩進むとやってみる価値があるかも知れないに変わる。そしてさらにやるべきだとなって初めて受注につながるのである。(図1-7)
- 実際に顧客から注文をもらうためには、顧客の側内部で、各役職層の全てで同じ意識変化が起こる。現場担当者、職長、部門長、経営者層といった稟議書の決済ルートでもある。この決済ルートに従って各層での意識変化がグルグルと回っていく。これら全てをクリアできなければ新規顧客開拓は絵に描いた餅に終わる。
- この時、顧客は会社よりも訪問してきた個人を見ている。最初は個人戦である。これが既存顧客なら会社としての取引があるので最初からそうかも知れないという心理状態で面談に応じてくれるかも知れない。新規顧客を訪問すると迷惑そうな顔をされる、あるいは時間を取ってもられないということの方が普通である。するとすぐに精神的にまいってしまい、いろいろと理屈をつけて新規開拓に出かけなくなってしまう。これが今の営業現場で起こっている現実であるl。そしてこれまでは会社としてこの段階をバックアップすることが難しかったのも事実である。
- 顧客も暗いトンネルの中にいる:
- 顧客とソリューションプロバイダの営業担当者は同じ時代を過ごし、同じ所でつまずいている。顧客も我々同様に、暗くて見えないトンネルを歩いていて、自ら解決すべき問題をみつけられなくなっている。だからこそ、ただリクエストを聞くだけの御用聞き営業では顧客の声を聞けない。
- それだけにソリューションプロバイダが、本当の意味でソリューションを語り、自分たちのプライドやつまらぬ感情に左右されている場合ではなく、早く市場の変化に合わせて自分を変え、ソリューションを理解し、顧客を暗いトンネルから明るい出口に導かなければならないのである。現場の営業担当者は意地でも自らのやり方を変革させる必要がある。
- 人間誰もが持っている感情は、個人・部内・企業において大きな壁となり、言葉の意味を変え、会社の方針までの違う色に塗り替える力をもっている。逆にこの感情を上手くコントロールできれば、我々は十分にこれまでとは違う方向に進めるのである。
- <コラム>: 量販店参入で分かったビジネスモデルの変わり目:
- カワシマ商事(現アスクラボ)を設立した当時の市場は、PCの新機種が発売されるたびに、何の苦労もなく顧客から注文がもらえた。特にボーナスシーズンの休日ともなると、注文が多すぎて注文書が書けないほどだった。
- しかしそんな時代が長く続く訳はなく、非常に強い危機感を感じていた。NECが圧倒的に強かった当時のPCは売っているのではなく「買われている」だけで、いわゆる営業活動は不要だった。
- ライバルが存在すれば、このメーカーの方がよい、これを一緒に購入した方がいいといったアドバイスや啓蒙活動などの営業が必要となる。それらを営業担当者は経験していないのに、自分の営業力で売れていると勘違いしていた。
- それから少しして、量販店はPC販売に乗り出してきた。PCのその字の如く量販可能な商品になってきたのである。大きな店舗にPCを陳列し、ある程度の知識をもったアルバイトでも売れるなら、PC専門店の専門知識を基にアドバイスやサポートするというビジネスモデルが通用しなくなる兆候が出てきた。
- 顧客の側にもPCに詳しい人、利用技術を持った人が増え、新規購入から追加・買換購入が多くなってくると、購入時の判断材料も変化する。その中で専門スタッフを採用し、彼らが車で時間をかけて客先に売りに行くことはコスト的に不利になる。これと同じことがいま、企業情報システムの市場でも起こっている。
>Top
2. Finance is the common language to communication with the management:
- Face-to-face with directors by finance as the common language:
- It is necessary to understand and analyze the financial data in order to have the viewpoint from corporate management; which clarify the management issues of the company in the last fiscal year. To detect the financial statement is to find out solution of the client.
- Most of directors do not think that corporate issues could be solved only by IT systems. Combined improvement by hardware, software as well as human factors can solve the corporate issues. In such an environment, the solution provider need to have the same measure which can reach directors' sentiment.
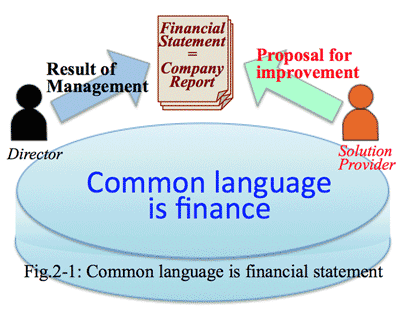
- The common measure, or language, is the financial statement of the company (Fig 2-1), from which we can read corporate issues of the common. This is a common mechanism in any industry; distribution, manufacturing, service, etc. in finding corporate issues such as stock value, debt amount, from banks, interest rate, inventory, accounts receivable collection rate, and so forth.
- We can see the essential issues from the financial result:
- Regarding to the issue of inventory, which includes the ways of ordering or management at the field operation, whose problems are usually not paid attention to, or are postponed. These problems resulted increase of inventory. To improve the item of the financial statement, improvement of site problems is needed, where the solution provider has opportunity to provide the solution.
- The solution may include factors of either human system, or introduction of software or hardware.
- <Case> This was a case of Asclab. To a certain client many vendors approached, including major IT venders and us. When our SE was guided to the client's office and met with the president; his first words was 'I think your company has excessive inventory." The president admiringly said, "You are the first visitor mentioning that point." Actually there was stock piled along the passageway from the entrance to the office stores, the SE who had checked the financial statement recognized its excessive inventory. The other competitors were similarly guided to the office passing through the passage, but neglecting the stocks along it and could not point out the inventory issue. Generally speaking customers tend to disclose only information which could be understood by the visitors. Thus the business knowledge is very important tool for sales and technical staff of the provider.
- ROI (Return on Investment) is a criterion to decide how to invest:
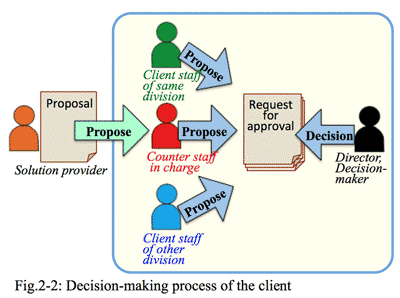
- A solution provider submits a proposal to a client, in which how it is read and what point is focussed?
- In our own company, there are several internal decision documents requiring to buy some fixture or equipment, to go on a business trip, or to receive some outside lectures or training, etc. The company could not automatically approve all these requests, because the company must consider regular monthly payments, such as pay for salaries, pay for principal and interest to banks, or pay for ¥materials to the supplier, etc.
- The decision maker decides priority among these payments considering the situation of sales amount, profit, and cash flow of the company; and decide affirmatively as long as the request of ROI should be plus, that is, income is larger than expense. ROI is such an important criterion to make the company decide (Fig. 2-2).
- What is the company money, and where it is?
- Someone believes money is stored in the safe in the company, but it is not correct. Profit is the result of business, which is gained by the sales of goods or systems made by SE and sold by sales person to the client. Even the president or decision-maker has the authority to decide the priority how to pay.
- For example, monthly gross margin is assumed ¥1 million; in which ¥500K is paid for salaries, and ¥100K is reserved for company profit, and the remained ¥400K is paid for other expenses such as various equipment and fixtures. Here a request document applied of ¥50K happened. As long as the same ¥100K is reserved for company profit, in order to approve increase of payment for the payment for other expenses, the portion of payment for salaries needs to be decreased from ¥500K to ¥450K.
- Similar process is occurring in the client company regarding to the proposal submitted by the provider, requiring the client should decide whether to accept the order and pay for it.
- To submit information for making a decision by the client:
- Sales and technical staff of the provider is required to understand what happening in the client company and what is the decision-making route after submission of the proposal, which is also useful to have viewpoint of corporate management.
- Conversely it is useful to make the proposal which is easily decided by the client; particularly the proposal should be made considering payment capability or ROA (Return on Asset), so that it may be acceptable and appreciated by the client.
To analyze financial statement of the client mean to understand what are real issues or worries of the client (Fig 2-3).
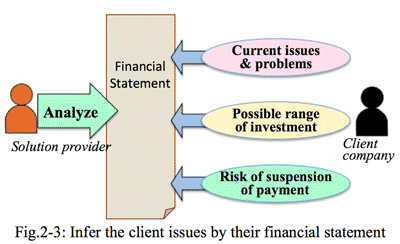
- For example, some hypothesis could be estimated such as too many inventory, bad inventory turnover, or long receivables turnover period. The provider visiting the client could pay attention to such hidden problems of the client. Without such prior information anyone is difficult to recognize the issues.
- The financial situation of the client regulate amount of investment; for example, it is obvious that the client with annual profit ¥10M could not introduce the system with annual leasing fee ¥50K or ¥100M. If the provider proposes such expensive amount of system, the client feels sense of distrust; instead the provider should always consider limit of the budget of the provider, and propose with having viewpoint of the corporate management.
- To know financial knowledge is also useful for the provider to have risk management viewpoint. There may be such cases; even the sales staff of the vendor frequently visit the client and submit the proposal, the deal might not be authorized by the leasing company, or might be declared bankrupt in half an year after getting order, and the sales would be in vain. If the provider could estimate such risks by checking financial statement, appropriate measure could be taken in advance.
- It is the first step to check the financial statement of the client, it should be careful not to talk directly to the client, "We have checked your company's financial statement."
- The information should be internal purpose only in the provider.
- If economic conditions changed, the client issues would also change:
- The economic rule has changed from the age 'goods generally rises in prices' to the age of 'goods generally falls.' This affects inventory issue; management risk regarding to the inventory issue is relatively smaller, because which may rise in the future.
- But now the condition has changed; PC or digital consumer electronics are lump of technologies, and those prices fall down according to progress of technologies. It the present time that to have goods is a risk, which is the biggest difference between the age of economic good time and bad time. Companies are always requested to purse solutions of these issues; solution providers are required to furnish solutions considering of these changes.
- The solution providers could not make not only good proposals but also to have effective conversation with the client without knowing the knowledge of finance. Your proposal should describe mentioning effectiveness by introduction of the system, such that 'your operation will be improved by using this system, resulting such effectiveness appears in your financial statement, though your system cost increases such amount monthly.' That kind of description could be persuade in making the client conclude the decision.
- <Column> Outsourcing business in a small market:
- Asclab started its business from selling PC, then became a solution provider. Since a volume retailer entered, the PC market became smaller, and Asclab shifted to the business of more value-added office computer system and software development. In addition, we have developed to make outsourcing business which is stable services for the client who introduced mainframe computer.
- The reason of such shift of our business is the size and future possibility of the market in Tsuyama City, which is much smaller than that of large cities. In Tsuyama City, there are considerable as many industries as traditional local industry, supermarket, hospital, etc. But supply of IT systems to these industries would not be a stable business in such size of market.
- On the contrary, such local market is rather difficult to secure eligible dedicated engineers of IT systems, or at most one or several engineers only. Once such engineers left the company, the company suddenly would become unable to operate the system. Here is the need of a business model of outsourcing of IT engineers for local industries. Thus Asclab succeeded to explore a new type of stock-based outsourcing business in addition to software development.
2. 経営層に判断材料を与える共通言語は財務:
- 共通言語財務で経営層に対峙:
- 経営の視点で考えることの基本は、財務の解読と分析ができることである。過去1年間の行動を示した決算書には、その企業が抱える経営課題が現れるからである。決算書を読み解ければ、顧客の課題も解決策も見えてくる。
- ほとんどの経営者が、会社の課題がITだけで解決するとは考えていない。そこに人間が関わっている以上、ハードウェアとソフトウェアと人間のそれぞれの仕組みの改善を組み合わせることができて初めて、経営課題の解決が実現できる。そのような状況下で、ソリューションプロバイダが顧客企業の経営増と対峙するには、経営層にも通じる尺度が必要である。
- それが、会社の成績表である決算書であり、財務こそが企業経営の共通言語となる。(図2-1) 実際決算書からは企業の問題点や経営課題がどこにあるかが読み取れる。これは、流通業や製造業、サービス業などすべての企業に共通である。株価の変動、銀行からの借入金、金利の高低、在庫の多少、売掛金回収率など、経営課題は様々な形で決算書に表れる。
- 結果からその過程に潜む課題が見える:
- 例えば、在庫の課題を考える。その背景には、発注の仕方や管理の仕方など現場の仕組みの中で、なおざりにされたり、先送りにされたりした問題点が隠れている。現場の課題が時間の経過と共に現れ結果として在庫が増えてきている。決算書の内容を改善するには、現場の課題・仕組みを追求しなければならず。そこにソリューションプロバイダの活躍の場がある。
- 但し、経営課題を解決するには、人間系の仕組みを直すことか、ソフトウェアが必要か、あるいはハードウェアの必要なのかを拾い出すことが経営課題解決の大きな要素になる。
- <事例>アスクラボの実話である。ある顧客には、大手ITベンダーを始め、多数の競合会社が営業活動を仕掛けていた。事務所に案内され、先方の社長に初めて会った時、そのSEは開口一番「御社は在庫が相当多いですね」と指摘した。その社長は「それを言ったSEはあなたが初めてだ」と非常に感心し、それをきっかけに取引が始まった。実は、同社の入口から事務所までの通路は倉庫になっており、事前に財務諸表を見ていたSEは、その通路を通りながら在庫が多いことを実際に確かめていた。競合他社も同じようにその通路を通って事務所に案内されていたが、気に留めていなかったために在庫が多いという事実を指摘できなかった。顧客は一般に「自分の話を理解してくれる相手にしか情報を出さない」というのが現実である。その意味で、営業担当者やSEにとって業務知識は非常に重要なツールである。
- ROIはお金を払う優先順位の基準:
- ソリューションプロバイダは顧客に提案書を提出するが、顧客側ではその提案書をどう読み、何を検討しているのだろうか?
- 自社の場合を考えて見ても、業務に必要な備品、出張や研修受講など、様々な場面で社内の稟議書を書く場面がある。会社はすべての経費申請に応える訳にはいかない。会社は、社員の給料や銀行借入金の元利返済、仕入に対する支払など毎月現金が必要となっている。
- 決裁者は、その時々の売上状況、利益状況、キャッシュフローを見ながら、優先に行うべきこととそうでないことに優先順位をつけていく。これがROIという基準で、そこでは経費以上の収入が見込めることが必要となる。このような判断をした対象だけが実行されるということになる(図2-2)。
- 会社のお金とは何か?に答えられない:
- 会社のお金は、会社の金庫の中に入っている訳ではない。利益は営業担当者が苦労して顧客に商品を販売し、SEが徹夜して構築したシステムを納めた結果である。社長なり決裁者と言えど、優先的に何に使うのかの権限を持っているに過ぎない。
- 例えば、毎月に粗利が100万円で、その内50万円を給料に、10万円を会社の利益に、残り40万円を設備・備品などの経費に使っているとする。5万円の稟議書に対し、利益を変えないとすれば、給料が50万円から45万円に減る。それでも5万円の稟議を通すべきかということになる。
- それと同じプロセスが、ソリューションプロバイダが出した提案書に対しても起こっている。顧客の会社のお金でその提案内容を購入して欲しいと迫っているのである。
- 判断材料があれば経営者の共感を得られる:
- 顧客の社内で何が起きているのか。どのような決済ルートで、どのような判断基準で提案書を利用しているのか。営業担当者やSEは、このようなことを把握しておくことが、経営者の視点で考えることにつながる。
- 逆に言えば、財務の視点に立てば、顧客が判断しやすい顧客の立場に立った提案書を作成できることになる。顧客の支払能力や総資本回転率などを判断し提案書を作成することが、顧客の経営者に大きな共感を与えることができる。
- 財務を分析することは、顧客の悩み・課題を知ることに繋がる (図2-3)。例えば、在庫が多い、在庫回転率が悪い、債権回収期間が長いといった予測(=仮説)が立てられる。予測があれば、客先を訪問しても、在庫の状況はどうなっているのかなど課題が潜んでいるかも知れない部分に注意を払える。事前に何もしていなければ、なかなか気づかない物である。
- 財務が理解できると、顧客の財務状況を把握できるし、そこから顧客が投資できる費用をある程度考えられる。例えば、年間1000万円しか利益がでていない顧客に対し、年間5000万円や1億円のシステムのリース料を提示した所で顧客が導入できる訳がないことが明白である。そんなことをするうと顧客は逆に「うちの現状を分かっているのか」と不信感を抱きかねない。これらも考慮しないと「経営者の視点」での提案活動は不可能となる。
- 加えて財務を知ることは、不景気な時代に会ってはソリューションプロバイダ自身のリスク管理の面からも不可欠である。取引開始時の売掛債権の判断材料になる。例えば、営業担当者やSEが客先に何度も通い、提案書を作成してもリース会社の与信が通らないとか、長期のシステム構築案件を受注した所、半年後に倒産してしまったということでは売上にならない。財務内容を知り、リスクを予め予測できれば、自社が不利益を被らないように準備することが可能となる。
- 顧客の財務状況を調べることは、ソリューションを提案するために顧客を知ることの第一歩である。この時気をつけなければならないのは、中堅中小企業など非上場の顧客に対し「御社の財務を分析してきた」などと直接的に話をしないこと。財務分析の結果は、あるまで自社の内部情報として取り扱うべきである。
- 経済ルールが変われば顧客の課題も変わる:
- 経済のルールが変わり、時代は「物を持っておけば値上がりする」から「物をもっておけば値下がりする」になってしまった。在庫問題をみて、ある程度在庫を持っていても経営リスクがなかったのは、これらは値上がりする可能性があった。
- しかし今、技術の固まりとなったPCやデジタル家電は、その技術が進歩するほど単価が急激に下がる。そこでは物を持つことのリスクが非常に大きくなる。これが景気の良い時代と悪い時代の大きな違いである。企業は、その中で色々な問題や課題に直面しており、ソリューションプロバイダはITを使えば、それらをどう解決できるのかを求められている。
- しかし、課題の根本が経済ルールにあるだけに、ソリューションプロバイダは財務を知らずして、顧客に提案書を作成できないし、それ以前に的を射た会話すらできないことになる。「経費はかかりますが、上手くシステムを運営できれば、こういう効果が決算書に見えてきますよ。」こう表現した提案書を作れなければ、顧客はいつになっても、その提案をジャッジメントしてくれない。
- <コラム>市場が小さかったから始めたアウトソーシング
- アスクラボは、PC販売から始め、ソリューションプロバイダへの転身してきた。量販店がPCを売りださい、市場が小さくなる中で、より高い付加価値を求めてオフコンの販売、そしてソフト開発という事業に乗り出して行った。そしてこれらの経験を活かし安定した収入を得るために今は、メインフレームを自社導入したアウトソーシングビジネスも展開している。
- そのきっかけも津山という我々の市場が非常に小さく、都市部と違って市場の先行きに不安を感じていた。津山の市場にも、当然、地場産業やスーパーマーケット、病院といった企業がある。しかし、地域の経済規模から見て、システム構築だけでは安定的な仕事の確保が難しい。
- ただ、この地域の企業は規模が小さいために、専任の情報システム要因を確保しにくかったり、例え確保できても1人から数人レベルでしかなかったりが普通。もし、そうした人たちが会社を辞めてしまうと、その企業は途端に情報システムがつかなくなり、非常に困る状況となる。かといって人数を増やすほどの企業規模がないので、アウトソーシングというビジネスモデルが成り立つ。アスクラボとしては、安定的な仕事の確保のために、新しいニーズを発掘し、ソフト開発に加え、アウトソーシングによって固定的なストックビジネスが立ち上がった。
>Top
3. Indispensable financial skills for solution business:
- It it important to have a viewpoint to analyze financial statement:
- Through analysis of financial statement, we could find out problems of the client company; then we could make persuasive proposal, which would lead to develop new clients. Clients tend to believe to a sales person who has financial skills.
- Financial knowledge is not only for the accounting staff; this idea has made the solution provider's proposal not persuasive. It is not necessary to be an accounting specialist, but is useful to get rid of prejudice that BS and PL are difficult to understand. It is sure that basic understanding of fiance or having sympathy of it would improve sales result.
- Regarding inventory; if there seems too many inventory, check the length of 'inventory turnover period'.
- Inventory turnover period=Inventory/Av. monthly sales
- where, inventory=product, semifinished product, work in progress (WIP)
- average monthly sales=sales/number of months per period
- When this index is big probably due to either 1) additional order of inventory piling up on the existing inventory, or 2) double order of inventory.
- As a solution, it may be needed that improvement of the internal business process or by changing the IT system.
- To check ability to pay of the client, check the current ratio:
- Current ratio= current asset/current liability
- Current asset=asset expected to be converted to cash within a year
- Current liabilities=liabilities due to be paid to creditors within a year
- If current ratio of the client is lower (=less able to pay), collection of the payment could be difficult, causing deterioration of cash flow, finally becoming
- The financial statement is applicable to our daily life:
- It is composed of BS, PL, Business annual report, Appropriation statement, Disposal of loss, Supplementary statement, etc, of which the basic knowledge of BS and PL is indispensable.
- BS and PL:
- A Company must close its financial statement at the end of every fiscal year, clarifying its sales and profit of the last one year.
- There may be such understanding at the front-end, 'All's well that ends well', or 'completion of the project is the end.' But the corporate management thinks time-scale as well as the financial statement, considering 'When was the critical pass for success,' or 'Is there any other way to complete earlier?'
- BS is a statement to look the company's history chronologically; how it has secured the finance, how it has spent or stored.
- While PL described the business activities of the last one year, how business it has performed, how it has spent expenses, how the profit remained.
- Comparing with medical check, for example, PS points out the possibility of diabetes, while BS point out the data three years ago was worse than that; then it may be diabetes now, but chronological improve suggest that it would be no problem to continue the present care and life style.
- Inventory:
- Most of this issue is how to minimize the inventory. It is same thing that there is ¥100M worth inventory and ¥100M cash without no inventory. The inventory could be converted into cash, but could not in some cases. For example, the inventory of PC, which may be out of dated models or bad inventory. The payment could not be possible, unless the inventory converted into cash; actually it is impossible to pay the bonus by the inventory goods. In such case, the company need to borrow money from the bank, but it requires a certain interest which affect profit of the company.
- It differs the corporate management that the profit should be liquidated or converted into an inventory. Directors or accounting staff consider to minimize the inventory, while the front-end staff misunderstand the inventory is a kind of profit.
- Market-value accounting:
- Another misunderstanding usually happens in market-value accounting; book-value has been applied during high growth age in contrast.
- Companies owns land or stock as its asset, and in economic growth period these asset rises in value (so-called land myth). Formerly it had believed to have a land could increase value of its asset; because it became larger than the interest cost borrowed from a bank. It could even borrow money from a bank no object by mortgaging the land.
- Now on the contrary, the value is falling. According to the change of accounting rules, the price in the account book must be rewritten into market-value from the former book-value; say, the land bought at ¥100M was devaluated to the market value to ¥50M. This means ¥50M profit in the operation would be offset by the devaluation of ¥50M of the asset.
- Cash flow:
- Corporate account is accrual basis. For example, when you sell a product and slip an invoice, then the amount is booked as account receivable; no money transactions at that moment. Accrual accounting recognize revenue or expense when it is incurred or the invoice is issued.
- Banks had observed the company with a focus on its profit. Because there had been a safety valve named land asset, which became no more safe due to devaluation of the mortgage value. Now the concept of cash flow is getting focussed. For example the bank lend ¥100M to a borrower with repayment of ¥1M monthly has concerns that the borrower could return the cash of ¥1M monthly.
- The life of ordinary people looks like basically cash flow type, though payment by credit card is getting popular. The transfer of cash and household account book correspond each other, unlike that of company.
- Current ratio:
- Current ratio is an indication of the ratio current asset which can be liquidated within a year divided by current liabilities which can be paid within a year.
- For example, an early morning a pedlar stocked fish at the river bank at ¥100M promising to pay within a day, and went to sell it to a mountainous region spending ¥10K of traffic charge. He could sell it all at ¥130K with getting cash ¥90K and remained ¥40K on credit. His PL will be that sales ¥130K, sales cost ¥100K, gross profit ¥30K, general expense ¥10K, operation profit ¥20K; in his purse there is only ¥80K cash while he must pay ¥100K today. Such a situation is called 'surplus bankruptcy.'
- Equity capital ratio:
- To make company assets, what portion is owner's fund and what portion is borrowed from outside lenders; the latter fund must be refunded, so the higher ration of owner's fund make the company safer.
- When you buy a house at ¥10M, if you can prepare your own fund ¥50M and the make loan ¥50M from a bank; this case is that equity capital ration is 50%, which is safer that the case of borrowing 100% at loan if the income decreased due to economic change.
- Financial statement contains various evaluation criteria:
- Financial analysis has two aspects; internal analysis and outside analysis. Internal analysis focusses information to evaluate corporate activities, in particular whether 1) the goal is performed, 2) the advantage compared with competitors, 3) further investment is possible. External analysis aims to check safety and availability by mutual transactions.
- There are two methods; real analysis and ratio analysis. In addition, 1) composition ration in the ratio analysis as the total is 100, 2) trend ratio as the standard period is 100, 3) relation ratio compared with other items, 4) period analysis compared with the previous period, 5) mutual comparison with other companies, and 6) standard analysis compared with statistical standard value, etc.
- Each index is listed in fig.3-1 below.
3. ソリューション営業に不可欠な財務スキル:
- 財務諸表を分析するための視点は重要である
- 財務諸表を分析することで、顧客企業が抱える問題点が見出せ、その問題点からソリューションを発見し提案することが新規顧客開拓につながる。顧客は財務スキルのある営業担当者を信頼するからである。
- 財務知識は経理部門だけ必要な知識という考えがソリューションプロバイダの提案力を低下されている。財務の専門家になる必要はないが、BSやPLは複雑だという先入観は捨てて、ある程度まで理解でき、親近感を持てれば営業成績の向上につながる。
- 在庫について: 例えば、在庫金額が非常に多ければ、棚卸資産の回転期間の長短を調べる。
- 棚卸資産回転比率=棚卸資産/平均月商
- 棚卸資産=商品・製品・半製品・仕掛品
- 平均月商=売上高/決算月数
- この指標が大きいのは、1) 在庫があるのに追加発注する、2) 二重発注などがある
- ソリューションとしては、社内業務改善、あるいはシステムの変更による改善
- 顧客の支払能力を調べるには、流動比率によってすぐに分かる。
- 流動比率=流動資産/流動負債
- 流動資産=1年以内に現金化できる資産
- 流動負債=1年以内に返済しなければならない負債
- もし、流動比率が低い(=支払能力が劣っている) 顧客に多額の商品を販売すると、その回収に数ヶ月かかるとすると、会社の資金繰りの悪化をまねる。資金が不足すると黒字倒産の恐れがでてくる。回収不能(貸倒)という事態になると、連鎖倒産の可能性も否定できない。
- 財務諸表は身近な生活に置き換えられる。
- 財務諸表には、BS、PL、営業報告書、利益処分案、損失処理案、付属明細書などがある。中でもBSとPLの基礎知識は不可欠である。
- BSとPL:
- 企業は毎年、決算書を締め、その1年間の売上・利益を明確にしなければならない。そのには年1回という時間軸が基本にある。
- ところが実際の現場には「結果として上手く行けばよい」「できた時が完成」と思っていることが多いのではないか。しかし経営者は結果の善し悪しだけでなく「いつ上手く行ったのか」「もっと早く完成する方法はないか」など決算書の持つ時間軸を見ている。
- BSは、会社の歴史を時系列で見るための資料である。これまで資金をどう調達し、どう使ってきたか、あるいは貯めてきたかを示している。
- 一方PLは、ここ1年間の商いの様子を見る資料である。どんな商いをし、経費はいくらで利益をはどれだけ残したかを示している。
- 健康診断に例えると、PLでは、今日の時点で糖尿病ではないかという指摘となり、これをBSでみると3年前はもっとデータが悪かったということが分かる。すると今日の時点で糖尿病であるが、時系列的には改善してきているので、今の治療や生活態度を続ければよいといった判断ができる。
- 在庫:
- 課題の多くは在庫の削減である。決算書上は、倉庫の1億円の在庫があることと、在庫はゼロだが1億円の現金があることとは同じことになる。しかし在庫はお金になるであろう物であり、必ずしも現金に変わらない可能性がある。
- 例えばPCでは型遅れもあれば不良在庫もある。現金に変わらなければ支払ができないということになる。年末のボーナスを在庫で支払う訳にもいかない。すると銀行からお金を借りて手当することになるが、そこには金利が発生するのでその分利益が減る。
- 決算書では同じ利益でも、利益を現金化するか在庫にするかによって企業経営は違ってくる。経営者や経理にとっては在庫を減らそうというが、現場の一般社員は利益と理解しているという勘違いもある。
- 時価会計:
- 在庫に並んで勘違いの要因になっているのは時価である。これに対するのは簿価である。高度成長期は簿価が基準だった。
- 企業は土地や株を資産として保有している。景気が良ければこれらの資産評価も上がる。いわゆる土地神話である。土地さえ持っていれば、資産価値が上がり、銀行からお金を借りて金利を払うより遙かに値上がり幅が大きかった。現金を持たなくても土地を担保にいくらでも借りられた。
- 今は逆に評価が下がっている。決算書上も、これまでは購入時の価格を試算として載せていればよかったのに、会計基準が変わったために、1億円で買った土地が5000万円に値下がりすれば、その5000万円の値下り分を特別損失として載せなければならないので、本業で5000万円の利益を出しても利益は相殺される。
- キャッシュフロー:
- 企業会計は発生主義である。例えば物を売って伝票を切ると、売掛金として会社の資産に計上されるが、実際にはお金は動いていない。発生主義とは伝票を切るという行為の発生を記録しているからである。
- これまでは銀行も、会社の利益を中心に見てきた。土地を中心として担保という安全弁があったからである。しかし今は、その担保価値が値下がりしているので安全弁が安全でなくってきた。そこで重視され始めたのがキャッシュフローであり。例えば銀行が1億円を毎月100万円ずつの返済を条件に融資したとすれば、毎月現金100万円を支払う能力があるかどうかに意味がある。
- 一般的に会社員の生活はキャッシュフロー型である。最近はカード決済があるものの、企業の場合と違い、お金の動きと家計簿の記載がほぼ連動している。
- 流動比率:
- 1年以内に現金になるであろうお金と1年以内に現金で支払わなければならないお金の比率である。
- 例えば、魚の行商人の場合、早朝、河岸で本日中に全額支払う約束で10万円分の魚を仕入れ、交通費1万円をかけて山間部に行商に行くとする。魚は13万円で完売できたとしても現金回収は9万円で残り4万円は売掛金になったとする。この場合のPLは、売上高13万円、売上原価10万円、売上総利益3万円、一般管理費1万円、営業利益2万円となるが、現金としては、本日中に支払わなければならない10万円に対し、財布の中身としては8万円しかない。この場合、黒字なのに資金不足となり黒字倒産となる。
- 自己資本比率:
- 会社がもっている資金を作るのに、どれだけが自分のお金で、どれだけ外部からお金を調達しているかを表す。外部から調達したお金は返さなければならないので、全て自分のお金なら一便安全ということになる。
- 自宅を1000万円で購入する場合も、半分の資金500万円をローンするとすれば自己資本比率は50%となり、少々の収入変動があっても半分は返済の必要がないので全額借入の場合より安全になる。
- 種々の判断材料が潜む財務諸表:
- 財務分析には「内部分析」と「外部分析」とがある。内部分析は、掲げた目標を達成しているか、同業他社と比べてどこが劣っているか、設備投資が可能かなど、経営活動を検討する上での手掛かりを掴む手段である。外部分析はその企業と取引しても安全か、利益獲得に貢献してくれるかなどを検討するための分析である。
- 分析の方法には、実数分析と比率分析がある。さらに、1) 比率分析の中には全体を100として各項目の割合を分析する構成比率、2) 基準期間を100として割合を分析する趨勢比率、3) まったく別の項目との割合を分析する関係分析、4) 前期と比べ分析する期間分析、5) 他の企業と比べ分析する相互比較、6) 統計的な標準値と比べ分析する標準分析などがある。
- 各指標の算出方法と意味、解釈の仕方は、表3-1を参照。
- <Fig. 3-3>
Balance Sheet of A Company (Wholesales) , as of xxxx, Unit:¥1,000
- Re **: The Corporate Las provides 10% of dividends must be appropriated as a legal reserve; until the total of aggregate amount of legal reserve and additional paid-in capital equals 25% of the common stock.
- Profit & Loss of A Company (Wholesales) (Period: from xxxx to xxxx) Unit: ¥1,000
- Analysis sheet of A Company: (Standard ratio & figures are referred from SME Agency in Japan)
#
Main index
主要指標名
算式
計算結果
標準値
#
Main index
主要指標名
算式
計算結果
標準値
1
Ordinary profit to assets (ROA)
総資本対経常利益率
=86100/
3592500
2.40
%
3.60
%
7
Payables turnover period
支払勘定回転期間
=1370000/
471903
2.90 mo
1.40
mo
2
Ordinary profit to sales
売上高対経常利益率
=86100/
6017370
1.43
%
2.10
%
8
Current ratio
*3
流動比率
=2693170/
2482550
108.48 %
151.10 %
3
Gross profit to sales
*1
売上高対総利益率
=992860/
6017370
16.50 %
22.50 %
9
Fixed asset ratio
固定比率
=899330/
723350
124.33
%
129.80 %
4
(Sales to) Total capital turnover
総資本回転率
=6017370/
3592500
1.67 turn
2
turn
10
Fixed asset to long-term capital
固定長期適合率
=899330/
1109950
81.02
%
69.80
%
5
Inventory turnover period *5
棚卸資産回転期間
=1253610/
501448
2.50
mo
1.62 mo
11
Equity capital to total capital
総資本対自己資本比率
=723350/
3592500
20.14
%
34.40
%
6
Fixed asset turnover period *2
固定資産回転期間
=899330/
501448
1.79 mo
1.13 mo
12
Quick ratio *4
当座比率
=1393850/
2482550
56.15
%
114.90 %
- Analysis comment: The above blue colored indices is higher the better, green colored indices is lower the better.
*#
Problems of A-company
Assumed management issues
Problem-1
Gross margin is quite a lower than the standard.
Decrease of sales may be caused by fall of sales unit price, more sales of less profitable goods, or rise of purchase material unit price.
Problem-2
Fixed asset turnover period is quite a longer than the standard.
There may be ineffective investment of tangible & intangible fixed asset, which should be curbed to appropriate level.
Problem-3
Current ratio is quite a lower than the standard.
Regarding Problem3 & 4, Establish long-term finance policy, particularly transferring from short-term to long-term debt, as well as liquidation of the asset.
Problem-4
Cash to current liability ratio is quite a lower than the standard.
Problem-5
Inventory which is 2.5 times of monthly sales is too large.
There may be dead stock of inventory, which should be liquidated as soon as possible.
Problem-6
Both sales amount and ordinary income decreases from the previous FY.
Measures to increase sales is urged, including review and improvement of products line, selling method, etc.
- Various index for financial analysis; formula and analytical viewpoint
表(Fig) 3-1
指標, Index
算式, Definition
指標の意味・見方, Meaning & check points
収益性
Profitability
analysis
総資本対経常利益率 (%)
Return On Assets
経常利益/総資本
Ordinary profit/Total capital
Operational efficiency; higher the better
利益率
Profit rate
売上高対経常利益率 (%)
Ordinary profit to sales
経常利益/売上高
Ordinary profit/Sales
Check sales cost, SGA, interest & discount rate, if it is lower.
売上高対総利益率 (%)
Gross profit to sales
売上総利益/売上高
Gross profit/Sales
Check product mix, price policy, sales cost, production cost, if it is lower than competitors.
売上高対販売管理費率 (%)
Operating expenses to sales (SGA ratio)
(販売費+一般管理費)/売上高
(Selling cost+Administrative cost)/Sales
Check fixed cost such as personal cost, etc., if it is higher.
売上高対支払利息率 (%)
Interest expense to sales
(支払利息+割引料-受取利息)/売上高
(Interest & discount cost - Interest income)/Sales
Max 3% in manufacture; Over 5% is revenue pressure.
回転効率
Turnover
総資本回転率 (%)
Total capital turnover
売上高/総資本
Sales/Total capital
Check capital investment, inventory, receivable collection period, if it is lower.
受取勘定回転期間
Receivables turnover period
(受取手形+売掛金+割引手形)/平均月商
(Promissory note+ Accounts receivable+ Discount bill)/Sales (mo)
Check receivables collection period, non-performing loan, if it is longer.
棚卸資産回転期間
Inventory turnover period
棚卸資産/平均月商
Inventory/Sales (mo)
Check useless or dead inventory, if it is longer.
固定資産回転期間
Fixed asset turnover period
固定資産/平均月商
Fixed asset/Sales (mo)
Check idle asset, if it is longer
支払勘定回転期間
Payables turnover period
(支払手形+買掛金)/(材料仕入高+外注加工費+商品仕入高)/決算月数
(Notes payable+ Accounts payable)/(Material purchased+ Subcontract cost+ Goods purchased)
Check payables & compare with 'account receivable turnover period), if it is longer.
安全性
Safety analysis
流動比率 (%)
Current ratio
流動資産/流動負債
Current asset/Current liability
Average 120-130%; shorter is better. Check current asset and liability.
固定比率 (%)
Fixed asset ratio
固定資産/自己資本
Fixed asset/Equity capital
it is preferable less than 100%, unless fixed asset to long-term capital is 70-80%.
固定長期適合率 (%)
Fixed asset to long-term capital
固定資産/(自己資本+固定負債)
Fixed asset/(Equity capital+Fixed liability)
70-80% is preferable; if over 100% oppresses short-term solvency
総資本対自己資本比率 (%)
Equity capital to total capital
自己資本/総資本
Equity capital/Total capital
30-40% is preferable; higher has more resisting power.
当座比率 (%)
Quick assets ratio (Cash to current liability), or Acid test
当座資産/流動負債
Quick asset/Current liability
more than 100% is preferable; higher ratio has more solvency against current liability.
Liquid asset = Cash+Notes receivable+Account receivable+Temporary securities
借入金利子負担率 (%)
Interest to sales
{(支払利息+割引料)-受取利息}/売上総利益
{(Interest expense+Discount expense)-Interest income}/Gross profit
Check higher interest rate and off-the-book loan, if it is higher; or deferred/expensed interest, if it is lower
成長性
Growth analysis
売上高増加率 (%)
Sales growth rate
(当期売上高-前期売上高)/前期売上高
(Previous sales- Current sales)/Previous sales
more than 10% is preferable; growth rate of sales should be bigger than that of expense, or down of profit is not bigger than down of sales.
経常利益増加率 (%)
Ordinary profit growth rate
(当期経常利益-前期経常利益)/前期経常利益
(Previous ordinary profit-Current ordinary profit)
- Assume corporate issues from finding problems:
- From the below financial statement of A-company, wholesaler, calculate several indices and compare with the standard index of the industry, which is published by SME Agency in Japan annually. It is preferable to analyze several financial periods rather than one financial period.
- Several analysis and its comment are listed below. (from Problem-1 to Problem-6)
- Here are hypothesis for a solution:
Regarding the inventory issue, followings are hypotheses:
- Hypothesis-1: Reduce ¥400M of inventory
- Hypothesis-2: Sell a portion of inventory of ¥300M with gross margin 5% (Sales amount will be ¥315.79M)
- Hypothesis-3: Dispose a portion of inventory of ¥100M with no charge.
- Hypothesis-4: Repay a portion of debt of ¥300 to the bank.
- 問題点から経営課題を推測する:
- では、卸売業A社の財務諸表から、実際に幾つかの指標を計算し、標準比較で分析してみる(Fig. 3-3)。標準値には、中小企業庁が毎年発行している中小企業の経営指標を使う。実際の分析では1期だけでなく、出来れば数期分を分析した方がよい。
- いくつかの財務分析とその評価は以下参照(問題点1〜6)
- 問題点は棚卸資産の多さにあるので、経営改善として以下在庫削減策を仮説として導ける。
- 仮説1: 棚卸資産を4億円圧縮
- 仮説2: 内3億円を粗利5%で販売
- 仮説3: 内1億円は商品価値がないので廃棄
- 仮説4: 短期借入金を銀行に返済
- BS before and after of solution measure is adopted: (Fig.3-4)
- Hypothesis-1: The inventory of current asset reduced ¥400M.
- Hypothesis-2: The company sold a portion of inventory ¥300M with gross margin 5%, and received cash ¥315,790K for the sales of it. Consequently the cash account increased ¥21.79M as a result of reduction of interest expense ¥6M (interest rate is 2%) by repayment of ¥300M to the bank.
- Hypothesis-3: The total liabilities and shareholders' equity decreased ¥378,210K as a result of compression of inventory of ¥400M and increase of cash ¥21.79M.
- Hypothesis-4: The company sold a portion of inventory ¥300M at ¥315.79M, and could repay a portion of short-time debt ¥300M to the bank; then decreased ¥300M of short-term debt of current liabilities.
- Consequently, the income before tax decreases ¥78.21M, and whose portion of income tax (effective tax rate 40%) becomes exempted; resulting current liabilities, etc. decreased ¥31,278K.
- The change of BS is above as before and after this implementation. The total liabilities decreased ¥331,278M as a result of decrease of shot-term debt ¥300M and others ¥31,278K.
- The retained earnings (here net income) deceased ¥46,932K, as well as the total shareholders' capital decreased ¥46,932K as well.
- The total liabilities decreased ¥331,278K, and The total shareholders' equity decreased ¥46,932; thus The total liabilities & shareholders's equity decrease ¥378,210K.
- The bottom line of debt and credit match each other becoming ¥3,214,290K.
- <Fig. 3-4>: Change of BS after
implementing the solution:
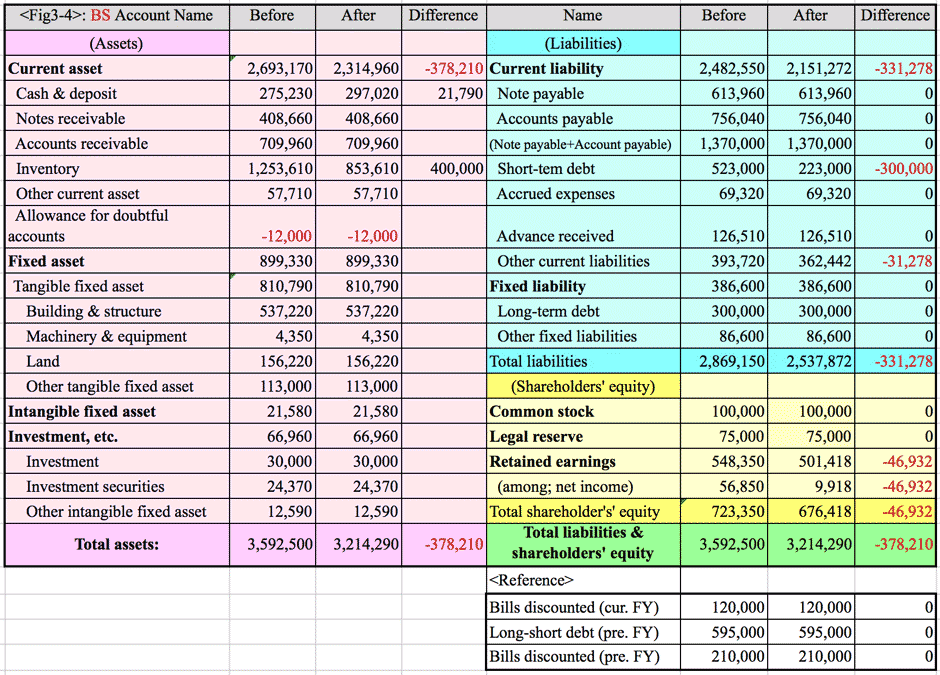
- PL before and after of the solution measure is taken: (Fig. 3-5)
- The final inventory decreased ¥400M.
- Sales increased ¥315.79M, and sales cost increased ¥300M respectively, resulting gross profit, or operating income increased ¥15.790M.
- The transfer of inventory removal and extraordinary loss increased ¥100M due to disposal of ¥100M inventory.
- The interest expenses (interest rate 2%), or non-operating expense decreased ¥6M.
- The ordinary income increased ¥21.79M, but the income before taxes decreased ¥78.21M due to disposal of useless inventory ¥100M.
- The taxes (effective tax rate 40%) decreased ¥31.278M, the net income and unappropriated surplus of current FY decreased ¥46.932M respectively.
- The cash flow increased ¥21.79M.
- <Fig. 3-5: Change of PL after
implementing the solution:
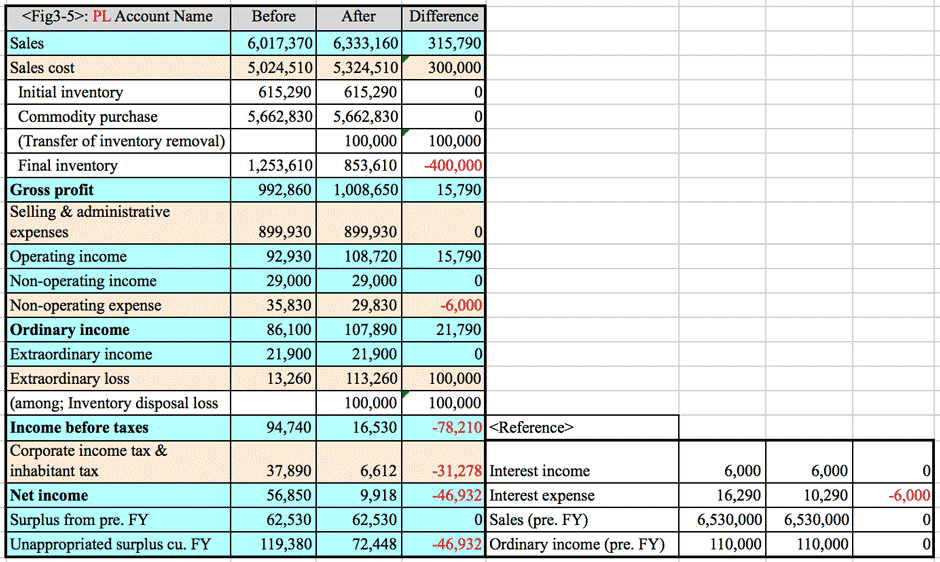
- <Column>
- The author had not borrowed money from a bank until establishment of this company; when I went to a bank for funding for the first time, the branch general manager said to me, "Are you really managing the company without knowing the trial balance sheet?"
- I learned accounting as one of liberal arts at the university, but I failed to get the credits of the subject. The branch general manager introduced me a correspondence course of accounting of the bank, where the listeners are obliged to summit 12 reports to finish the course. I could fullfil the course. It is important for anyone to have clear motivation to attain one's goal.
- During the course, I recognized any such an item as account receivable, inventory, or note receivable would be booked as a profit in accounting, though which could not be guaranteed to be a profit. Profit in the ordinary image and that in the accounting is different. From then, I have challenged to aim zero debt management as well as reduction of inventory.
- Assume that there is an inventory of ¥60M; if this inventory could be zero, which means there arouse ¥60M cash. And if there is regarding account receivables which needs two months to collect. If the company's monthly sales is ¥60M, it is equivalent to the sleeping cash of ¥120M.
- If this account receivable could be collected in a month, which means ¥60M cash was arisen. Together with the reduction of inventory and this earlier collection, the company could make ¥120M cash available.
- It is obvious that the knowledge of accounting is indispensable for corporate management; which was, I recognized later, the start of cash-flow based management.
- <コラム> 落第生が始めたキャッシュフロー経営:
- 筆者は会社を設立するまで銀行でお金を借りたことがなく、初めて銀行に行ったとき、支店長から「試算表も知らずに会社を経営しているのか?」と注意された程であった。
- 大学時代には一般教養で財務を受講していたあが、毎回単位が取れなかった。その支店長から銀行の通信教育を紹介され、1年間全12回のレポートを提出し、無事に終了できた。目標が明確だと人は実現できるのである。
- この通信教育を通じて、初めて分かったことの1つに売掛金、在庫、手形のいずれもが「利益」計上されることである。将来、利益になるはずだが、受け取れない可能性もあるのにです。一般的にイメージする利益と会計上の利益は別物ということである。そこから借入金ゼロに向けたチャレンジが始まり、在庫削減に取り組むようになった。
- 仮に¥60Mの在庫があれば、これをゼロにすれば¥60Mの資金が浮くことになる。また売掛債権も、債権回収の2ヶ月かかるとし、月商が¥60Mなら¥120Mの資金が寝ていることになる。これを1ヶ月で回収できれば¥60Mの資金が浮き、在庫と合わせて¥120Mのキャッシュを生むことになる。
- 今から考えれば、会社経営には財務の知識が重要であり、偶然キャッシュフロー重視の経営をスタートさせていたことになる。
>Top
4. SFA for output-based management could not cultivate sales skills:
- SFA (Sales Force Automation):
- Many companies have introduced SFA system to strengthen sales capability, but now a few companies could not use the system effectively. I think there is a reason why the necessary sales skills to develop new market could not be gained only by controlling the numerical sales target and activities of sales staff.
- The concept of SFA was proposed in the first half of 1990s in US, where most of the sales staff are contract employees easily changing jobs. SFA they want was a mechanism to be able to control clients information to continue sales activities even though the staff were changed. Then Japanese companies mostly adopted lifelong employment such mechanism would not be so serious.
- Since latter half of 1990s, Japanese companies increased to adopt performance-base pay system, which accordingly increased to introduce SFA. SFA system itself developed to adopt Japanese behaviors such as daily report and monthly probable clients status list, which was appreciated as a certain level of contribution of sales efficiency.
- Since 2000, SFA has been widely acknowledged as a tool to strengthen sales activities, around that times Asclab adopted SFA, but was no exception to be a good user of SFA.
- The front-end activities never changes by introduction of SFA system.
- SFA is a tool aiming to strengthen sales activities, increase business opportunities, raise close rate of order, and then increase sales and profit. But actually satisfactory result could not be attained by introduction of SFA system. Why? Because the situation of the front-end activities could not change by introduction of SFA (Fig. 4-1). Followings are the major reasons:
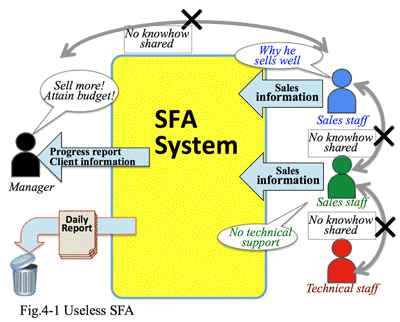 Managers would not check daily reports everyday, who are too busy to attend internal meetings and preparation for it, or who are fully occupied to promote their own business activities.
Managers would not check daily reports everyday, who are too busy to attend internal meetings and preparation for it, or who are fully occupied to promote their own business activities.- Sales staff who input daily report could receive none or very limited appropriate advice from their managers; the situation has not improved yet since hand-writing days of daily reports.
- No merit of inputting daily report gives less incentive to continue to input daily report. Or even inputting it, the contents will be shortened or omitted.
- SFA assumes that the role of managers who would check daily reports of their staff everyday, give proper advice, accompany them in visiting clients, or ask support from other divisions in order to perform the negotiation. And through the team work the manager and the staff could learn lots of knowhow for sales and getting orders.
- But the team activity using daily report has already collapsed. The managers themselves are obliged to concentrate their own negotiations to attain the short-term budget, rather than spare their time for the requests of their staff.
- Then the following problems occur:
- The staff learned the lecture for proposal-based sales, which becomes useless. Because they could not ask questions about this, and even dared to ask, the reply would be that they had already taught it.
- Without practical skills for proposal-based sales, they feel difficult to prepare the proposal. So they abandon to promote proposed-based sales, and return to the usual request-based sales, responding to the patterned requests for estimates by the existing clients.
- The sales activity still depends on individual sales person, and the team activity could not function any more.
- Thus the budget norm burdens each sales staff, particularly in such an economic severe situation, which make it impossible to change the marketing style if each one wants to change.
- Japanese sales style is featured as bottom-up type:
- Request-based sales is targeted to the existing client focussing numerical control of the sales. This is probably due to Japanese business behavior emphasizing long-term human relationship, in particular with person-in-charge of the partners. Both sellers and buyers have common tradition to respect courtesy each other, and to contact with other companies would be regarded as making light of the existing relationship. (Fig.4-2)
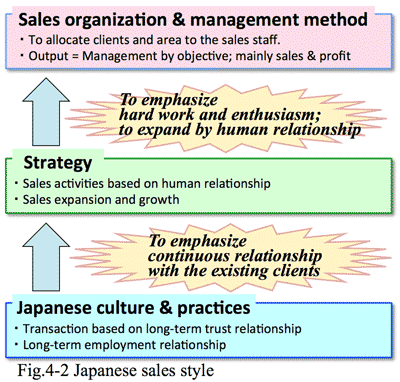
- Thus it would be the favorable strategy to maintain good relationship with the existing client by contacting frequently to secure orders; hard work and enthusiasm are particular important to strengthen human relationship. This would be a typical bottom up style which has affinity with output management.
- The supervisors instruct to their staff to be in charge of particular clients and/or areas to follow the assigned projects; this allocation makes easier in tracing numerical control by performance of each staff. (Fig.4-3)
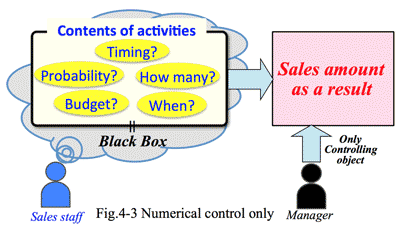
- SFA introduced under such environment will surely function as a control tool to support supervisors who check the project status according to the reports of their staff.
And now the this request-based market is shrinking; SFA tool is also shrinking as well which was aimed to control quantity control of sales under favorable economic conditions which has grown according to frequency
of visiting clients.
- Communication postulates shared awareness:
- Even managers emphasized and urged, "The target figure has not yet attained!" in meetings, or "further proposals to clients, or approach to top management of clients," the front-end staff could not actually move forward.
- To begin with, the present managers have no interest other than the attained figures, who are also evaluated by the top management in terms of the attained figures. They could not show any concrete stories how to cultivate new clients other than indication only target figures.
- The staff who are to report to such managers recognize that they are evaluated only by the attained figures. Therefore they don't want to learn the knowledge or how to gain it, or mindset or skill-set needed to explore new client which should be learned from their seniors. Thus the staff are unconsciously trained without considering the story needed to cultivate new clients.
- Eventually, there arouses discrepancy in awareness between managers and staff, whose awareness are held in a black-box which could not communicate each other.
- Humans have their own process of understanding in unconscious way. Ten staff have ten different processes, including that of manager vs. front-end staff, senior vs. junior, among colleagues, or engineer vs. sales staff. Each has each different perception, causing direction of the integrated vectors could be varied.
- Humans have their own process of understanding in unconscious way. Ten staff have ten different processes; manager vs. front-end staff, senior vs. junior, among colleagues, or SE vs. sales staff, each has each difference perception, causing the direction of the vectors could swing. (Fig. 4-4)
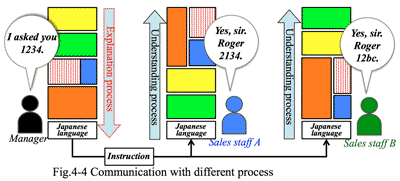
- Manager accompanies the sale staff to the client:
- Asclab considered that there would be no other alternatives but to remove the factors which could deteriorate sale power in order to save the company, though the sales and profit could deceased temporally. Following three decisions are adopted:
- To ease the target performance, and ordered all staff including sales and technical to receive lectures for proposal-based sales method.
- All corporate executives should support promotion of proposal-based sales; and control sales process using SFA tool.
- The unattainable figures should be responsible to all corporate executives; and aim to increase skills of sales staff as well as streamline the organization.
- By these reforms, accompanies sales activities increase and the reform seemed in steady progress; but the sales power could not be enhanced. Most of the sales staff have no proposal-based negotiation, because they had only responded to requests of the existing clients. They could not find out needs of the client which should be proposed by us.
- Then managers instructed the sales staff to accompany the propose-base sales activities of the manager's own project. The sales staff who accompanies the manager could communicate well with the client, but still the following problems became obvious:
- Problem-1: Sales staff has no awareness of person concerned, who feels to support the manager.
- Problem-2: Sales staff feels difficulty in raising questions to the manager, who once scorned.
- Problem-3: Sales staff does not know to whom he should raise technical question.
- Problem-4: Technical staff seems uncooperative when the sales staff directly raise questions bypassing the manager.
- Problem-5: There exist persons who seem difficult to ask questions.
- Problem-6: Engineers tend to require the question should be via manager who know the background of question and situation, including information related to calculating man-hour of the support. (Fig4-5)
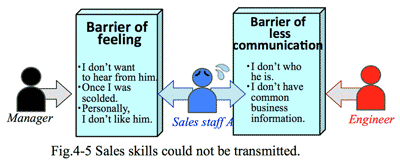
- These problems are related to human sentiment or mechanism how to share information between different divisions. These could be adjusted and solved by the manger concerned, but who are actually busy in involvement to follow his own project outside office, while the market requires speedy response to answer the question.
- To promote propose-based sales activities, support of experts becomes essential, but the front-end staff do not know who's who of the internal experts. In addition highly experienced and skilled experts are generally senior ranked status, whom the front-end staff hesitate to raise direct questions, let alone face-to-face questions.
- Generally SFA tool is a closed system within sales division aiming to share information of clients concerned between managers and their staff.
- In order to strengthen sales power, it is urged to remove factors impeding smooth communication between manager and their staff, including sharing information of team sales activities and sales policies, etc. Proposal-base sale activity could not be performed by personal skills of the sale staff, but team activity would be indispensable collecting special skills supported by other divisions.
- Quality of sales matters for survival of the company.:
- Now the market trend has shifted from the age of quantity (high growth period) to the age of quality (matured period); from how to efficiently proceed the clients' needs to how to maintain relationship with clients. Thus the power of sales = sales volume × sales quality. SFA had functioned to increase the parameter of sales volume.
- But from now on, increase of sales quality becomes more important; the only solution is to cultivate human resources whose skills fit to the market needs. It is now pointed that OJT method is not necessarily effective; we need to have more favorable environment for effective enhancement of human skills through daily activities.
- Managers are required not only to instruct sales goals but also to give necessary knowledge for the staff promoting to be more autonomous; i.e., to shift from output control to process control. This means target of the market is changing from request-based sales to proposal-based sales, or from marketing for person-in-charge to marketing for top executives to acquire new client, expanding new business sphere.
- Without success of this transfer, the sales staff might become a kind of cost center in the future. In such situation, younger staff in particular would lose their dreams for success, which would jeopardize survival of the company.
- <Column> Information sharing by colored labels:
- When new IT products such as PC are published, price of the old models tend to fall drastically, which is one of reasons of dead stocks.
- There is a model number on the package of PC, which most of accountants could not recognize which are new or old.
- Then, we attached a different color label of each package; blue label for the latest model, yellow for current prevailing model, and red for old model. Thus anyone can distinguish difference of models of PC, and share information as the stockpile.
- This segmentation could lead to minimized inventory and improve cash flow not by using particular IT system. This experience became one of our ideas how to segment improvement by process and that by IT system.
4. アウトプット管理のSFAでは営業スキルは育たない:
- SFA(セールス・フォース・オートメーション)
- 営業力を強化するために多くの企業がSFAシステムを導入しているが、期待通りの効果を得ていない企業が少なくない。売上とそれをもたらす営業担当者の行動を管理するだけでは、新規開拓に必要な営業スキルを育てられないからである。
- SFAは、1990年代前半に米国で提唱され始めた概念である。米国の営業職は契約社員が多く、また転職率も高い。彼らが求めたSFAは「担当者が変わっても継続的に営業するための顧客管理の仕組み」であった。当時の日本はまだ終身雇用が前提だったので、当然受入れられなかった。
- それが1990年代後半から、日本でも成果報酬制度を導入する企業が増え、それと併行してSFAの導入件数も増えてきた。SFAシステムも日本的習慣である日報やヨミ表(商談確度別月別受注予定表)に対応してきたので、一定の営業事務の効率化が可能となった。
- そして2000年に入り、SFAのコンセプトは営業力を強化し、商談件数と成約率をアップを重視するように変化した。アスクラボがSFAを導入したのも丁度その頃で、期待通りの効果を得られなかったのは例外ではなかった。
- システムを導入しても現場は変わらない:
- SFAを導入する目益は営業力強化である。それによって商談件数と成約率をアップし、売上を高め、さらには利益を高めるための道具である。にもかかわらずSFAを導入してもなかなか成果を見い出せないのはなぜか。それはSFAを導入しても現場の状況が変化しないからである(図4-1)。それには幾つかの理由がある。
- 上司は営業担当者の日報を毎日見ていない。上司は社内会議や、そのための資料作り、あるいは自分の商談活動で手一杯で、毎日日報を見る時間がない。
- 営業担当者は日報を入力しても、上司から適切なアドバイスを受けられない。例えアドバイスがあっても少ない。状況は手書きの日報時代とあまり変わらない。
- 日報を入力してもメリットがなく、入力しなくなる。入力したとしても内容を省略している。
- 上司は、本来、日報を見ることで部下の活動を知り、アドバイスしたり同行したり、他部門へ協力を要請したりするなど商談成約に向けて支援するのが役割である。そして上司と部下からなるチーム活動を通じて、部下は上司や他部門から営業・受注に必要な多くのことを学ぶ。
- ところが、日報を使ったチーム活動がすでに崩壊している。厳しいアウトプット管理により上司は、中長期的な新規顧客開拓や提案営業に向けて部下の要請に時間を割くより、短期的な予算達成のために自己商談の発掘と成約に全力を上げざるを得ない。
- すると次のような問題が発生する。
- 部下は提案営業の研修を受けたが、実践に役立たない。上司に聞いても的確な回答がなく、前に教えたと叱られる状況。
- スキルがないため提案営業に手間取り予算達成ができなくなる。結果、個人の予算を達成するために提案営業を断念し、既存顧客への御用聞き営業、見積依頼に対応する営業に戻ってしまう。
- 相変わらず担当者個人の営業活動となり、チームとして動けない。
- こうして見ると、景況が悪化する中で、予算が個人の肩に重くのし掛かり、これまでのやり方を変えたくても変えられないのが現状である。
- 日本の営業スタイルはボトムアップ型:
- 既存顧客をターゲットにしたリクエスト営業(御用聞き営業)のマネジメントは、数字を中心とした管理で対応できた。日本の風土や習慣が、長期的な人間関係を重んじたり、相手側の担当者が知り合いであるといったことを重視したりしてきたからである。長年の付き合いだから今更他社と付き合うなんて、相手の顔も立たないなど、日本的な礼儀を重んずる文化を、顧客も売り手側も共通認識としてもっていたこともある(図4-2)。
- そこでの戦略は、人間関係を重視した営業活動による既存顧客との継続的な取引引と、既存顧客に食らいつき足繁く通って受注を確保するというものである。営業担当者の頑張りや熱意を重視し、人間関係の強化を売上拡大につなげるのである。これは典型的なアプトプット管理であり、ボトムアップの体制である。
- 営業活動では、担当の誰もが見込み案件の有無や受注タイミング、予算、商談の確度などの要素を把握しているが、全てが営業担当者個人の頭というブラックボックスの中にある。
- そのため上司は、営業体制を整えると称して営業担当者に顧客や地域を割当て、「Aさんは、このお客を、Bさんはこの地域を担当して下さい」ちの指示を出す。管理と称して実績数字が達成できたか、達成できなかったかという数字中心の管理に終始してしまう(図4-3)。これが現在の営業体制と管理の実態である。
- そんな環境・体制のまま導入したSFAは、営業部門の上司が部下の商談状況をヨミ表から把握し、部下の予算進捗に淡っ背手叱咤激励づるための管理ツールの域から脱せなかった。そして今、このリクエスト営業が通用する市場は、残念ながら縮小傾向にある。SFAの失敗には、好景気下の「量の時代」に象徴される顧客への訪問回数に比例して売上が上がった時代が反映されている。
- 共通認識がないとコミュニケーションが成り立たない:
- 管理者が、いくら会議の場で「数字が達成できていない」と力説し、また、ユーザーへの提案、新規顧客開拓、トップへのアプローチを叱咤激励したとしても、営業担当者を動かすことはできない。
- そもそも現在のマネジャーは、営業担当者のマインドやスキルなど、実績数字以外のことに興味を持っていない。マネジャー自身も上層部から数字で評価されているからである。部下に対しても数字で評価し、数字以外のことには興味が薄く、結果として新規顧客開拓に必要なストーリーを考えない営業作業者を無意識に育成している。
- 部下である営業担当者も数字だけで管理されていることに気づいている。そのため、上司が持っている知識や、その習得方法、できる営業担当者の判断や活動の仕方、失敗例や成功例から学ぶことなど、スキルアップに必要な事実を積極的に習得しようとはしない。断片的な経験知識しかないために、営業活動を流れとして捉えられない。
- 結果として、マネジャーと営業担当者それぞれの頭の中にある営業のためのプロセス=ブラックボックスに違いが生じ、コミュニケーションが取れないでいる。
- 人はそれぞれが無意識に自分なりのプロセスを持っている。10人の営業担当者には10種類のプロセスがある。マネジャーと営業担当者という上下関係、同僚という横の関係、SEと営業担当者という職種が違う関係の中では、同じことを言っても十人十色に受け止め方が違ってくる。それぞれに受け止め方が違えば、全体のベクトルが合わないのは当然である。(図 4-4)
- 上司が同行営業しても"他人事"に終わる:
- アスクラボでもこのような状況に陥った。そこで生き残るには、一時的に売上・利益が減少しても営業力強化を妨げる要因を排除し、改革するしか選択肢はないと考えた。そこで次の3つの決断を下した。
- 実績管理を和らげる。営業担当者、技術者の全員に、提案営業の研修を受けさせる。
- トップを含め、幹部全員が提案営業の実践を支援する。そのためにSFAを使って営業にプロセスを管理する。
- 実績の低下分は、トップを含む幹部自らが穴埋めする。これらにより、営業担当者のスキルアップと同時に組織体制を整える。
- この決断により、同行営業が増え、改革が進んでいるように見えたが、これでも一向に営業力は高まらない。営業担当者の多くは、既存顧客の見積依頼に対応するだけだったので、提案営業に値する商談を持っていなかった。つまり提案するためにニーズを発見できていなかった。
- そこで上司は、自分の商談に営業担当者を動向させ提案営業を実践して見せることで、彼らを独り立ちさせる方法に切り替えた。同行した営業担当者は顧客との話も問題なくこなすので、今度は順調にいくように見えたが、新たに以下の問題が浮き彫りになった。
- 問題(1): 営業担当者は、上司の作業を手伝うという意識で当事者意識が持てない。
- 問題(2): 上司に質問しづらい。以前酷く怒られた覚えがあるため。
- 問題(3): 技術者の誰に聞けば良いか分からない。
- 問題(4): 技術者に聞いても非協力的で、上司や先輩を通じて質問しないと相手にしてもらえない。
- 問題(5): 質問したくても「あの人には聞きたくない」という相手がいる。
- 問題(6): 技術者は、営業担当者から直接質問されても質問の背景や内容が分からないため「上司を通して欲しい」という。商談内容や方針が把握できず、支援内容が関係する工数を算定できないためという。(図4-5)
- これらの問題は、人の感情や商談情報の他部門との共有に起因している。上司が調整すれば解決する問題に見えるが、以前に比べると上司自身が営業活動に出かけ、社内にいることが少なく、一方で市場が要求するスピードが速くなっていることも現実である。
- 顧客に提案営業をするには、エキスパートの支援が必要だが、現場担当者には、社内のエキスポートの存在を十分把握できていない。経験・知識の豊富なエキスパートは一般的に高い役職についているため、現場スタッフには直接質問がしづらく、まして対面での質問はなおさらである。
- 一般に、SFAは営業部門に閉じたシステムで、営業担当者とその上司が情報共有するためのツールなので、顧客との接触情報しか入力されていない。
- 営業力を強化するには、マネジャーと営業担当者間のコミュニケーションの妨げ要因を排除し、商談成約に向けたチーム営業、組織営業に必要な商談の活動方針や検討経緯という情報を共有する必要がある。提案型営業は、専門スキルが要求されるので、営業担当者個人では完結できずチーム活動が不可欠となる。
- 営業の質を高められるかどうかが企業の存続を問う:
- 今、顧客ニーズはどのように処理するかから、業績をどのように維持するかに移り、市場は量の時代 (好況)から質の時代 (成熟期) に変化した。そこで、営業力=営業の量×営業の質と考えると、SFAは営業の量を拡大することで営業力を強化しようという発想が強いアウトプット管理のツールである。
- しかし、これからの営業力を高めるには質の増大が重要で、そのためには市場が求める人材を育成するしかない。OJTの効力低下が指摘されているが、もう一度人材が育つ環境、即ち仕事を通して自然に育つ環境を作り出さなければならない。
- そのためには、マネジャーがまず売上指標を支持命令するだけの管理ではなく、営業担当者が必要とする知識を伝え、本人の自主性を後押しする管理へ変わる必要がある。アウトプット管理からプロセス管理へ移行するのである。そして既存顧客との取引を継続しながら、縮小傾向にあるリクエスト営業から拡大傾向にある提案型営業へ、あるいは窓口担当向け市場から経営者マネジメント層向け市場へと対象を変えることで新規顧客を獲得し商圏を拡大するのである。
- この切り替えに成功しないと、営業担当者が将来的にコストセンターになる可能性がある。そしてその現状を見た若い営業担当者が夢を失い、マインドを下げ、さらに利益を生み出せない可能性がある。そうなれば、成長できないばかりか、強いては会社の存続事態が危ぶまれる。
- <コラム記事> 色違いの紙の札で始めた情報共有:
- PCに代表されるIT関連商品は、新機種が登場すると旧機種の価格が著しく落ちる傾向がある。これが不良在庫を生む要因の1つである。
- PCの梱包には型式番号があるが、経理担当者にはこの番号による機種の新旧はほとんどわからない。
- そこで、PCの梱包に青・黄・赤の3色の紙を貼ることにした。最新機種は青、まあまあの現行機種は黄、型落ちは赤い紙を貼った。これにより誰でも簡単に、PCの最新、現行、型落ちのモデルの違いを識別できる情報共有化が実現した。
- このようにITを使わずに仕組みに改善で在庫を減らしキャッシュフローの改善を体験できた。この経験が現在の仕組みの改善とシステムの改善を明確に分ける姿勢につながっている。
>Top
5. To make business process and story for IT sales:
- In the above chapter 4. I pointed out the limit of business model to control mainly the sales amount, which has been a preferable mechanism from the seller's viewpoint particularly in economic good times. Once a client opened trading account, continuous increase of sales would be guaranteed by continuous small turnings of sales. Managers could confirm increase of sales only by checking the output in terms of sales. (Fig.5-1)
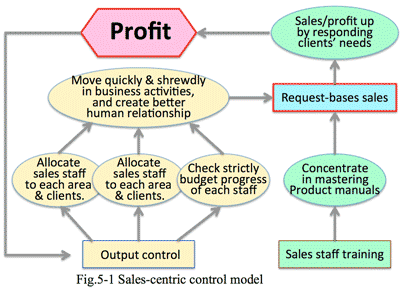
- The output control promotes sales style to emphasize human relationship and frequent contacts according to requests of the client.
- The content of activities for request-based sales and human relationship with the client could not be understood by anyone but the sales staff oneself, which also could not be shared in the company.
- The result reward based on output control promotes individualism in the organization.
- To visualize mindset of the capable sales staff:
- Even under the output control environment, a part of sales staff have performed proposal-base sales. In particular, most of the original members since establishment of the company or the division have been obliged to practice proposal-based sales activities.
- What is the difference of capable or not-capable sales staff? Capable staff always consider process of the sales, and retain skill map of the members who can respond proper answer to a certain question.
- The idea of "process" is a natural thinking particularly in manufacturing process, which defines when and how the activity of each person should be performed.
- What about the sales field, which has been mostly depended on individual capability, not on organizational one. The important role of the organization to increase skills of sales staff has been neglected. In addition pay-per-performace system escalated individualism has impeded to realize organizational sales activities.
- This phenomenon is not limited in IT industry, which is observable in almost all industries such as car sales, home sales, department stores, financial institutions, etc. It is important to visualize action or mindset pattern of the sale staff who have realized proposal-based sales and development of new clients, then proliferate such patterns to all sales staff to be able to take the first step of the new action plan. (Fig. 5-2)
- There will be no solution without process:
- It could not propose a solution without considering there is a process in sales activities. The sales staff who can cultivate new client considers the present problem is one of the total process, judging the location of the problem concerned in the total process and performing appropriate response to it.
- A sales staff who cannot take this process could not recognize where is the problem concern, being to take no action at all or take unplanned action. This is applicable not only sales staff but managers too. The staff who can prepare in advance can act effectively with confidence. Conversely one who cannot prepare it may be rude to the client and lose confidence.
- The process for sales activities will be divided as follows:
(Fig.5-3)
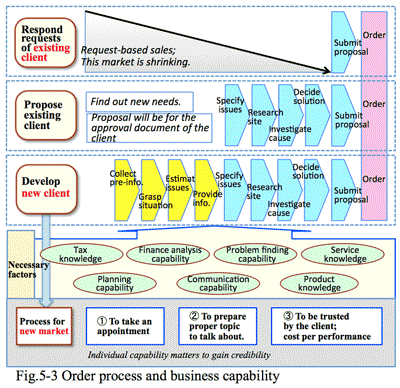
- To consider how to cultivate prospective purchasers (PP); such as to hold a seminar or exhibition is one of them.
- To cultivate project for finding PP; such as to pick up participants at a seminar who show an interest on the subject, and follow up by DM or ask someone who have more interest.
- To know the client (to collect information); such as to check HP or financial statement of the client.
- To approach person-in-charge of the client; such as to prepare to make documentation to attract the client, collecting necessary skills from internal experts.
- To approach top executive of the client; prepare hypothesis as a solution for the corporate management based on the informations got from the former contacts.
- To know the field site of the client (to check the business); to check the object of the field survey and prepare documentation for the research, getting advice from internal experts.
- To assume or confirm issues of the client; to clarify problems of the client, and find out the essential issues in them. (Fig. 5-4):
- To prepare solution for the issues of the client; to consider a solution of the extracted issue. The client bought effect of the product, not the product itself. (Fig. 5-5)
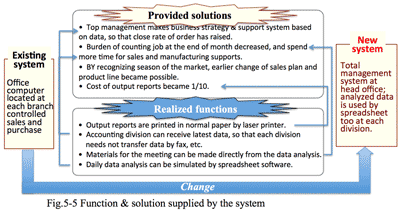
- To propose the solution; to collect necessary players to make a proposal, and assign role of each player in time for submitting the proposal.
- To follow up the proposal; to consider timely follow-up to secure the contract after submission of the proposal.
- To make a contract with the client; to consider probable risks related to the project getting advice fro different internal know-how and experiences.
- To transfer the project to SE in charge; to perform the contract starting detailed communication with the client. The sales staff continue to watch this procedure.
- Development of new customers requires all such process and collaboration of various skilled staff who can decide autonomous judgement depending on such atypical situation. Each member is required to supply necessary skills and expertise, raising proper questions time to time.
- Particularly important post-sales additivities:
- Sales staff must recognize the importance of post-sales process: (Fig. 5-6)
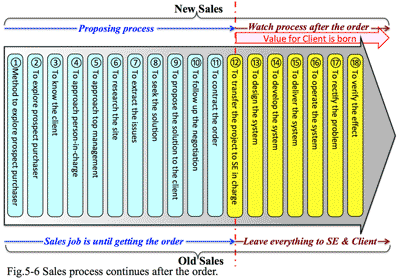
- It should be noticed that the client required the effect by the order not the only purchase of hardware and software; the contract is one of the checkpoints. Considering the effect supplied by operation of the system, verification of the effect and control of the system would the the next responsibility for the supplier to watch.
- During the process of installation and operation, various troubles may happen, such as 1) no smooth operation is possible by an foreseeable accident, 2) no cooperative staff of the users, 3) no due performance of procedure of operation. All these troubles could be know-how for the solution provider; to accumulate and find solutions against these become know how trouble shooting of utilization, which would be a base for proposal-based or consultation-based sales.
- Most of sales staff had considered that once the project was transferred to SE after the contract, the role of the sale staff finished, having no intention to keep and integrate all data of the client, because the manager required sales-centric output control. Thus sales staff had regarded that getting the order is success, while losing it is unsucess; neglecting various experiences, know how, teaching and being taught by the client or SE or advice from seniors.
- But actually, there is a key to success there to shift from request-based sales to proposal-based sales. History may repeat itself. The present economic downturn may change into economic upturn. But even the economic condition changed, it necessarily means the old fashioned sales style could not come back. Rather severer sales style could be required. It is also true that history could not go back.
- The ratio of output control should be decreased:
- It takes time to return request based sales to proposal-based sales. But the change into proposal-based sales should be prompted to respond to rapidly changing market. In order to promote this, it is necessary to prepare favorable environment and to remove unfavorable causes. (Fig. 5-7)
- The following environment should be established:
- To establish process for proposal-based sales
- To have common recognition of proposal-base sales among all members including manager, expert, sales and technical staff.
- Manager should give overall support for process of proposal-based sales from practical viewpoint.
- To establish systematic function of experts to supply high level skills necessary for proposal-based sales to sales staff.
- Conversely, the following environment should be removed:
- To terminate output control of sales progress, and to support process for sales activities instead.
- To
- In addition the following environment as a common should be established:
- Business activities and Q&A should be opened and shared.
- Managers should be conscious of making their staff have clear target and self-directing, by way of teaching and coaching method, aiming to increase project numbers and success rate of order, as well as skills up of sales and engineering staff.
- Experts should return proper answer to the questions, aiming to increase project numbers and success rate of order, as well as skills up of sales and engineering staff.
- Communication should be essential, dispensing with persona sentiment, and such Q&A are to be stored in the system.
5. IT営業のためのプロセスとストーリーを作る:
- 第4章で、売上を中心に管理するビジネスモデルの限界を指摘した。このビジネスモデルは、好況の時代には売り手側にとって都合の良い仕組みであった。終身雇用や長い取引慣行を重んじる日本文化を背景に、顧客が一度取引口座を開いてくれれば、後は小回りの利く営業活動を続けることで売上を増やせたからである。そして、そこではアウトプット=売上を管理していれば、実際に売上を伸ばすことがで きた。(図5-1)
- アウトプットを管理し、売上予算の進捗を厳しく追及すると、リクエスト営業=高頻度で小回りの利いた対応や人間関係を重視する営業が促進される。
- リクエスト営業の活動内容や顧客との人間関係は、営業担当者本人にしか分からず、社内で共有できていない。
- アウトプット管理による営業担当者への成果報酬は、個人主義を助長する。
- できる営業担当者の頭の中を可視化する
- アウトプット管理の環境下でも、一部の営業担当者は、これまでも提案営業を実践してきている。新会社や新事業部門の設立当初からのメンバーのほとんどは新規顧客獲得のための提案営業を実践せざるを得なかった。
- できる営業担当者と、できない営業担当者との違いはどこにあるのか?できる営業担当者は、営業のプロセスを考え、誰に何を利けば何が分かるかといったスキルマップを保有している。
- 「プロセス」という考え方は、製造業に代表されるモノ作り現場ではごく自然な考え方で、モノを作るための工程や各人の行動が明確にされる。
- これに対して営業現場はどうか?個人の力量だと考えられてきた営業活動は、そのプロセスを組織として把握していない。営業活動を支援したくてもできないのが実態である。結果、営業担当者のスキルを上げるという企業にとって重要な人材育成がなおざりにされてきた。成果報酬が個人主義を助長し、チームとしての組織営業の実現を阻害することになる。
- これはIT業界に限ったことではなく、自動車販売、住宅販売、百貨店、金融などすべての業種・業態、すべての営業現場で同じことが起こっているはずである。すでに提案営業・新規顧客開拓を実践できているできる営業担当者の行動パターンや思考パターンを可視化し、それを見せることで、具体的ないアクションプランが描け全員営業への第一歩を踏み出せることになる。(図5-2)
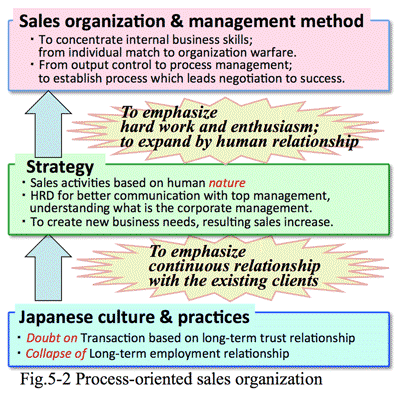
- プロセスなしにソリューションなし:
- 営業にもプロセスがあるということを理解できないとソリューションの提案は成り立たない。新規顧客を開拓できる営業担当者は、直面している問題を全体プロセスの一部として捉えている。今、発生している問題が、プロセスのどこに位置する問題かを判断し、それに対して必要な対応を下し、実行している。
- このプロセスを取られない営業担当者は、問題の所在を認識できないため行動が起こせなかったり、行き当たりばったりの行動になったりする。これは営業担当者だけでなくマネジャーも同様である。プロセスにそって事前準備できれば、顧客へのアプローチにも自信が持て確度が高まる。逆に事前準備なしに客先に出向くことは、それ自体失礼であり顧客の信頼を失っても仕方がない。
- 営業提案というプロセスは、以下のように分解できる。(図5-3)
- 見込み客の発掘手段を考える:セミナーや展示会などの開催もその方法の一つ。
- 見込み客案件を発掘する:セミナーの参加者の中から興味をもつ人を選び、DMや既存顧客の紹介を依頼する。
- 顧客を知る(情報を収集する):HPの検索や財務諸表の分析。
- 担当者にアプローチする:好感をもってもらうための資料作成するにはどんなスキルが必要か、また社内の誰に聞けばよいのか。
- 経営層にアプローチする:担当者へのアプローチを踏まえて、経営的な課題や業界の問題点の仮説を考える。経営層向けの資料を用意する。
- 顧客の現場を知る(業務を調査する):現場調査の目的や調査に必要な資料の作成など、社内の同業界への営業経験者に聞く。
- 顧客の課題を想定・確認する:顧客の問題点を明確にし、本質的な課題を抽出する。(図5-4)
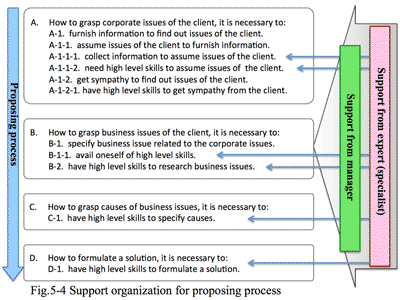
- 顧客の課題の解決策を策定する:抽出した課題に対するソリューションの検討。顧客は商品購入による効果を買う(図5-5)
- 顧客へ提案する:提案書作成に必要なプレーヤーを集め、いつまでに各プレーヤーが資料作成すべきか検討する。
- 顧客への提案をフォローする:提案・見積書の提出後のクロージングに向けたフォローアップ。どのタイミングでフォローすべきか検討。
- 契約を結ぶ:どのようなリスクを想定して契約書を作成するのか、これまでのスキルとは異なるプレーヤーが必要となる。
- 担当SEに引き突く:契約後、SEが案件を引き継ぎ、顧客との詳細打ち合わせを開始する。営業担当者は、今後の経過をウォッチする。
- 新規顧客開拓という"非定型業務"の中で自己判断できる人材を育てるには、このような営業プロセスの整備が必要である。その上で、それぞれのプロセスが必要とするタイミングや顧客の反応、必要なスキルや質問を投げかけるべきプレーヤーなど、本来のあるべき姿を一度は見せる必要がある。プロセスの不足部分があれば、それを自分で判断できるように導くしか方法はない。
- 重要度が高まる"受注契約後"の営業活動
- さらに、特にこれからの営業担当者は、契約を獲得してからのプロセスを重要視しなければならない。(図5-6)
- 顧客は、ハードとソフトを発注したのではなく、それらを利用した効果を発注しており、契約は顧客にとって一つの通過点でしかない。情報システムを導入運用して提供される効果を受注したと思えば、その効果が出るまでの検証と管理責任が発生する。
- 構築運用の過程では、ある問題が発生して上手く導入できなかった、顧客社内の抵抗勢力の営業を受けた、導入のために決めたことを実行できなかったなど様々な障害が発生する。しかし、ここで発生した事象に対応することがソリューションプロバイダにってのノウハウである。これらのノウハウや利用技術、トラブルシューティングを蓄積することが提案型・コンサルティング型営業のベースとなる。
- 多くの営業担当者は契約を結んだ後、SEにお任せしているため一元的な顧客のデータ収集ができていない。その理由は、マネジャーが売上中心のアウトプット管理をしてきたことになる。営業担当者は受注したら成功、獲れなかった失敗を長年やってきた。その結果、営業活動の過程での経験やノウハウ、自分自身が調査して顧客に答えたこと、顧客に教えてもらったこと、SEから教えてもらったこと、先輩たちからのアドバイスなどの経験やノウハウを軽視してきた。
- 現実にはそこにこそ、リクエスト営業から提案営業へ移行する鍵が隠されている。歴史は繰り返される。今の景気低迷も、そのうちに終焉し、経済が立ち直って生きても、昔と同じ営業スタイルが戻ってくるとは限らない。むしろ今よりもっと厳しい営業スタイルが求められる可能性の方が高い。歴史は後戻りできないのも事実である。
- アプトプット管理のウエイトを落とす:
- リクエスト営業を提案営業へ転換するには時間が必要である。市場の速い変化に対応するためには、できるだけ早くアウトプット=売上によるマネジメントを改める必要がある。それには提案営業を実践させる環境を整備し、それを阻害する要因を排除する必要がある。(図5-7)
- そのために以下の必要な環境整備を整える。
- 提案営業のプロセスを制定する。
- 提案営業のプロセスについて、マネジャー、エキスパート、営業担当者および技術者全員が共通認識を持つ。
- マネジャーは提案営業プロセス全般に亘り、実践面から支援する。
- 提案営業プロセスに必要な高度なスキルを営業担当者に提供できるエキスパートの位置づけ、支援体制を整える。
- 逆に、提案営業の実践を阻害する要因を排除する。
- アウトプット管理によって売上の進捗追求を止め、営業活動のプロセスを支援できるようにする。
- 売上中心の評価基準を見直す。プロセスにおけるチーム活動への貢献度評価のウエイトを高め、提案営業に必要な組織営業の弊害を排除する。
- また上記に共通な以下の環境整備として
- 活動内容や質疑応答などの情報をオープンにし、共有化を図る。
- マネジャーは部下に対し、明確な目標と主体性を持たせることを意識する。ティーチングとコーチングを使い分け、商談件数や商談成約率を高め、営業担当者や技術者のスキルアップに貢献する。
- エキスパートは、質問に適切に回答し、商談件数や商談成約率を高め、営業担当者や技術者のスキルアップに貢献する。
- コミュニケーションにおいては、感情を抜きに本質的な事柄を対象にし、その蓄積が可能なシステムを利用する。
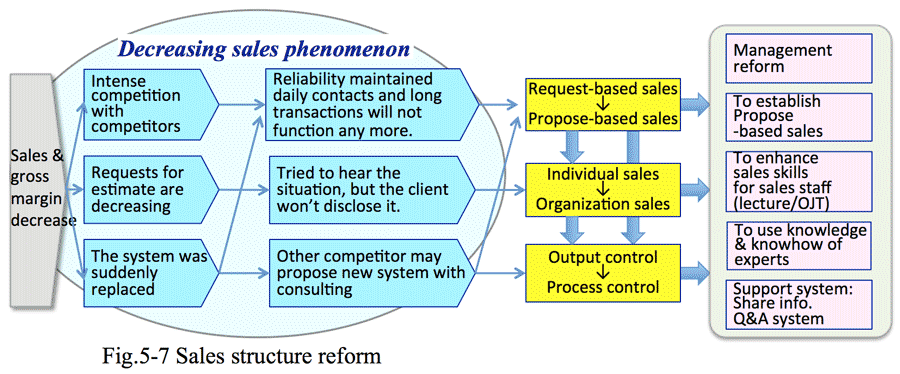
- <Column> Analog delivery slip:
- Asclab made new form of delivery slip for sales orders to minimize bad inventory.
- Items included in the new format are user name, number of estimate, accepting date of order, number of order, project name, estimated date of delivery, terms of transaction, name of department in charge & person in charge, placing date of order, name of manufacturer, name of order destination, name of product type, name of product item, quantity, standard price, delivery price, invoice price, date of arrival of goods & quantity, delivery (unfinished), order (unfinished), etc.
- Sales staff are required to input all these data, then accounting division can following the transaction, particularly price of purchased goods, price of order, due date, collection date, etc. without confirming with sale division in charge.
- First, the front-end sales staff strongly opposed this new form, because it is time-consuming to input all these data. It seems natural that sales division who needs not consider cash flow of the company dislikes to fill in such detailed information.
- However, from the viewpoint of accounting division, awareness of this issue is different; most of the staff of sale division are out of office in daytime. If some goods were delivered to the office in daytime, a person received this could not understand the goods were delivered as scheduled or were addressed to whom, furthermore there were often no price description on the delivery slip.
- Under such situation, no one could confirm the goods are complete set or not, causing further delay of delivery or payment, or in the worst case, unexpected cancellation happened.
- After adopting this new form of delivery slip, each copy was retained in the relevant division and accounting division, enabling any delivered goods could be recognized addressed to whom or for what client.
- Furthermore, accounting division could support sales division regarding to the delivery of goods or materials, returning with additional information such as price of order, delivery information from stored information at the accounting division.
- This is a typical case of analog type improvement without using IT.
- <コラム記事> アナログの受注伝票
- アスクラボでは、不良在庫を作らないためと社内業務の改善のために独自の受注伝票を作成した。
- 受注伝票に書き込む項目としては、ユーザ名、見積番号、受注日、受注番号、物件名、納入予定日、取引条件、担当部著・担当者、発注要指定日、メーカー名、発注先名、型名、 品名、数量、標準単価、納入金額、仕切り金額、入荷日&数量、納入未完、発注未完など。
- これらをすべて担当営業が記入することで仕入金額、売上金額、締め日、集金日などを明確にし、担当営業に確認しなくても経理部門の業務が流れるようにする。
- 当然、現場の営業は猛反発した。なぜこんなに手間のかかる伝票を書かなければならないのだというのである。会社の資金繰りなど行っていない営業部門にすれば嫌がっても仕方がない。
- しかし、経理の視点にたつと問題意識が違う。営業担当者は、昼間外出中が多く、営業が注文した物品が留守の間に会社に届くと、それを受け取る人達は、その商品がいつ注文され、どの顧客向けかもわからない。納品書に単価が書かれていないこともざらだった。
- こうした状況下では、品物が揃っているか分からない。その結果、納品遅れや入金遅れ、最悪の場合顧客にキャンセルされることもあった。
- この新受注伝票を使い始めてから、受注伝票に番号をつけ、自分の部と経理にそれぞれ控えを渡すことにした。これにより、荷物を受け取る人が、誰の発注か、どの顧客向けかの情報が一目瞭然になった。
- さらに、経理部門から、「どこそこ向けの商品が揃った」と営業をアシストすることも可能になった。経理に蓄積された発注単価や納期情報も営業にフィードバックできるようになった。
- これもまたITを使わないアナログな仕組みの改善の例である。
>Top
6. Mechanism to radicate sales process management:
- a
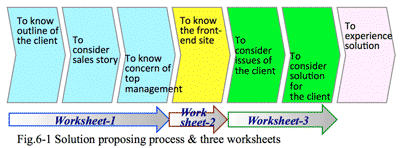
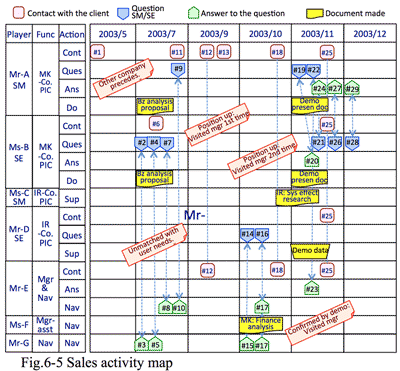
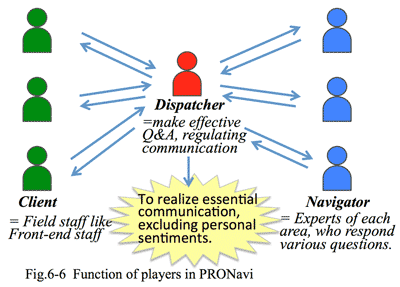
6. 営業プロセスマネジメントを定着させるための仕組み:
- 営業プロセスを抽出しても、それが定着しなければ意味がない。
- 営業プロセスを定着させるには、マネジャーと営業担当者の双方はPDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Action)のサイクルを回し、できること、できないことを明確にし、できない部分をつぶしていかなければならない。
- 営業プロセスを導入しても、直ぐに新規顧客開拓、提案営業ができる訳ではない。リクエスト営業の経験しかない営業担当者にすれば、営業プロセスに沿って動くことに半信半疑であり、最初の段階で失敗すれば、また元のリクエスト営業中心に戻ってしまう。営業プロセスを現場に定着させるための仕組作りが必要である。
- ワークシートで確認事項を明確にする。
- 第一の取り組み例は、ワークシートの活用である。特定のプロセスにおいて実施しなければならない項目を基に記入用紙を設計することで、平イング漏れや各種の見落としを防ぐのが目的である。(図6-1)
- 以下では、工業用・建設用樹脂塗料メーカZ社に対して、課題の抽出からソリューションの策定までのプロセスを、3種のワークシートで追ってみる。
- a
- a
- a
>Top
7. Nature's sleight of hand:
- a
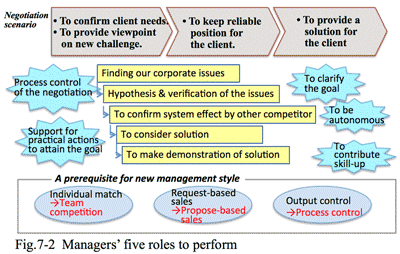
- a
7. 営業プロセス実践に向けたマネジャーの役割:
- a
- a
- a
- a
- a
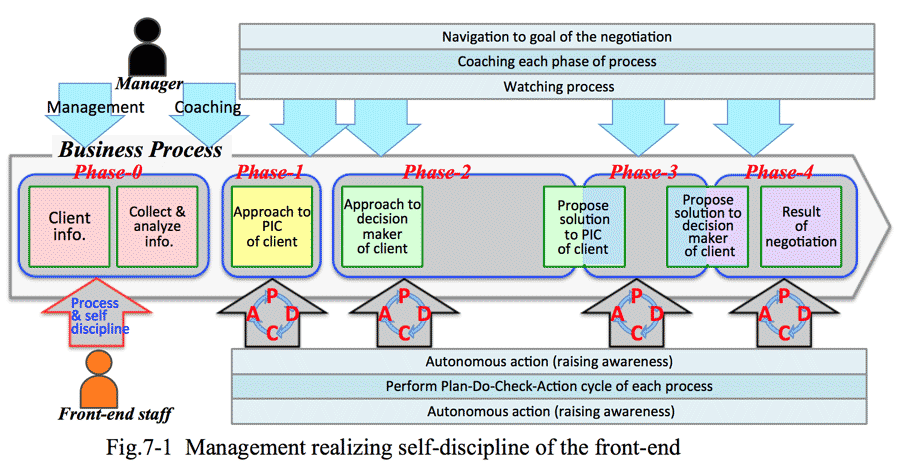
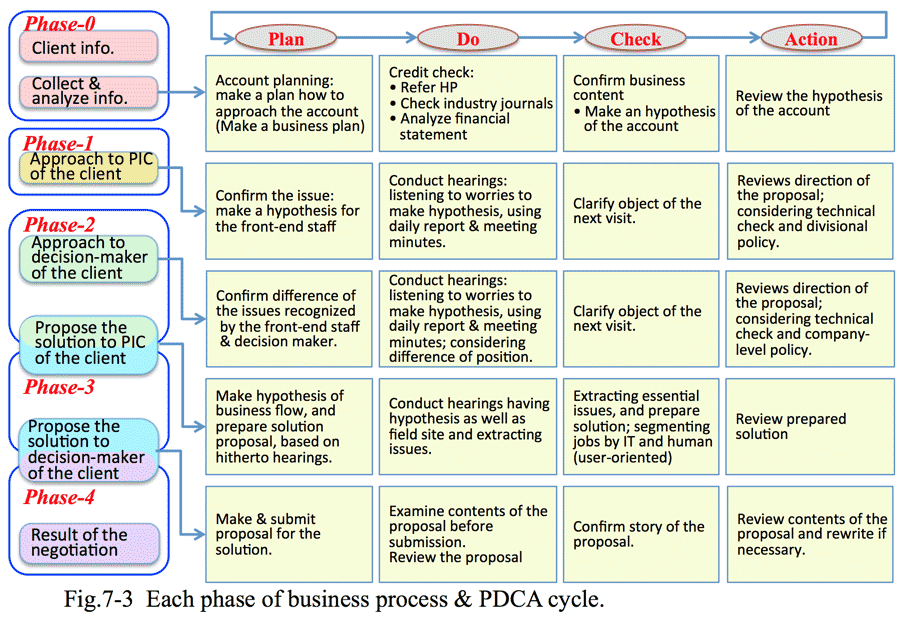
>Top
8. Nature's sleight of hand:
- a
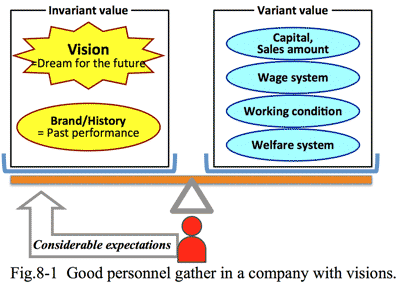
- a
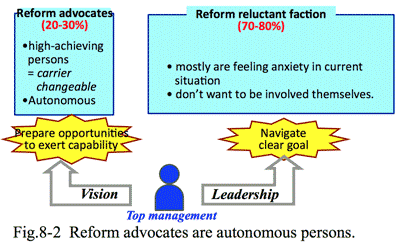
8. 営業プロセス実践に向けた経営者の役割:
- a
- a
- a
- a
- a
>Top
9. Nature's sleight of hand:
- a
- a
- a
- a
- a
- a
9. 営業プロセス実践が導くBSC経営:
- a
- a
- a
- a
- a
>Top
10. Nature's sleight of hand:
- a
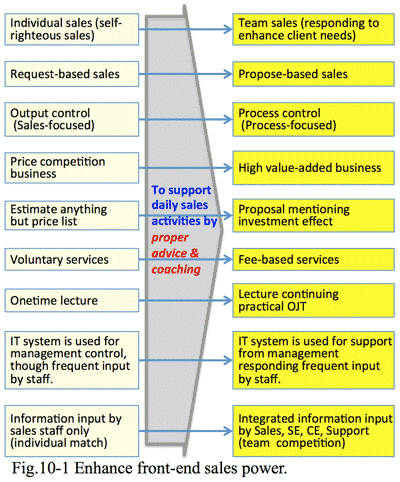

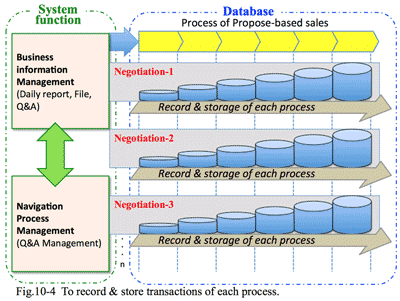
- a
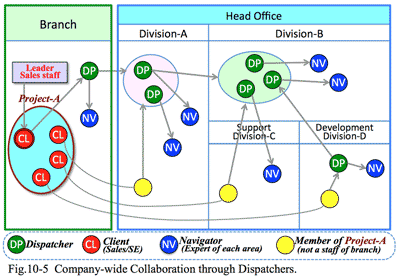
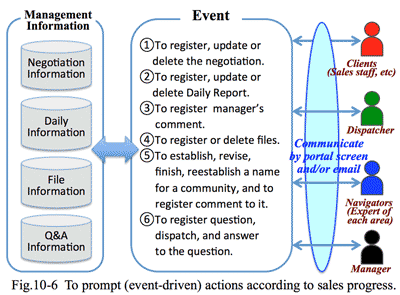
10. プロナビの概要:
- a
- a
- a
- a
- a
>Top
11. Antimatter matters:
- a
- a
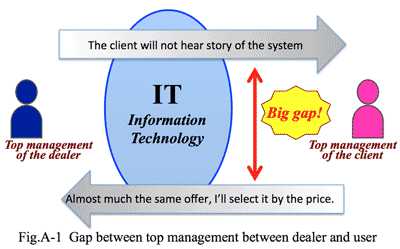
- a

- a
- a
11. 参考文献:生きるための新経営道場:
【第1回】従来の収益モデルが崩壊した中小企業市場
- a
- a
- a
- a
- a
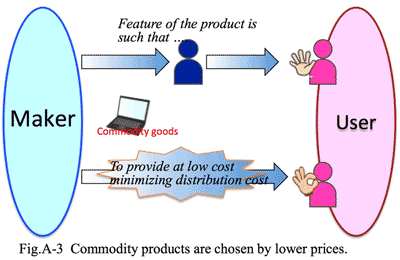
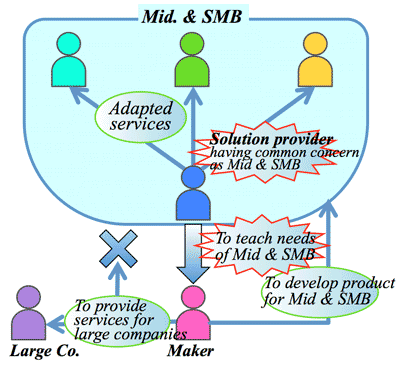
【第2回】見えてきた特約店制度の限界
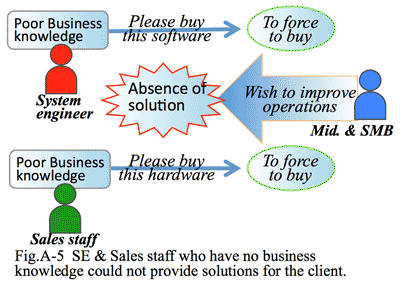
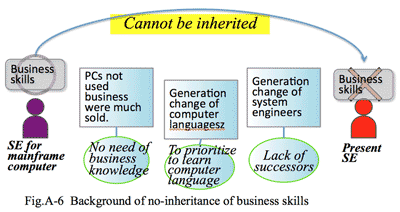
【第3回】業務に節通下人材不足が存在価値を下げている
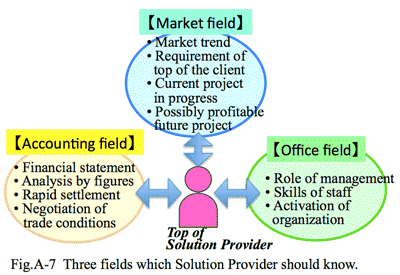
【第4回】経営者は現場に戻ろう
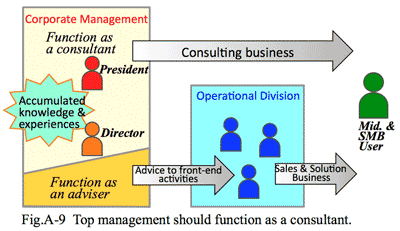
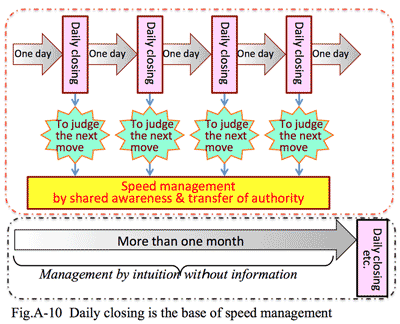
【第5回】経営基盤を強化しよう
【最終回】企業理念と経営ビジョンを掲げよ
Comment
- a
- a
 |
IT Sales Process Management
|
Cat: ECO |
|
| Author, Ken Kawashima (川嶋 謙) translated by Kanzo Kobayashi (小林寛三) | up 15z31 |
||
Title |
IT Process Management fro New Business Development |
新規開拓のためのIT営業プロセスマネジメント |
|---|---|---|
Index |
Original resume |
Remarks |
0. The day when a local small dealer starts consulting for a major company:What is 'a good company'?:
|
0. 地方の中小ディーラーが大企業をコンサルティングする日:良い会社とはどんな企業か?
|
>Top
1. Changing market requires skills of the front-end staff:Solution providers propose solutions for a client company; if there were no problems to be solved, there would be no need of such proposals. But acutely almost all companies have some problems to be solved, and which are getting more difficult according to rapid and big change of the market.
|
1. 変化した市場構造が求める営業担当者のスキル:ソリューションプロバイダは、顧客企業にソリューションを提案する。問題がなければ解決すべきことや提案すべきことは何もないが、ほとんどの企業が何らかの問題を抱えている。しかもその問題を正しく把握することが難しくなってきている。ソリューションプロバイダがターゲットにする市場構造が大きく変化してきたからである。
|
>Top2. Finance is the common language to communication with the management:
|
2. 経営層に判断材料を与える共通言語は財務:
|
>Top3. Indispensable financial skills for solution business:
|
3. ソリューション営業に不可欠な財務スキル:
|
|
|
||||
| 表(Fig) 3-1 |
指標, Index | 算式, Definition | 指標の意味・見方, Meaning & check points | |
| 収益性 Profitability analysis |
総資本対経常利益率 (%) Return On Assets |
経常利益/総資本 Ordinary profit/Total capital |
Operational efficiency; higher the better | |
| 利益率 Profit rate |
売上高対経常利益率 (%) Ordinary profit to sales |
経常利益/売上高 Ordinary profit/Sales |
Check sales cost, SGA, interest & discount rate, if it is lower. | |
| 売上高対総利益率 (%) Gross profit to sales |
売上総利益/売上高 Gross profit/Sales |
Check product mix, price policy, sales cost, production cost, if it is lower than competitors. | ||
| 売上高対販売管理費率 (%) Operating expenses to sales (SGA ratio) |
(販売費+一般管理費)/売上高 (Selling cost+Administrative cost)/Sales |
Check fixed cost such as personal cost, etc., if it is higher. | ||
| 売上高対支払利息率 (%) Interest expense to sales |
(支払利息+割引料-受取利息)/売上高 |
Max 3% in manufacture; Over 5% is revenue pressure. | ||
| 回転効率 Turnover |
総資本回転率 (%) Total capital turnover |
売上高/総資本 Sales/Total capital |
Check capital investment, inventory, receivable collection period, if it is lower. | |
| 受取勘定回転期間 Receivables turnover period |
(受取手形+売掛金+割引手形)/平均月商 (Promissory note+ Accounts receivable+ Discount bill)/Sales (mo) |
Check receivables collection period, non-performing loan, if it is longer. | ||
| 棚卸資産回転期間 Inventory turnover period |
棚卸資産/平均月商 Inventory/Sales (mo) |
Check useless or dead inventory, if it is longer. | ||
| 固定資産回転期間 Fixed asset turnover period |
固定資産/平均月商 Fixed asset/Sales (mo) |
Check idle asset, if it is longer | ||
| 支払勘定回転期間 Payables turnover period |
(支払手形+買掛金)/(材料仕入高+外注加工費+商品仕入高)/決算月数 (Notes payable+ Accounts payable)/(Material purchased+ Subcontract cost+ Goods purchased) |
Check payables & compare with 'account receivable turnover period), if it is longer. | ||
| 安全性 Safety analysis |
流動比率 (%) Current ratio |
流動資産/流動負債 Current asset/Current liability |
Average 120-130%; shorter is better. Check current asset and liability. | |
| 固定比率 (%) Fixed asset ratio |
固定資産/自己資本 Fixed asset/Equity capital |
it is preferable less than 100%, unless fixed asset to long-term capital is 70-80%. | ||
| 固定長期適合率 (%) Fixed asset to long-term capital |
固定資産/(自己資本+固定負債) Fixed asset/(Equity capital+Fixed liability) |
70-80% is preferable; if over 100% oppresses short-term solvency | ||
| 総資本対自己資本比率 (%) Equity capital to total capital |
自己資本/総資本 Equity capital/Total capital |
30-40% is preferable; higher has more resisting power. | ||
| 当座比率 (%) Quick assets ratio (Cash to current liability), or Acid test |
当座資産/流動負債 Quick asset/Current liability |
more than 100% is preferable; higher ratio has more solvency against current liability. |
||
| 借入金利子負担率 (%) Interest to sales |
{(支払利息+割引料)-受取利息}/売上総利益 {(Interest expense+Discount expense)-Interest income}/Gross profit |
Check higher interest rate and off-the-book loan, if it is higher; or deferred/expensed interest, if it is lower | ||
| 成長性 Growth analysis |
売上高増加率 (%) Sales growth rate |
(当期売上高-前期売上高)/前期売上高 (Previous sales- Current sales)/Previous sales |
more than 10% is preferable; growth rate of sales should be bigger than that of expense, or down of profit is not bigger than down of sales. | |
| 経常利益増加率 (%) Ordinary profit growth rate |
(当期経常利益-前期経常利益)/前期経常利益 (Previous ordinary profit-Current ordinary profit) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
>Top4. SFA for output-based management could not cultivate sales skills:
|
4. アウトプット管理のSFAでは営業スキルは育たない:
|
>Top5. To make business process and story for IT sales:
|
5. IT営業のためのプロセスとストーリーを作る:
|
 |
|
|
|
>Top6. Mechanism to radicate sales process management:
|
6. 営業プロセスマネジメントを定着させるための仕組み:
|
>Top7. Nature's sleight of hand:
|
7. 営業プロセス実践に向けたマネジャーの役割:
|
 |
|
 |
|
>Top8. Nature's sleight of hand:
|
8. 営業プロセス実践に向けた経営者の役割:
|
>Top9. Nature's sleight of hand:
|
9. 営業プロセス実践が導くBSC経営:
|
>Top10. Nature's sleight of hand:
|
10. プロナビの概要:
|
>Top11. Antimatter matters:
|
11. 参考文献:生きるための新経営道場:【第1回】従来の収益モデルが崩壊した中小企業市場
|
|
【第2回】見えてきた特約店制度の限界 |
|
【第3回】業務に節通下人材不足が存在価値を下げている |
|
【第4回】経営者は現場に戻ろう |
|
【第5回】経営基盤を強化しよう |
|
【最終回】企業理念と経営ビジョンを掲げよ |
Comment |
|
|