>formula>Glossary |
Mathematical Formulas
|
Cat: SCI |
Kanzo Kobayashi |
16201u/18116r |
Title
Mathematical Formulas
数学公式
Index
- Number & equation:
- Equation:
- Trigonometric function:
- Set:
- Logic:
- Group:
- Permutation & Combination
- Binomial theorem:
- Probability theory:
- Plane figure:
- Vector:
- Vector equation:
- Spatial vector:
- Equation of a sphere:
- Equation of a plane:
- Tangent plane:
- Statistics:
- Approximate solution:
- Fractional function:
- Sequence:
- Infinite series:
- Limit of a function /Exponential & logarithm:
- Differentiation:
- Equation of tangent line:
- Approximate equation:
- Indefinite integral:
- Definite integral:
- Application of definite integral:
- Volume:
- Progression:
- Differential equation:
- Determinant:
- Movement of point:
- Eigenvalue of matrix:
- Quadratic curve:
- Polar coordinates:
- Complex plane:
- Probability distribution:
- Complex numbers & shapes:
- Jacobian:
- xxxx:
Why?
- LaTeX can express mathematical formula in the original outlook in expression.
- This list is a practice of $math \ expression \ by \ \LaTeX.$
- LaTeXを使えば、本来の式で表示可能。
- 以下は、$\LaTeX$による数式表現の練習。
Resume
Remarks
Remarks
>Top 1. 数と式 (Numbers and equation)
- 交換法則 (Commutative law): $A+B=B+A$
- 結合法則 (Associative law): $(A+B)+C=A+(B+C), \ (AB)C=A(BC)$
- 分配法則 (Distributive law): $A(B+C)=AB+AC, \ (A+B)C=AC+BC$
- 指数法則 (Exponential law): $a^ma^n=a^{m+n},\ (a^m)^n=a^{mn},\ (ab)^n=a^nb^n$
- 乗数公式 (Multiplier formula): (double sign corresponds)
- $m(a±b)=ma±mb$
- $(a±b)^2=a^2±2ab+b^2$
- $(a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2$
- $(x+a)(x+b)=x^2+(a+b)x+ab$
- $(ax+b)(cx+d)=acx^2+(ad+bc)x+bd$
- $(a+b+c)^2=a^2+b^2+c^2+2ab+2bc+2ca$
- $(x+a)(x+b)(x+c)=x^3+(a+b+c)x^2+(ab+bc+ca)x+abc$
- $(a±b)^3=a^3±3a^2b+3ab^2±b^3$
- $(a±b)(a^2∓ab+b^2)=a^3±b^3$
- $(a^2+b^2+ab)(a^2+b^2-ab)=a^4+a^2b^2+b^4$
- $(a+b+c)(a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ca=a^3+b^3+c^3-3abc$
- $(a^2+b^2+c^2)(x^2+y^2)=(ax±by)^2+(bx∓ay)^2$
- 因数分解 (Factorization):
- $a^n-b^n=(a-b)(a^{n-1}+a^{n-2}b+a^{n-3}b^2+...+b^{n-1})$ (n: positive integer)
- $a^n-b^n=(a+b)(a^{n-1}-a^{n-2}b+a^{n-3}b^2+...-b^{n-1})$ (n: even number)
- $a^n+b^n=(a+b)(a^{n-1}-a^{n-2}b+a^{n-3}b^2+...+b^{n-1})$ (n: odd number)
- $ax^2+bx+c=a(x-α)(x-β)$
- $(ax+b)(cx+d)=acx^2+(ad+bc)x+bd$
- 整式の除法 (Division of integer expression):
- $a^m \div a^n=a^{m-n}$
- $A=BQ+R$ (degree of R < degree of B)
- 実数の絶対値 (Absolute value of real number):
- $\begin{equation}
\
|a|=\left \{
\begin{array}{l}
a \ (when, a≧0) \\
-a \ (when, a<0)
\end{array}
\right.
\end{equation}
$
- $\ |a|=|-a|, \ |a|^2, \ |ab|=|a||b|, \ \begin{array}
|\frac{b}{a}
\end{array}=\frac{|b|}{|a|}$
- $PQ=|b-a| \ $ (Distance between points $P(a)$ and $Q(b)$)
- 平方根と立方根 (Square root and Cube root):
- $\begin{equation}
\sqrt{a^2}=|a|=
\left \{
\begin{array}{l}
a \ (when, a≧0) \\ [
-a \ (when, a<0)
\end{array}
\right.
\end{equation}
$
- $a+b\sqrt{m}=0 \Longleftrightarrow a=b=0 \ $ (where, $\sqrt{m}$ is irrational)
- 剰余定理 (Remainder theorem); 乗数・除数 (Multiplier/Divisor):
- $A=BQ+R \ $(where, $0≦R<B), \ Q: $商 quotient, $R$: 剰余 residue)
1. 数と式:
- 交換法則
- 結合法則
- 分配法則
- 指数法則
- 乗数公式 (複合同順)
- 因数分解
- 整式の除数
- 因数分解(たすき掛け)
>Top 2. 方程式 (Equation):
- 二次方程式 (Quadratic equation):
$ax^2+bx+c=0 \\
x=\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$
$D=b^2-4ac$ (where, D: discriminant)
- $|x|<C \Longleftrightarrow -C<x<C \\
|x|>C \Longleftrightarrow x<-C \ ,or \ C<x
$
- 平行移動 (Parallel translation):
$y-b=f(x-a) \ $ (shift of the $f(x)$ to the point $P(a,b)$)
2. 方程式:
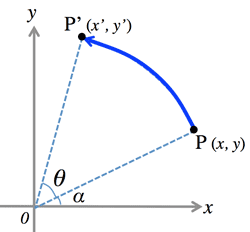
>Top 2b. ラジアン (Radian):
- 1R=$\frac{180º}{\pi}\approx 57º17'45''$
$l=r\theta, \; S=\frac{1}{2}r^2\theta=\frac{1}{2}lr$
- 回転 (Rotation):
- $x'=r\cos{(\theta+\alpha)}$
$=r(\cos\theta\cos\alpha-
\sin\theta\sin\alpha)$
$y'=r\sin{(\theta+\alpha)}$
$=r(\sin\theta\cos\alpha+
\cos\theta\sin\alpha)$
- $f:\pmatrix{x'\cr y'}=
\pmatrix{\cos\theta & -\sin\theta \cr \sin\theta & \cos\theta}\pmatrix{x\cr y}$
- $f^{-1}:\pmatrix{x'\cr y'}=
\pmatrix{\cos\theta & \sin\theta \cr -\sin\theta & \cos\theta}\pmatrix{x\cr y}$
- $\pmatrix{\cos\alpha & -\sin\alpha \cr \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha}^n=\pmatrix{\cos{n\alpha} & -\sin{n\alpha} \cr \sin{n\alpha} & \cos{n\alpha}}$
2b: ラジアン
- ラジアン:
- 原点周りの回転:
>Top 2c. 一次変換 (Linear Transformation):
- $f: \cases{x'=ax+by \cr y'=cx+dy}$
$f: \pmatrix{x' \cr y'}=\pmatrix{a&b \cr c&d}\pmatrix{x\cr y}$
- 一次変換の線形性 (Linearity of Linear Transformation):
$f(\vec{u}+\vec{v})=f(\vec{u})+f(\vec{v})$
$f(k\vec{u})=kf(\vec{u})$
39: 一次変換
- 写像 (Mapping):
>Top 3. 三角函数 (Trigonometric function):
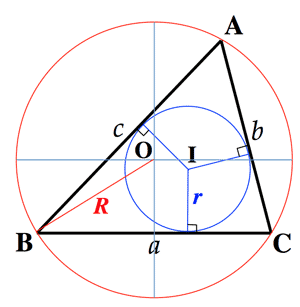
- 正弦定理 (Sine theorem):
$\frac{a}{sinA}=\frac{b}{sinB}=\frac{c}{sinC}=2R$
(where, R is radius of circumscribed circle)
- 第一余弦定理 (First Cosine theorem):
$\begin{cases}
a=b\cos{C}+c\cos{B} \\
b=c\cos{A}+a\cos{C} \\
c=a\cos{B}+b\cos{A}
\end{cases}$
- 第二余弦定理 (Second Cosine theorem)
$\begin{cases}
a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos{A} \\
b^2=c^2+a^2-2ca\cos{B} \\
c^2=a^2+b^2-2ab\cos{C}
\end{cases}$
- 三角形の面積 (Area of a triangle):
$S=\triangle ABC=\frac{1}{2}bc\sin{A}$
$S=\frac{abc}{4R}=2R^2\sin{A}\sin{B}\sin{C} \;$ (R: circum-radius)
$S=rs \;$ (where, $2s=a+b+c$; r: radius of innner circle)
- ヘロンの公式 (Heron's formula):
$S=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}
\hspace{10mm} $ (where, $\;2s=a+b+c$)
- 球の面積と体積 (Volume & Area of a sphere):
$V=\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3, \ S=4\pi r^2$
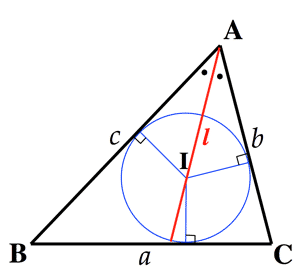
- 二等分線の長さ (Length of bisector):
$l=\frac{bc}{b+c}・\frac{\sin{A}}{\sin{\frac{A}{2}}}$
- 加法定理 (Addition theorem):
$\begin{cases} \sin(\alpha\pm\beta)=\sin{\alpha}\cos{\beta}\pm\cos{\alpha}\sin{\beta}\\
\cos(\alpha\pm\beta)=\cos{\alpha}\cos{\beta}\mp\sin{\alpha}\sin{\beta}\\
\tan(\alpha\pm\beta)=\frac{\tan{\alpha}\pm\tan{\beta}}{1\mp\tan{\alpha}\; \tan{\beta}}\\
\end{cases} $
- 積和公式 (Product-Sum formula):
$\begin{cases}
\sin{\alpha}\cos{\beta}=\frac{1}{2}\{\sin(\alpha+\beta)+\sin(\alpha-\beta)\}\\
\cos{\alpha}\sin{\beta}=\frac{1}{2}\{\sin(\alpha+\beta)-\sin(\alpha-\beta)\}\\
\cos{\alpha}\cos{\beta}=\frac{1}{2}\{\cos(\alpha+\beta)+\cos(\alpha-\beta)\}\\
\sin{\alpha}\sin{\beta}=\frac{1}{2}\{\cos(\alpha+\beta)-\cos(\alpha-\beta)\}
\end{cases}$
- 和積公式 (Sum-Product formula):
$\begin{cases}
\sin{A}+\sin{B}=2\sin{\frac{A+B}{2}}\cos{\frac{A-B}{2}}\\
\sin{A}-\sin{B}=2\cos{\frac{A+B}{2}}\sin{\frac{A-B}{2}}\\
\cos{A}+\cos{B}=2\cos{\frac{A+B}{2}}\cos{\frac{A-B}{2}}\\
cos{A}-\cos{B}=-2\sin{\frac{A+B}{2}}\sin{\frac{A-B}{2}}
\end{cases}$
- 半角の公式 (Half-angle formula):
$\begin{cases}
\sin^2{\frac{\alpha}{2}}=\frac{1-\cos{\alpha}}{2}, \\
\cos^2{\frac{\alpha}{2}}=\frac{1+\cos{\alpha}}{2},
\end{cases} $
- 二倍角の公式 (Double-angle formula):
$\begin{cases}
\sin{2\alpha}=2\sin{\alpha}\cos{\alpha}\\
\cos{2\alpha}=\cos^2{\alpha}-\sin^2{\alpha}=1-2\sin^2{\alpha}\\
\tan{2\alpha}=\frac{2\tan{\alpha}}{1-\tan^2{\alpha}}
\end{cases} $
- 三倍角の公式 (Tripple-angle formula):
$\begin{cases}
\sin{3\alpha}=3\sin{\alpha}-4\sin^3, \; \cos{3\alpha}=4\cos^3{\alpha}-3\cos{\alpha}\\
\tan{3\alpha}=\frac{3\tan{\alpha}-\tan^3{\alpha}}{1-3\tan^2{\alpha}}
\end{cases}$
- Where, $(A+B+C=\pi) $
$\begin{cases}
\sin{A}+\sin{B}+\sin{C}=4\cos{\frac{A}{2}}\cos{\frac{B}{2}}\cos{\frac{C}{2}}\\
\cos{A}+\cos{B}+\cos{C}=4\sin{\frac{A}{2}}\sin{\frac{B}{2}}\sin{\frac{C}{2}}+1\\
\tan{A}+\tan{B}+\tan{C}=\tan{A}\tan{B}\tan{C}
\end{cases}$
3. 三角函数:
1. 正弦定理:
2. 第一余弦定理
3.
第二余弦定理
- 拡張ピタゴラスの定理
- 合同条件に対応
7. 加法定理:
- sin: ±→±
- cos:±→∓
8/9. 積和/和積公式:
- ←加法定理①+②
- $α+β=A\\
α-β=B\\
α=\frac{A+B}{2}\\
β=\frac{A=B}{2}$
- 半角公式:
α=β
11.三倍角公式:
- sin3: 3 -4 3
- cos3: -(3 -4 3)
正弦定理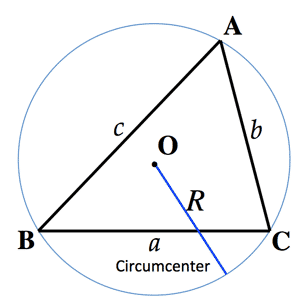
余弦定理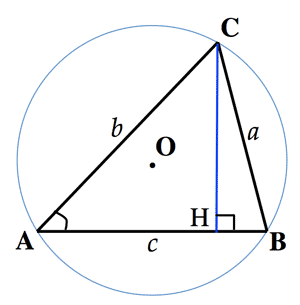
三角形の面積
二等分線の長さ
- 合成公式 (Synthesis formula):
$a\sin{\theta}+b\cos{\theta}=\sqrt{a^2+b^2}\sin{(\theta+\alpha)} \\$
(where, $\; \cos{\alpha}=\frac{a}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}, \; \sin{\alpha}=\frac{b}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}$
)
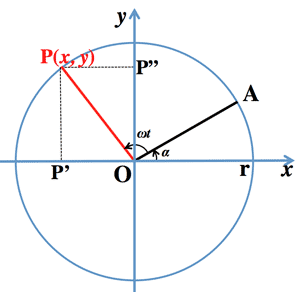
- 単振動 (Simple harmonic motion):
$x=r\cos(\omega t+\alpha) \\
y=r\sin(\omega t+\alpha) $
(where, $\; r$: 振幅 Amplitude, $\; \alpha$: 初期位相 Initial phase,
$
\frac{2\pi}{|\omega|}$: 周期 Period cycle)
単振動
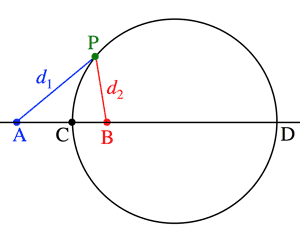
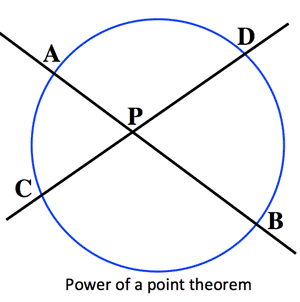
円と比例 (Circle and Proportion):
- 方冪の定理 (Power of a point theorem):
$\overline{PA}・\overline{PB}=\overline{PC}・\overline{PD}$
方冪の定理
>Top 4. 集合 (Set):
- 交換法則 (Commutative law):
$A\cup B=B\cup A,\; A\cap B=B\cap A$
- 結合法則 (Associative law):
$(A\cup B)\cup C=A\cup (B\cup C)\\
(A\cap B)\cap C=A\cap (B\cap C)$
- 分配法則 (Distributive law):
$A\cap (B\cup C)=(A\cap B)\cup (A\cap C)\\
A\cup
(B\cap C)=(A\cup B)\cap (A\cup C)$
- 冪等法則 (Idempotent law):
$A\cap A=A,\;A\cup A=A$
- 吸収律 (Absorption law):
$A\cap (A\cup B)=A,\; A\cup (A\cap B)=A$
- ド・モルガンの法則 (de Morgan's law):
$\overline{A\cap B}=\overline A\cup \overline B,\; \overline{A\cup B}=\overline A\cap \overline B$
- $A\cap U=A,\; A\cup U=U,\; A\cap \phi=\phi,\; A\cup \phi=A$
- $n(A\cup B)=n(A)+n(B)-n(A\cap B)$
- $n(\overline A)=n(U)-n(A)$
4. 集合:
ドモルガンの定理
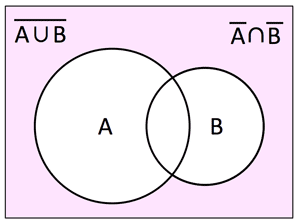
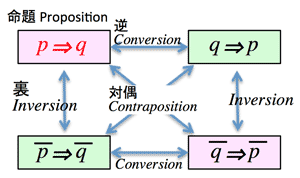
>Top 5. 論理 (Logic):
- 包含 (Implication): if P then Q
$P\rightarrow Q$
$(P\rightarrow Q)\rightarrow (\neg Q\rightarrow \neg P)$
- 裏 (Inverse): if not P then not Q
$\neg P\rightarrow \neg Q$
- 逆 (Converse): if Q then P
$Q\rightarrow P$
- 対偶 (Contrapositive): if not Q then not P
$\neg Q\rightarrow \neg P$
- 否定 (Negation): P and not Q
$P\wedge \neg Q$
- First-order logic:
$A\rightarrow B\Longleftrightarrow \neg A\vee B$
we have:
$\neg A \vee B\Longleftrightarrow B \vee \neg A\\
\Longleftrightarrow \neg B \rightarrow \neg A\\
\Longleftrightarrow
A \rightarrow B$
5. 論理:
- 包含: Implication
- 裏:
- 逆:
- 対偶:
- 否定:
Truth table:
A
B
Ā
A→B
Ā∨B
(A∧¯B)
1
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
>Top 6. 群 (Group):
- 閉じている (Closure):
For all $a, b$ in $G$, the result of the operation, $a・b$ is also in $G.$
- 結合法則 (Associativity):
For all $a, b$ and $c$ in $G, (a・b)・c=a・(b・c).$
- 単位元 (Identity element): $e$
There exists an element $e$ in $G$, such that for every element $a$ in $G$, the eduation $e・a=a・e=a$ holds.
($e$ is identy element)
- 逆元 (Reverse element): $a^{-1}$
For each $a$ in $G$, there exists an element $b$ in $G$ such that $a・b=b・a=e$, where $e$ is the identity element. (here, $b=a^{-1}$)
- 可換群 (Abelian group; Communativity of addition):
$a・b=b・a$ always holds are called Abelian
group.
6. 群:
- 演算について閉じている
- 結合法則
- 単位元
- 逆元
- 交換法則を満たす可換群(Abel group)
>Top 7. 順列と組合せ (Permutation and Combination):
- 順列 (Permutation):
$\ {}_nC_r=n(n-1)(n-2)…(n-r+1)=\frac{(n-r)!}{n!}$
- 重複順列 (Repeated permutation):
$\ {}_n\Pi_r=n^r$
- 円順列 (Circular Permutation):
$(n-1)!$
$\frac{(n-1)!}{2} \;$ (where it is reversible, $\; n\geqq3$)
- 同じものを含む順列 (Multiset Permutations):
$\frac{n!}{p!q!r!...}\;$ (where $p+q+r+...=n$)
- 組合せ (Combination):
$\ {}_nC_=\frac{ {}_nP_r}{r!}=
\frac{n(n-1)(n-2)...(n-r+1)}{r!}=
\frac{n!}{r!(n-r)!}\;$ (where $n\geqq r$)
- 組分けの方法 (Grouping of combination):
$\ {}_nC_a \times {}_{n-a}C_b \;$ (where $a+b+c=n$)
- 最短通路 (Shortest route problem):
$\ {}_{(n+m)}C_n=\frac{(n+m)!}{n!m!}$
- 重複組合せ (Repeated combination):
$\ {}_nH_r={}_{n+r-1}C_r$
7. 順列と組合せ:
>Top 8. 二項定理 (Binomial theorem):
- 二項定理 (Binomial theorem):
$(a+b)^n= \sum_{r=0}^n {}_nC_r a^{n-r}b^r \;$ (where $n$ is positive integer)
$\ {}_nC_r a^{n-r}b^r \;$ (general term)
- 二項係数の関係式:
$\ {}_nC_0+{}_nC_1+{}_nC_2 +...+ {}_nC_n=2^n$
$\ {}_nC_0+{}_nC_2+{}_nC_4 +...={}_nC_1+{}_nC_3+{}_nC_5 +...=2^{n-1}$
$\ {}_nC_1+2{}_nC_2+3{}_nC_3 +...+ n{}_nC_n=n・2^{n-1}$
$\ {{}_nC_0}^2+{{}_nC_1}^2+{{}_nC_2}^2 +...+{ {}_nC_n}^2=\frac{(2n)!}{(n!)^2}= {}_{2n}C_n$
- 多項定理 (Polynomial theorem):
$(a+b+c+...)^n= \sum \frac{n!}{p!q!r!...}a^p b^q c^r... \;$ (where $n$ is natural number)
8. 二項定理:
>Top 9. 確率論 (Probability theory):
- 加法定理 (Addition theorem of probability):
$P(A\cup B)=P(A)+P(B)\;$ (where, $(A\cap B)=\emptyset)$
$P(A\cup B)=P(A)+P(B)-P(A\cap B) \;
$ (general case)
- 余事象の定理 (Complementary event):
$P(\overline A)=1-P(A)$
- 独立事象・積の定理 (Independent event):
$P(A \cap B)=P(A)P(B)$
- 反復試行 (Repeated trials):
$p_r=\ {}_nC_rp^rq^{n-r}\;$ (where, $p_r$ means 'probablity which occurs $r$ times in the $n$ independent trials; $\; p+q=1$)
- 期待値 (Expected value):
$p_1+p_2+p_3+...+p_n=1 \\
E(X)=\sum_{k=1}^{n}(x_n p_n)
$
9. 確率:
- 加法定理
- 余事象の定理
- 独立事象・積の定理
- 反復試行
- 期待値
>Top 10. 平面図形 (Plane figure):
- 三角形の合同定理 (Congruence of triangles):
$\triangle ABC \cong \triangle DEF$
- Side-Angle-Side: If two pairs of sides of two triangles are equal in length and the included angle is equal, then the triangles are congruent.
- Side-Side-Side: If three pairs of sides of two triangles are equal in lenght, then the triangles are congruent.
- Angle-Side-Angle: It two pairs of sides of two triangles are equal in measurement and the included side is equal, then the triangles are congruent.
- 中点連絡定理 (Midpoint theorem):
$MN \parallel BC, \; MN=\frac{1}{2} BC$
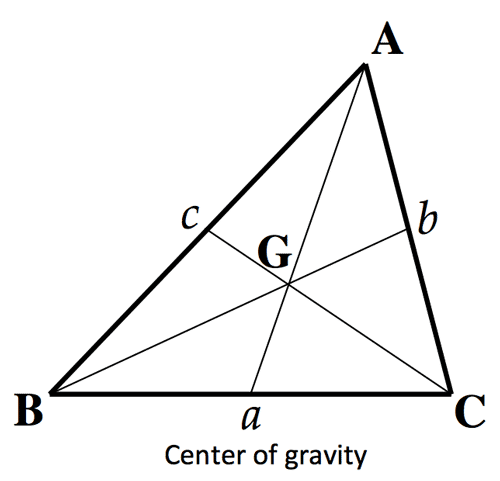
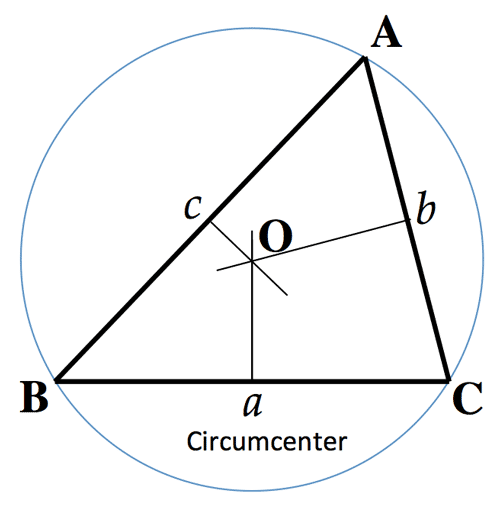
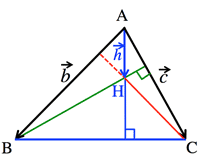
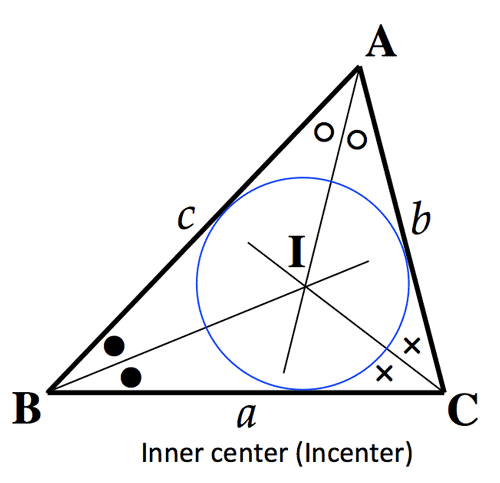
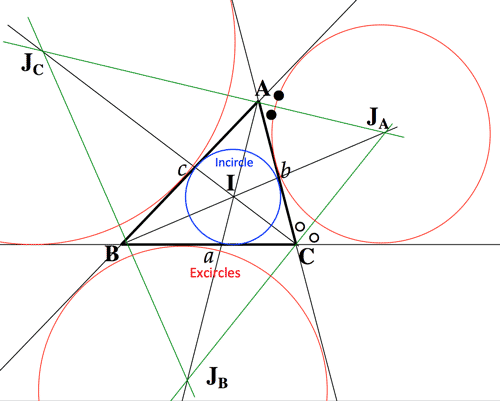
- 三角形の五心 (重心 Center of gravity; 外心 Circumcenter; 垂心 Orthcenter; 内心 Incenter; 傍心 Excenters)
- パップスの定理 (Pappus's theorem):
$\overline{AB}^2+\overline{AC}^2=2(\overline{AM}^2+\overline{BM}^2)$
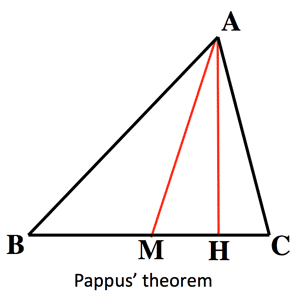
10. 平面図形:
中点連絡定理
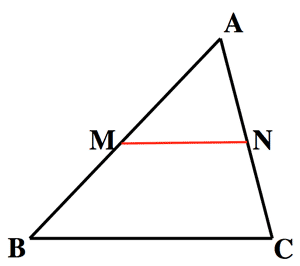
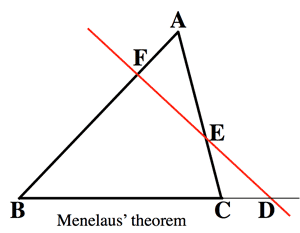
- メネラウスの定理 (Menelaus' theorem):
$\frac{BD}{DC}\frac{CE}{EA}\frac{AF}{FB}=1$
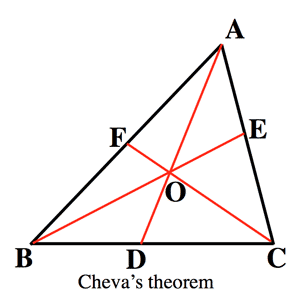
- チェバの定理 (Cheva's theorem):
$\frac{BD}{DC}\frac{CE}{EA}\frac{AF}{FB}=1$
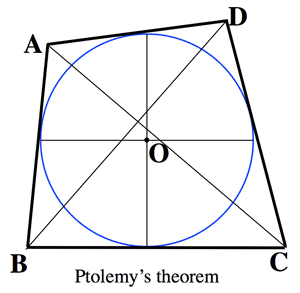
- トレミーの定理 (Ptolemy's theorem):
$AB・CD+BC・DA=AC・BC$
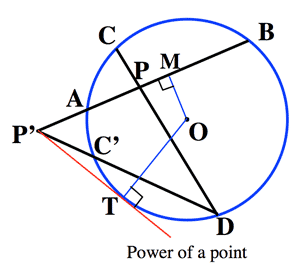
- 方冪の定理 (Chord theorem):
- P: 円内
$PA・PB=PC・PD=r^2-{OP}^2$
- P: 円外
$P'A・PB=P'C'・PD={OP'}^2-r^2$
- PT: 接線
${P'T}^2=P'A・PB$
>Top 11. ベクトル (Vector):
- $\overrightarrow{BA}=-\overrightarrow{AB}$
- $\overrightarrow{AA}=\overrightarrow0$
- $\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}=\overrightarrow{BA}=
\overrightarrow{OA}-\overrightarrow{OB}$
- $\overrightarrow{a} \parallel \overrightarrow{b} \Longleftrightarrow \overrightarrow{a}=k \overrightarrow{b}$
- Dividing point:
$\overrightarrow{OP}=\displaystyle \frac{n\overrightarrow{a}+m\overrightarrow{b}}{m+n} $
(where, $mn>0$ Internally dividing point, $mn<0$ Externally dividing point)
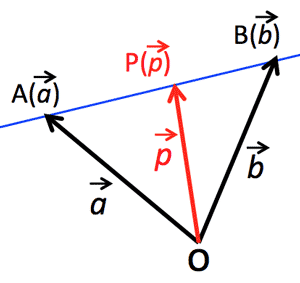
- Position vector on a line:
$\overrightarrow{AP}=t\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a}=t(\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{a}); \;
\overrightarrow{p}=(1-t)\overrightarrow{a}+t\overrightarrow{b}\\
\overrightarrow{p}=s\overrightarrow{a}+t\overrightarrow{b}, \; (s+t=1)$
- Linear indepedence:
$p\overrightarrow{a}+q\overrightarrow{b}=\overrightarrow{0}$ \Longleftrightarrow p=q=0
- Linear dependence:
$\overrightarrow{a} \parallel \overrightarrow{b} \Longleftrightarrow \overrightarrow{a}, \overrightarrow{b} $ are linear dependence.
- Linear dependence in a space:
$p\overrightarrow{a}+q\overrightarrow{b}+r\overrightarrow{c}=\overrightarrow{0} \Longleftrightarrow p=q=r=0$
- Unit vector:
$\overrightarrow{a}=a_1\overrightarrow{e_1}+a_2\overrightarrow{e_2} \; \overrightarrow{a}
=(a_1, a_2)$
- Component of a vector:
$\overrightarrow{a}=(a_1, a_2)$
$\overrightarrow{a}=a_1\overrightarrow{e_1}+a_2\overrightarrow{e_2}$
$\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|=\sqrt{{a_1}^2+{a_2}^2}$
$\overrightarrow{a} \pm \overrightarrow{b}=(a_1 \pm b_1, \; a_2 \pm b_2)$
$m \overrightarrow{a}=(ma_1, \; ma_2)$
- $\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{OB}-\overrightarrow{OA}$
$\overrightarrow{AB}=(x_2-x_1, \; y_2-y_1)$
$\overrightarrow{e}=\frac{\overrightarrow{a}}{\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right| }$
- Coordinates in a space
$\overline{AB}=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2+(z_2-z_1)^2}$
$P\left(\frac{nx_1+mx_2}{m+n},\; \frac{ny_1+my_2}{m+n},\; \frac{nz_1+mz_2}{m+n}\right)$
$\overrightarrow{a}=a_1 \overrightarrow{e_1}+a_2 \overrightarrow{e_2}+a_3 \overrightarrow{e_3}$
- $\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|=\sqrt{{a_1}^2+{a_2}^2+{a_3}^2}$
$\overrightarrow{a} \pm \overrightarrow{b}=(a_1 \pm b_1, \; a_2 \pm b_2, \; a_3 \pm b_3)$
$m \overrightarrow{a}=(ma_1, \; ma_2, \; ma_3)$
- Inner product:
$\overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b}=| \overrightarrow{\mathstrut a}| | \overrightarrow{\mathstrut b}| \cos \theta$
$\overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b}=a_1・b_1+a_2・b_2$
${\left| \overrightarrow{a}\pm \overrightarrow{b}\right|}^2={\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|}^2 \pm 2\overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b}+{\left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|}^2$
$\overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b}=|\overrightarrow{a}| \: |\overrightarrow{b}| \cos θ$
$\overrightarrow{a} \perp \overrightarrow{b} \Longleftrightarrow \overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b}=0$
- コーシー=シュワルツ不等式 (Cauchy-Schewartz Inequality):
$|\overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b}| \leqq |\overrightarrow{a}| \: |\overrightarrow{b}|$
$| |\overrightarrow{a}|-|\overrightarrow{b}| |\leqq |\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}| \leqq |\overrightarrow{a}|+|\overrightarrow{b}|$
- $\cos \theta = \frac{\overrightarrow{AB}・\overrightarrow{CD}}{|\overrightarrow{AB} | \: | \overrightarrow{CD} |}$
$\overrightarrow{OP}=\frac{n\overrightarrow{OA}+m\overrightarrow{OB}}{m+n}$
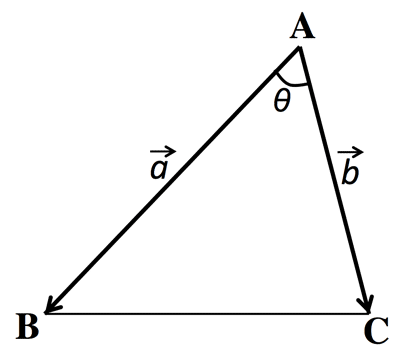
- 三角形の面積 (Area of a triangle):
$\triangle ABC=\frac{1}{2} |\overrightarrow{a}|\; | \overrightarrow{b} |\sin \theta=\frac {1}{2} \sqrt{|\overrightarrow{a} |^2| \; |\overrightarrow{b}|^2-(\overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b})^2}$
- $|\overrightarrow{a} |^2| \; |\overrightarrow{b}|^2-(\overrightarrow{a}・\overrightarrow{b})^2$
$=(a_1^2+a_2^2)(b_1^2+b_2^2)-(a_1b_1+a_2b_2)^2$
$=(a_1b_2-a_2b_1)^2$
$S=\frac{1}{2}|a_1b_2-a_2b_1|$
- $\triangle ABC=\frac{1}{2} \left|a_1b_2 - a_2b_1 \right|$
11. ベクトル:
6. 直線上の点
19. 三角形の面積
>Top 12. ベクトル方程式 (Vector equation):
- 直線の方程式 (Linear equation):
- 平行な直線 (Parallel line):
- $\overrightarrow{AP} \parallel \overrightarrow{v}\; $ [平行な直線]
$→\;\frac{x-x_1}{l}=\frac{y-y_1}{m}$
- $\overrightarrow{p}=\overrightarrow{a}+t\overrightarrow{v}\;$ [2点通過直線]
- $\overrightarrow{p}=(1-t)\overrightarrow{a}+t\overrightarrow{b}\;$
$→\;a(x-x_1)+b(y-y_1)=0$
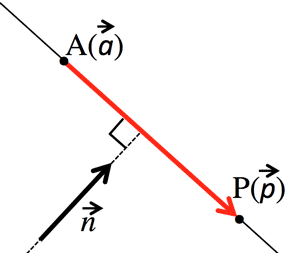
- 法線 (Normal line):
$(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a})・\overrightarrow{n}=0$
- $\Leftrightarrow\pmatrix{a\\b}・\pmatrix{x-x_0\\y-y_0}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow\; ax+by+(-ax_0-by_0)=0$
- $→\; \bar{HM}=\bar{OM}-\bar{OH}=\frac{|ax_0+by_0+c|}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}$
- $→\; a(x-x_1)+b(y-y_1)+c(z-z_1)=0$
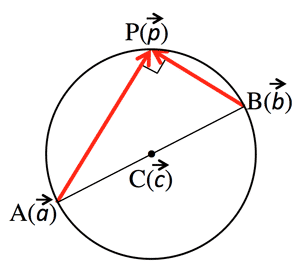
- 円の方程式 (Circular equation):
$(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{c})・(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{c})=r^2 \\
(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a})・(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{b}) =0$
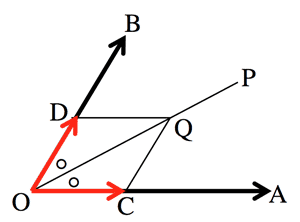
- 点Pの集合 (Set of Point P):
$\overrightarrow{OP}=s\overrightarrow{OA}+t\overrightarrow{OB}\\
\overrightarrow{OP}=(s+t)・\frac{s\overrightarrow{OA}+t\overrightarrow{OB}}{s+t}=(s+t) \overrightarrow{OQ}$
12. ベクトル方程式:
平行直線 (Parallel line):
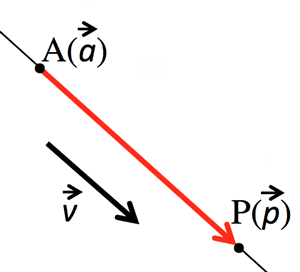
法線 (Normal line):
3. Bisector vector:
4. Circular equation:
5. Set of point P:
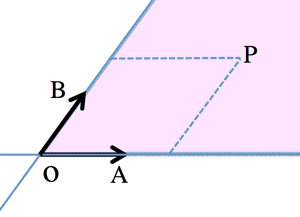
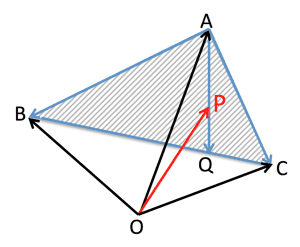
>Top 13. 空間ベクトル (Spatial vector):
- Area of spatial vector;
Point P on a plane ABC:
$\overrightarrow{OP}=l\overrightarrow{OA}+m\overrightarrow{OB}+ n\overrightarrow{OC}\\;$
- $l, m, n$ are no limit; P is a point in a space
- $l+m+n=1 \Longleftrightarrow \; \ $ P is point on a plane $ABC$.
- $l+m+n=1, l \geqq 0, m \geqq 0, n \geqq 0
\Longleftrightarrow \; $ P is a point on & inside of $\triangle ABC$
- $n=0, l+m=1 \Longleftrightarrow \;$ P is on a line $AB$
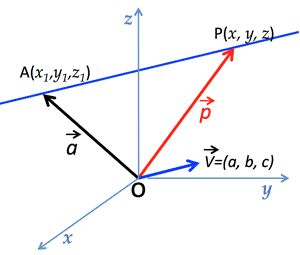
- Line equation:
- $\overrightarrow{p}=\overrightarrow{a}+t\overrightarrow{v}$
- $\frac{x-x_1}{a}=\frac{y-y_1}{b}=\frac{z-z_1}{c}=t \\
x=x_1+at, \: y=y_1+bt, \: x=z_1+ct
$
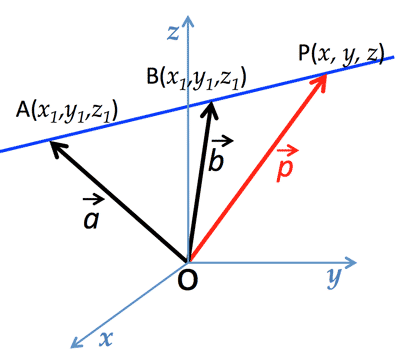
- Line passes points A & B:
$\overrightarrow{p}=\overrightarrow{a}+t(\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{a})$
$\frac{x-x_1}{x_2-x_1}=\frac{y-y_1}{y_2-y_1}=\frac{z-z_1}{z_2-z_1}$
13. 空間ベクトル:
- 空間ベクトルの領域
Area of spatial vector:
平面ABC上の点P:
2. Line equation:
3. Line passes points A & B:
>Top 14. 球の方程式 (Equation of a sphere):
- $|\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a}|=r \Longleftrightarrow (\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a})・(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a})=r^2$
- $(x-a)^2+(y-b)^2+(z-c)^2=r^2 \; (r>0)$
- $(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a})・(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{b})=0 \; $ (where, $\overrightarrow{OA}=\overrightarrow{a}, \; \overrightarrow{OB}=\overrightarrow{b}, \; \overrightarrow{OP}=\overrightarrow{p})$
- $(x-x_1)(x-x_2)+(y-y_1)(y-y_2)+(z-z_1)(z-z_2)=0$
14. 球の方程式:
- 点A(a,b,c)中心、半径rの球のベクトル方程式
- 球の方程式
- 2点A, Bを両端とする球の方程式; ベクトル方程式
- 球の方程式
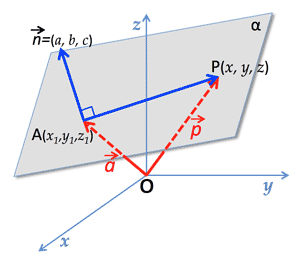
>Top 15. 平面の方程式 (Equation of a plane):
- Plane equation:
$(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{a})・\overrightarrow{n}=0$
$a(x-x_1)+b(y-y_1)+c(z-z_1)=0 \; $ (where, normal vector $\overrightarrow{n}=(a, b, c)$ )
$ax+by+cz+d=0 \; $ (where, normal vector $\overrightarrow{n}=(a, b, c)$ )
- Distance between plane α and point P
$h=\frac{|ax_0+by_0+cz_0+d|}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2+c^2}}$
15. 平面の方程式:
点Aを通り,
$\overrightarrow{n}$
に垂直な面
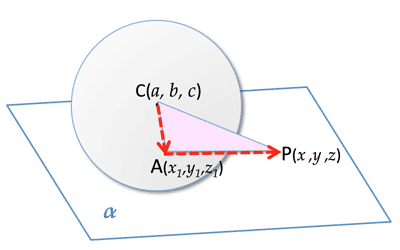
>Top 16. 接平面 (Tangent plane)
- $(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{c})・(\overrightarrow{p}-\overrightarrow{c})=r^2$
- $(x_1-a)(x-a)+(y_1-b)(y-b)+(z_1-c)(z-c)=r^2$
16. 球と直線:
>Top 17. 統計 (Statistics):
- 平均値 (Average value):
$\bar{x}=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^nx_if_i$
- $\bar{x}=x_0+c\bar{u}\\
\bar{u}=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^nu_if_i
$ (where, $\; u_i=\frac{x_i-x_0}{c})$
- Median: midpoint of frequency distribution
- Mode: value that occurs most frequently
$\bar{x}-M_o\fallingdotseq 3(\bar{x}-M_e) \;$ (Pearson empirical formula)
- 標準偏差 (Standard deviation):
$\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^n(x_i-\bar{x})^2f_i}$
$
=\sqrt{\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^n(x_i)^2 f_i-\bar{x}^2}$
- Where, temporary average (仮平均) is $x_0, \; u_i=\frac{1}{c}(x_i-x_0), \;$ c is class interval (階級の幅):
$\sigma=c\sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^n(u_i)^2f_i-\bar{u}^2}$
- 分散 (Variation):
$V=\sigma^2$
- 標準測度(Stardard measure):
$z=\frac{x_i-\bar{x}}{\sigma} \; $ (where, $i$= 1, 2, 3, ..., n)
- T score ($t$):
$t=\frac{x_i-\bar{x}}{\sigma}・10 + 50$
- 相関係数 (Correlation coefficient) $r$:
$r=\frac{\sum_{k=1}^N (x_k-\bar{x})(y_k-\bar{y})}{NS_xS_y}$
18. 統計:
class value $x$
fre-quency
$u$
$uf$
$x_1$
$f_1$
$u_1$
$u_1 f_1$
$x_2$
$f_2$
$u_2$
$u_2 f_2$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
-1
$\vdots$
$x_k =x_0$
$f_k$
0
0
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
1
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$\vdots$
$x_n$
$f_n$
$u_n$
$u_nf _n$
Total
$N$
$\sum _{i=1} ^n$
>Top 18. 方程式の近似解 (Approximate solution):
- Newton's method:
Tangential equation of $y=f(x)$ on point $(x_0,\; f(x_0))$:
$y-f(x_0)=f'(x_0)(x-x_0)$
$x_1=x_0-\frac{f(x_0)}{f'(x_0)}$
- Newton's method: ($α=\sqrt{2}$):
$x_{k+1}=\frac{1}{2}(x_k+\frac{a}{x_k})$ (Approximate solution of $\sqrt{a}$)
$x_1=x_0-\frac{{x_0}^n-a}{n {x_0}^{n-1}}$ (Approximate solution of $\sqrt[n]{a}$)
- シンプソンの公式 (Simpson's formula):
$g(x)=ax^2+bx+c$ passes 3 points (-h, α), (0, β), (h, γ)
$\int_{-h}^{h}g(x)dx=\frac{h}{3}(\alpha+4\beta+\gamma)$
$\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx\fallingdotseq\frac{h}{3}
\{(y_0+y_{2n})+4(y_1+y_3+\dots+y_{2n-1})+2(y_2+y_4+\dots+y_{2n-2})\}$
18. :
Newton's method: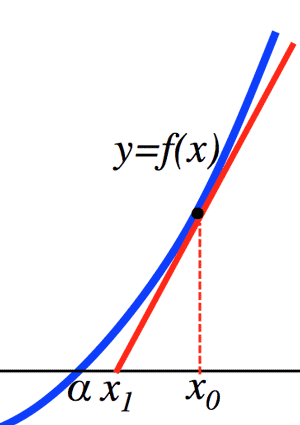
Newton's method2:
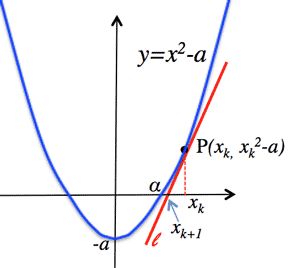
Simpson's formula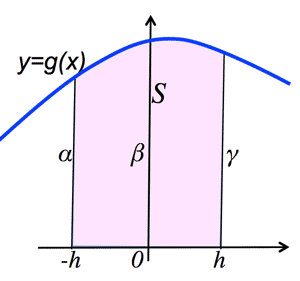
>Top 19. 分数函数 (Fractional function):
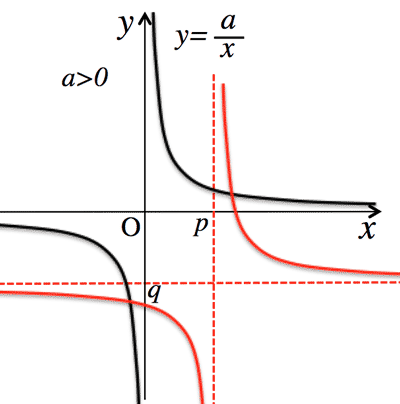
- Graph of $y=\frac{a}{x}$
- Graph of $y=\frac{a}{x-p}+q$
Asymptote is $x=p, \; y=q$
- Graph of $y=\frac{cx+d}{ax+b}$
Asymptote is $x=-\frac{b}{a}, \; y=\frac{c}{a}$
- 逆函数 (Inverse function):
$y=f(x)\Longleftrightarrow x=f^{-1}(y)$
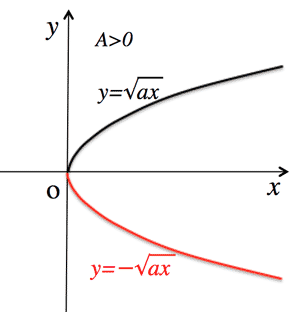
- 無理函数 (Irrational function):
$y=\pm\sqrt{ax}$ (Parabola)
$y=\pm\sqrt{r^2-x^2}$ (Circle)
$y=b\pm\sqrt{r^2-(x-a)^2}$ (Circle)
$y=\pm\frac{b}{a}\sqrt{a^2-x^2}$ (Ellipse)
19. :
Hyperbola:
Parabola:
Circular:
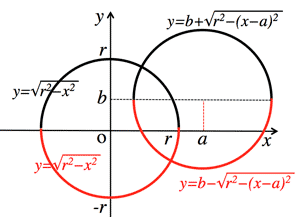
Ellipse:
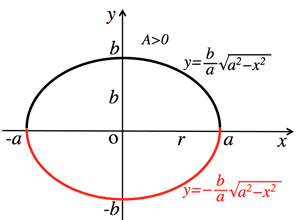
>Top 20. 数列 (Sequence or Progression):
- 等差数列 (Arithmetic progression):
$a_n=a+(n-1)d$
- 無限数列の極限値 (Limiting value):
(収束 convergence/発散 divergence/上に有界 bounded above/挟み打ちの原理 squeeze theorem):
$\displaystyle\lim_{n\to\infty}a_n=\alpha \;$ (where, $d=$ tolerance)
- 無限等比数列 (Infinite geometric sequence) {$r^n$}
- when, $-1\lt r\lt 1$: converge to $0$
- when, $r=1$ : converge to $1$
- when, $r\gt 1$: diverge to $\infty$ (there is limiting value.)
- when, $r\leqq -1$: diverge (there is no limit)
20:
21. >Top 無限級数 (Infinite series)
- $\sum_{n=1}^{\infty}a_n=a_1+a_2+a_3+ \dots a_n$
- 部分和 (Partial sum):
$S_n=a_1+a_2+a_3+\dots +a_n=\sum_{k=1}^n{a_k}$
- 無限等比級数 (Infinite geometric series):
$\sum_{n=1}^\infty ar^{n-1}=a+ar+ar^2+\dots +ar^{n-1}+\dots \\$
(where, $\; a$: 初項 the first term; $\; r (r\neq 0)$: 公比 geometric ratio)
無限等比級数の和 (Sum of infinite geometric series):
$S=\frac{a}{1-r} \; (-1\lt r\lt 1)$
- 循環小数 (Recurring decimal): (=有理数 Rational number)
$0.\dot{a_1}a_2\dot{a_3}=\frac{a_1 a_2 a_3}{9990}$
$0.a_1\dot{a_2}\dot{a_3}=\frac{a_1 a_2 a_3-a_1}{990}$
- 函数の極限 (Limit of a function)
- $\lim_{\theta\to 0}\frac{\sin\theta}{\theta}=1, \;
\lim_{\theta\to 0}\frac{\tan\theta}{\theta}=1 \;$ (where $\; \theta$ is Radian)
- $\lim_{x\to \pm\infty}\left( 1+\frac{1}{x}\right)^x=e, \;
\lim_{x\to 0}(1+x)^\frac{1}{x}=e $
- $\lim_{x\to 0}\frac{\log_e(1+x)}{x}=1, \; \lim_{x\to 0}\frac{e^x-1}{x}=1 $
21:
22. >Top 指数と対数 (Exponential and logarithm):
- 累乗根 (Power Root):
- $\begin{cases}
\pm\sqrt[n]{a}\;(\text{when}, n= \text{even number}, a>o)\\
\text{No root} \; (\text{when}, n=\text{even number}, a<0)\\
\sqrt[n]{a} \;(\text{when}, n=\text{odd number})\\
\end{cases}
$
- $(\sqrt[n]{a})^n=\sqrt[n]{a^n}=a$
- $\sqrt[n]{a}\sqrt[n]{b}=\sqrt[n]{ab}$
- $\frac{\sqrt[n]{a}}{\sqrt[n]{b}}=\sqrt[n]{\frac{a}{b}}$
- $\sqrt[n]{a^m}=(\sqrt[n]{a})^m$
- $\sqrt[n]{a^m}=\sqrt[np]{a^{mp}}$
- $\sqrt[m]{\sqrt[n]{a}}=\sqrt[n]{\sqrt[m]{a}}=\sqrt[mn]{a}$
- $\sqrt[n]{-a}=-\sqrt[n]{a} \; (n=$ odd number)
- 指数函数 (Exponential):
- where, $A>0, n=$ positive integer
- $a^0=1$
- $a^{-n}=\frac{1}{a^n}$
- $a^{\frac{1}{n}}=\sqrt[n]{a}$
- $a^{\frac{m}{n}}=\sqrt[n]{a^m}$
- $a^{-\frac{m}{n}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt[n]{a^m}}$
- $a^m × a^n=a^{m+n}$
- $\frac{a^m}{a^n}=a^{m-n}$
- $(a^m)^n=a^{mn}$
- $(ab)^n=a^nb^n$
- 対数 (Logarithm):
- $a^m=M \Leftrightarrow m=\log_a M \; (a>0, a\neq 1, M>0)$
(底 base; 真数 anti-logarithm)
- where, $a>0, a\neq1, M>0, N>0$
- $\log_a a=1, \; \log_a 1=0$
- $\log_a MN=\log_a M+\log_a N$
- $\log_a\frac{M}{N}=\log_a M-log_a N$
- $\log_a M^k=k\log_aM$
- $\log_a M=\frac{log_b M}{\log_b a}$
- $\log_b a=\frac{1}{\log_a b} \; (b.0, b\neq1)$
- $a^{\log_a M}=M$
- 指数方程式(Exponential equation)、指数不等式(Exponential inequation):
- where $a>0, a\neq 1, b>0, b\neq 1$
Direct $a^{f(x)}=a^{g(x)} \Rightarrow f(x)=g(x)$
or $f(x)\log a=g(x)\log b$
- Direct $a^{f(x)}>a^{g(x)} \Rightarrow f(x)>g(x) \; (a>0)$ or
$f(x)<g(x) \; (0<a<1)
$
- 桁数(Number of digits): $\alpha, \beta \text{integer}>0$
22. :
- Exponential and Logarithm function:
- a>1: Increasing function
- 0<a<1: Decreasing function
- x/y axis: Asymtote (漸近線)
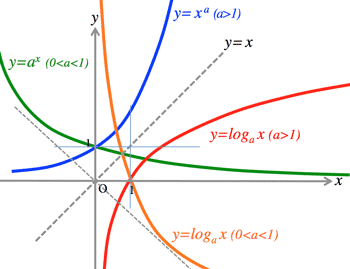
- Eg: When $\log_2 3=a, \log_3 7=b$
Express $M=\log_{42} 56$ by $a$ and $b$.
- $M=\frac{\log_3 56}{\log_3 42}
=\frac{\log_3 7+3\log_3 2}{\log_3 7
+\log_3 3+\log_3 2}=
\frac{b+\frac{3}{a}}{b+1+\frac{1}{a}}=
\frac{ab+3}{ab+a+1}$
>Top 23. 微分法 (Differentiation):
- 一次導函数 (First derivative):
$f'(x)=\lim_{\varDelta x \to 0}\frac{\varDelta y}{\varDelta x}= \lim_{\varDelta x \to 0}\frac{f(x+ \varDelta x)-f(x)}{\varDelta x}$
- 函数の微分法 (Differentiation of functions)
- $(x^{\alpha})'=\alpha x^{\alpha -1} \; (\alpha$ is real number)
- $\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) '=-\frac{1}{x^2}$
- $(\sqrt{x})'=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}$
- $(\sin{x})'=\cos{x}, \; (\cos{x})'=-\sin{x}$
$(\tan{x})'=\frac{1}{\cos^2{x}}=\sec^2{x}, \;
(\cot{x})'=-\frac{1}{\sin^2{x}}=-\csc^2{x}$
- $(e^x)'=e^x, \; (a^x)'=a^x \log{a} \; (a\gt 0, a\neq 1)$
- $(\log |x|)'=\frac{1}{x}, \; (log_a |x|)'=\frac{1}{x\log{a}} \; (a \gt 0, a\neq 1)$
- 合成函数 (Composite function):
- when $y=f(g(x))$,
$\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{dy}{du}\frac{du}{dx}=f'(u)g'(x)$
- $\{ f(ax+b) \}'=af'(ax+b)$
$\{ (f(x))^n \}'=n\{ f(x) \}^{n-1}f'(x)$
$(\sqrt{f(x)})'=\frac{f'(x)}{2\sqrt{f(x)}}, \; \{ log|f(x)| \}'=\frac{f'(x)}{f(x)}$
$(\log|y|)'=\frac{y'}{y}$
- Product rule:
$h(x)=f(x)g(x)\\
h'(x)=f'(x)g(x)+f(x)g'(x)
$
- Quaotient rule:
$h(x)=\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}\\
h'(x)=\frac{f'(x)g(x)-f(x)g'(x)}{(g(x))^2}
$
- when $y=f(u), u=g(v), v=h(x), $
$\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{dy}{du}\frac{du}{dv}\frac{dv}{dx}=f'(u)g'(v)h'(x)$
- 様々な微分法 (Various derivatives):
- when, $x=f(t), y=g(t)$
$\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{\frac{dy}{dt}}{\frac{dx}{dt}}=g'(t)f'(t) \; (f'(t)\neq 0)$
- when, $y=f^{-1}(x)\Longleftrightarrow x=f(y)$
$\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{\frac{dx}{dy}}=\frac{1}{f'(y)} \; (f'(y)\neq 0)$
- when, $f(x, y)=0, \;$ (Implicit function): differentiate both sides.
- Logalithmic differentiation: when $y=f(x), \; \log|y|=\log|f(x)|$: diffrentiate both sides.
- 高次導函数 (Higher-order differentiation):
- $\frac{d^n}{a^n}=n!$
- $\frac{d^n}{dx^n}\sin{x}=\sin\left( x+\frac{n\pi}{2}\right)$
- $\frac{d^n}{dx^n}e^x=e^x$
- $(fg)'=f'g+fg', \; (fg)''=f''g+2f'g'+fg''$
$(fg)'''=f'''g+3f''g'+3f'g''+fg'''$
- ライプニッツの公式 (General Leibniz formula):
$(f・g)^{(n)}=\sum_{k=0}^n\binom{n}{k}f^{(k)}g^{(n-k)} \\
=f^{(n)}g+ {}_nC_1f^{(n-1)}g'+{}_nC_2f^{(n-2)}g''+\dots + {}_nC_rf^{(n-r)}g^{(r)}+\dots + {}_nC_{n-1}f'g^{(n-1)}+fg^{(n)}$
23:
- 平均値の定理 (Mean value theorem):
when, $f(x)$ is continuous and differentiable in closed-interval $[a, b]$
$\frac{f(b)-f(a)}{b-a}=f'(c), \; (\exists c; \; a\lt c\lt b)$
when, $\frac{c-a}{h}=\theta$
$f(a+h)=f(a)+hf'(a+\theta h) \; (\exists \theta; 0\lt \theta \lt 1)$
when, $\overline{AB} \parallel y=0$, \; (Rolle's theorem)
平均値の定理
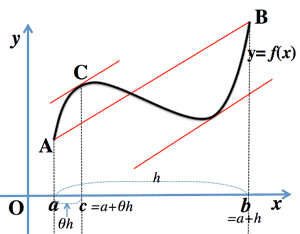
>Top 24. 接線の方程式等 (Equation of tangent line, etc.):
- 接線 (Tangent line):
$y-f(x_1)=f'(x_1)(x-x_1)$
- 法線 (Normal line):
$y-f(x_1)=-\frac{1}{f'(x_1)(x-x_1)} ,\; $(where,$\; f'(x_1) \neq 0)$
- 楕円 (Ellipse):
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{y^2}{b^2}=1$
$\frac{x_1x}{a^2}+\frac{y_1y}{b^2}=1$
- 双曲線 (Hyperbola):
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{y^2}{b^2}=\pm 1$
$\frac{x_1x}{a^2}-\frac{y_1y}{b^2}=\pm 1$
- 放物線 (Parabola):
$y^2=4px$
$y_1y=2p(x+x_1)$
- 漸近線 (Asymptote):
when, $\lim_{x\to \pm\infty}\left\{ f(x)-(ax+b) \right\}=0$;
$y=ax+b$ is asymptote of $\; y=f(x)$
$a=\lim_{x\to\pm\infty}\frac{f(x)}{x}, \; b=\lim_{x\to\pm\infty}(f(x)-ax)$
- 速度 (Velocity), 加速度 (Acceleration), それぞれの大きさ (Magnitude):
$v=\frac{dx}{dt}=f'(t), \; |v| \; $(magnitude)
$a=\frac{dv}{dt}=f''(t), \; |a| \;$ (magnitude)
24:
>Top 25. 近似式 (Approximate eqution):
- $f(a+h)\fallingdotseq f(a)+hf'(a), \; |h|\ll \delta$
- $f(x)\fallingdotseq f(0)+xf'(0), \; |x|\ll \delta$
- 誤差 (error): $E=a-A \;$ (where, $A$ is real value, $a$ is approximation)
$|E|\leq \delta \; (\delta$ is the limit of error.)
The above 1): $\frac{1}{2}h^2f''(a), \; $2):
$\frac{1}{2}x^2f''(0)$
- 二次近似式 (Secondary approximation):
- $f(a+h)\fallingdotseq f(a)+hf'(a)+\frac{f''(a)}{2}h^2, \; |h|\ll \delta$
- $f(x)\fallingdotseq f(0)+xf'(0)+\frac{f''(0)}{2}x^2, \;\; |x|\ll \delta$
- Taylor expansion:
$f(a+h)=f(a)+hf'(a)+\frac{h^2}{2!}f''(a)+ \dots +\frac{h^{(n-1)}}{(n-1)!}f^{(n-1)}(a)+\frac{h^{n}}{n!}f^{(n)}(a+\theta h) \; (0\lt\theta\lt 1)$
- Mclaurin expansion:
$f(x)=f(0)+xf'(0)+\frac{x^2}{2!}f''(0)+ \dots +\frac{x^{(n-1)}}{(n-1)!}f^{(n-1)}(0)+\frac{x^{n}}{n!}f^{(n)}(\theta x) \;\; (0\lt\theta\lt 1)$
- $e^x\fallingdotseq 1+\frac{x}{1!}+\frac{x^2}{2!}+\frac{x^3}{3!}+\dots+\frac{x^n}{n!}$
$\sin{x}\fallingdotseq\frac{x}{1!}-\frac{x^3}{3!}+\frac{x^5}{5!}-\dots+(-1)^{n-1}\frac{x^{2n-1}}{(2n-1)!}$
25:
>Top 26. 不定積分 (Indefinite integral):
- $\int kf(x)dx=k\int f(x)dx \;$ (where, $k$=constant)
- $\int \{ f(x)\pm g(x)\} dx=\int f(x)dx \pm \int g(x)dx \;$ (double-sign corresponds)
- $\int x^{n}dx=\frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1}+C$
In particular, $\int (ax+b)^{n}dx=\frac{(ax+b)^{n+1}}{a(n+1)}+C$
- $\int \frac{1}{x}dx=\log |x| +C$
$\int \frac{f'(x)}{f(x)}dx=\log \left|f(x)\right| +C$
In particular, $\int \frac{1}{ax+b}dx=\frac{1}{a}\log{}\left|ax+b\right| +C$
In particular, $\int \frac{1}{x^2-a^2}dx=\frac{1}{2a}\log{}\left|\frac{x-1}{x+a}\right| +C$
- $\int \frac{1}{x^2+a^2}=\frac{1}{a}\tan^{-1}\frac{x}{a}$
- $\int \frac{1}{x^2-a^2}=\frac{1}{2a}\log |\frac{x-a}{x+a}|$
- $\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}}=\sin^{-1}\frac{x}{a}$
- $\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2+x^2}}=\log |x+\sqrt{x^2+a}|$
- $\int \sin{x}dx=-\cos{x}+C$
$\int \cos{x}dx=\sin{x}+C$
- $\int \sin{(ax+b)}dx=-\frac{1}{a}\cos{(ax+b)}+C$
$\int \cos{(ax+b)}dx=\frac{1}{a}\sin{(ax+b)}+C$
- $\int \sec^2{ax}dx=\frac{1}{a}\tan{x}+C$
$\int \csc^2{ax}dx=-\frac{1}{a}\cot{x}+C$
- $\int \tan{x}dx=-\log{}\left|\cos{x}\right|+C$
$\int \cot{x}dx=\log{}\left|\sin{x}\right|+C$
26:
- $\int \sin^2{x}dx=\int \frac{1-\cos{2x}}{2}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\sin{2x}\right)+C$
$\int \cos^2{x}dx=\int \frac{1+\cos{2x}}{2}dx=\frac{1}{2}\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\sin{2x}\right)+C$
- $\int \sin^n{x}\cos{x}dx=\frac{\sin^{n+1}{x}}{n+1}dx+C$
$\int \cos^n{x}\sin{x}dx=-\frac{\cos^{n+1}{x}}{n+1}dx+C$
- $\int \frac{1}{\cos{x}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\log{\left|\frac{1+\sin{x}}{1-\sin{x}}\right|}=\log \left|\tan{(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{\pi}{4})}\right|+C$
$\int \frac{1}{\sin{x}}dx=\frac{1}{2}\log{\left|\frac{1-\cos{x}}{1+\cos{x}}\right|}=\log \left|\tan{\frac{x}{2}}\right|+C$
- $\int e^{ax}dx=\frac{1}{a}e^{ax}+C$
$\int a^xdx=\frac{a^x}{\log{a}}+C$
$\int \log{x}dx=x(\log{x}-1)+C$
- $\int (f(x))^a f'(x)=\frac{(f(x))^{a+1}}{a+1}$
- $\int \frac{f'(x)}{f(x)}=\log |f(x) |$
- 置換積分 (Substitution integral):
$\int f(g(x))g'(x)dx=\int f(t)dt \;\; $ (where, $g(x)=t)$
- Eg.: $\int 2x\cos(1+x^2)dx \;
(u=1+x^2 \Rightarrow du=2xdx)\\
\int \cos udu=\sin u=\sin (1+x^2)
$
- 部分積分 (Partial integral):
$\int f'(x)g(x)dx=f(x)g(x)-\int f(x)g'(x)dx$
or $F'(x)=f(x)\\
\int f(x)g(x)dx=F(x)g(x)-\int F(x)g'(x)dx
$
- 不定積分の漸化式 (Recurrence formula of indefinite integral):
$\int \sin^n{x}dx=-\frac{\sin^{n-1}{x}\cos{x}}{n}+\frac{n-1}{n}\int \sin^{n-2}{x}dx$
$\int \cos^n{x}dx=\frac{\cos^{n-1}{x}\sin{x}}{n}+\frac{n-1}{n}\int \cos^{n-2}{x}dx$
$\int x^ne^xdx=x^ne^x-n\int x^{n-1}e^xdx$
Eg:
$\int \ln xdx= \\
\frac{1}{3}\ln x
-\int \frac{x^3}{3}\frac{1}{x}dx=
\\ \frac{x^3\ln x}{3}-\frac{x^3}{9}=\\
\frac{x^3}{9}(3\ln x-1)
$
>Top 27. 定積分 (Definite integral):
- when, $F'(x)=f(x)$
$\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx=\left[ F(x)\right]_{a}^{b}=F(b)-F(a)$
- $\int_{a}^{b}\{ f(x)\pm g(x)\} dx=\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx \pm \int_{a}^{b}g(x)dx$
- $\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx=-\int_{b}^{a}f(x)dx$
- $\int_{-a}^{a}f(x)dx=2\int_{0}^{a}f(x)dx \;$ (even function)
$\int_{-a}^{a}f(x)dx=0 \; $ (odd function)
28:
- 置換積分 (Substitution integral):
when $x=g(t),{} a=g(\alpha), {} b=g(\beta)$
$\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}f(g(t))g'(t)dt$
- 部分積分 (Partial integral):
$\int_{a}^{b}f(x)g'(x)dx=\bigl[ f(x)g(x) \bigr]_{a}^{b}-\int_{a}^{b}f'(x)g(x)dx$
- $\int_{a}^{b}(x-a)(x-b)\ dx=-\frac{1}{6}(b-a)^3$
- $\int_{0}^{a}\frac{dx}{(a^2+x^2)}=\frac{\pi}{4a} \;\; (a\gt 0)$
- $\int_{0}^{a}\sqrt{a^2-x^2}dx=\frac{\pi}{4}a^2 \;\; (a\gt 0)$
- $\int_{0}^{a}\frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}}dx=\frac{\pi}{2} \;\; (a\gt 0)$
- $\int_{0}^{\frac{2 \pi }{k}}\sin{kx}\ dx=0$
$\int_{0}^{\frac{2 \pi }{k}}\cos{kx}\ dx=0$
- $\int_{0}^{2\pi}\sin{mx}\sin{nx}dx=
\int_{0}^{2\pi}\cos{mx}cos{nx}dx=
\begin{cases}0 & \text (m\neq n)\\ \pi & \text(m=n\neq 0)\end{cases}$
- $\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\sin^{2m}xdx=
\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\cos^{2m}xdx=
\frac{2m-1}{2m}・\frac{2m-3}{2m-2}・\dots ・\frac{3}{4}・\frac{1}{2}・\frac{\pi}{2}$
$\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\sin^{2m+1}xdx=
\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\cos^{2m+1}xdx=
\frac{2m}{2m+1}・\frac{2m-2}{2m-1}・\dots ・\frac{4}{5}・\frac{2}{3}・1$
- $\int_{0}^{a}f(x)dx=\int_{0}^{\frac{a}{2}}\{ f(x)+f(a-x)\} dx=\int_{0}^{a}f(a-x)dx$
- 積分の平均値の定理 (Average value of theorem of integration):
when $f(x)$ is continuous in the interval $[a, b]$:
$\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx=(b-a)f(c) \;\; (\exists c, \; a\lt c\lt b)$
9. 積分の平均値の定理
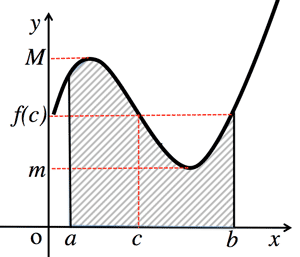
>Top 28. 定積分の応用 (Application of definite integral):
- 曲線と座標軸の間の面積 (Area between curve and axis):
$S=\int_{a}^{b}\left| y\right| dx=\int_{a}^{b}\left| f(x)\right| dx$
$S=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta} \left| x\right| dy=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}\left| g(y)\right| dy$
- 二曲線間の面積 (Area of between two curves)
$S=\int_{a}^{b}\left| f(x)-g(x)\right| dx$
$S=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}\left| p(y)-q(y)\right| dy$
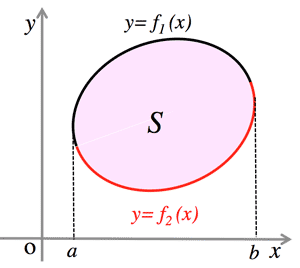
- 閉曲線の囲む面積 (Area of closed curve):
$S=\int_{a}^{b}\{ f_1(x)-f_2(x)\} dx$
- 媒介変数で表された曲線と面積 (Area by parametric representation):
$S=\int_{a}^{b}\left|y\right|dx=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}\left|g(t)\right|f'(t)dt$
(where $x=f(t), \; y=g(t) \; (g(t) \geqq 0); \; a=f(\alpha), \; b=f(\beta); \;
a\leqq x\leqq b$ and $ \alpha \leqq t \leqq \beta $ corresponds:)
28:
3. 閉曲線の囲む面積
>Top 29. 体積 (Volume):
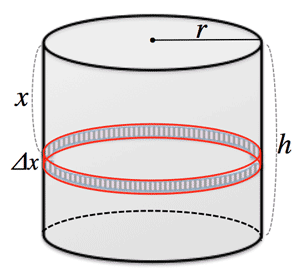
- 立体の体積 (3D Volume):
when sectional area is $S(x)$:
$V=\int_{a}^{b}S(x)dx$
- 回転体の体積 (Volume of rotating body):
(around X-axis):
$V=\pi \int_{a}^{b}y^2dx=\pi \int_{a}^{b}\{ f(x) \}^2dx$
(around Y-axis):
$V=\pi \int_{c}^{d}x^2dy=\pi \int_{c}^{d}\{ g(y) \}^2dy$
(two curves around X-axis):
$V=\pi \int_{a}^{b}[\{ f(x)\}^2-\{ g(x)\}^2]dx$
- 媒介変数で表された曲線と体積(Volume by parametric representation):
(where, $x=f(t), \; y=g(t), \; x$-axis and $x=a, \; x=b (a \lt b); \; a=f(\alpha), \; b=f(\beta)$)
$V=\pi \int_{a}^{b}y^2dx=
\pi \int_{\alpha}^{\beta}y^2\frac{dx}{dt}dt=
\pi \int_{\alpha}^{\beta}\{ g(t)\}^2f'(t)dt$
- 曲線の長さ (Length of curve):
$L=\int_{a}^{b}\sqrt{1+\{f'(x)\}^2}dx=\int_{a}^{b}\sqrt{1+\bigl(\frac{dy}{dx}\bigr)^2}dx$
- 媒介変数で表された曲線の長さ(Length by parametric representation):
where $x=f(t), \; y=g(t);$ between $\alpha \leqq t \beta$
$L=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}\sqrt{\{ f'(t)\}^2+\{ g'(t)\}^2}dt$
$=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}\sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^2
+\left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^2}dt$
- 直線運動 (Linear motion):
$s=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}|v| dt=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}|f(t)| dt$
- 平面運動 (Planar motion):
$s=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^2+\left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^2 }$
- 求積方法 (Mass calculation):
when, a small partial volume is $f(x)\varDelta x$ in a narrow interval $\left[ x, x+\varDelta x \right] $
$\lim_{\varDelta x\to 0}\sum f(x)\varDelta x=\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx$
- 水の側圧 (Lateral pressure of water):
$F=\int_{0}^{h}f(x)dx$
- 流水の全量 (Volume of flowing water):
when, sectional area is $A$, water velocity is $v(t)$, the flowing volume $V$ from $t_1$ to $t_2$:
$V=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}Av(t)dt$
29:
9. 側圧
>Top 30. 数列 (Progression):
- $S_1=a_1, \; a_n=S_n-S_{n-1}\; (n\geqq 2)$
- 等差数列 (Arithmetic progression):
$a_n=a+(n-1)d\; (d: common difference)$
$S_n=\frac{n(a+l)}{a}, \; (l: last term) \; S_n=\frac{n\{ 2a+(n-a)d\}}{2}$
- 等比数列 (Geometrical progression):
$a_n=ar^{n-1}$
$\cases{S_n=\frac{a(1-r^n}{1-r}=\frac{a(r^n-1)}{r-1} \; (r\neq 1) \cr S_n=na \; (r=1)}
$
- 積立預金 (Installment time deposit): (a=installment; r=cumulative interest rate; n=# of terms)
- Year-beginning pay:
$S=\frac{a}{r}(1+r)\{(1+r)^n- 1\}$
- Year-end pay:
$S=\frac{a}{r}\{(1+r)^n- 1\}$
- 償還金 (Redemption money): (A=loaned principal; r=cumulative interest rate; n=# of repayment; x=repayment of every term)
$x=\frac{Ar(1+r)^n}{(1+r)^n-1}$
- Sigma:
$\Sigma_{k=1}^nk=1+2+3+\dots +n=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}$
$\Sigma_{k=1}^nk^2=1^2+2^2+3^2+\dots +n^2=\frac{n(n+1)(2n+1)}{6}$
$\Sigma_{k=1}^nk^3=1^3+2^3+3^3+\dots +n^3=\bigl\{ \frac{n(n+1)}{2} \bigr\}^2$
- 連続自然数 Continuous natural number:
$\Sigma_{k=1}^nk(k+1)=1・2+2・3+\dots +n(n+1)=\frac{1}{3}n(n+1)(n+2)$
$\Sigma_{k=1}^nk(k+1)(k+2)=\frac{1}{4}n(n+1)(n+2)(n+3)$
- 階差数列 (Difference sequence):
$a_n=a_1+\Sigma_{k=1}^{n-1}b_k \; (n\geqq 2)$
30:
>Top 31. 微分方程式 (Differential equation):
- 1階微分方程式 (1st order): 例
$\frac{dy}{dx}=2x$
$y=x^2+C$
- 2階微分方程式 (2nd order): 例
$\frac{d^2y}{dt^2}=-g$
$-\frac{1}{2}gt^2+C_1t+C_2$
- $x^2+y^2=r^2$: 例
$x+y\frac{dy}{dx}=0 \\
\frac{dy}{dx}・\frac{y}{x}=-1 \\ \text{(where, tangent at $P(x,y)$ is perpendicular to raidius OP.)}$
- $y=a\sin{t}+b\cos{t}\\\text (sample)
\frac{dy}{dt}=a\cos{t}-b\sin{t}\\
\frac{d^2y}{dt^2}=-(a\cos{t}+b\cos{t})=-y \;
\text{(simple harmonic oscillation)}$
- 解法 (Solution):
- $\frac{dy}{dx}=f(x)$
\[ y=\int f(x)dx \]
- $\frac{dy}{dx}=f(y), \; \frac{dx}{dy}=\frac{1}{f(y)}$
\[ x=\int \frac{1}{f(y)}dx \]
- $\frac{d^2y}{dx^2}=f(x), \; \frac{dy}{dx}=\int f(x)dx$
- 変数分離形 (Variable separation method):
$\frac{dy}{dx}=f(x)g(y), \; \frac{1}{g(y)}\frac{dy}{dx}=f(x)$
\[ \int \frac{1}{g(y)}dy=\int f(x)dx \]
- $\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{y}{x}\\
\frac{dy}{y}=\frac{dx}{x}\\
\log{y}=\log{x}+C\\
y=xe^c
\\
y=ax \; \text{(a: constant)}
$
- $\frac{dy}{dx}=x+y+1$
$x+y+1=u, \; \text{(differentiate both sides)}\\
1+\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{du}{dx}\\
\therefore \; \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{du}{dx}-1 \; \frac{du}{dx}-1=x+y+1 \;;
\frac{du}{dx}=u+1 \\
\int \frac{du}{u+1}=\int dx, \; \log|u+1|=x+c \\
\therefore \; u+1=\pm e^{x+1}=\pm e^cc^x \\
x+y+1=Ce^x-1 \; (\text{where,} \pm e^c=C)
\\
y=Ce^x-x-2 \; \text{(C: constant)}
$
- $\frac{d^2y}{dx^2}-5\frac{dy}{dx}+6y=0 \\
\text{(cosider 'auxiliary equation)} \; t^2-5t+6=0; \; t=2 or 3 \\
\rightarrow \; y=c_1e^{2x}+c_2e^{3x}; \; c_1, c_2 \; \text{are constant.}$
- $\frac{dy}{dx}+ay+b=0\\
\frac{dy}{dx}=-a\left(y+\frac{b}{a}\right)\\
\frac{1}{\left(y+\frac{b}{a}\right)}=-adx\\
\log \left|y+\frac{b}{a}\right|=-ax+C_1\\
\left|y+\frac{b}{a}\right|=e^{-ax+C_1}
y+\frac{b}{a}=\pm e^{C_1}c^{-ax} \\
y=Ce^{-ax}-\frac{b}{a} \; (C=\pm e^{C_1})
$
- 定数係数1階線型微分方程式の公式 (1st order Linear DE with constant coefficients):
$\frac{dy}{dx}+ay=Q(x)\\
e^{ax}\frac{dy}{dx}+ae^{ax}y=e^{ax}Q(x) \; \text{(times $e^{ax}$)}\\
e^{ax}\frac{dy}{dx}+\left( \frac{d}{dx}e^{ax}\right) y=e^{ax}Q(x)\\
\frac{d}{dx}(e^{ax}y)=e^{ax}Q(x)\\
e^{ax}y=\int e^{ax}Q(x)dx+C
\; (C: \text{constant.})\\
y=e^{-ax}\bigl\{\int e^{ax}Q(x)dx+C \bigr\}
$
- 運動方程式 (Vertical motion of equation):
when, resitance is $kv, m$ is mass, and $g$ is gravity acceleration, the vertical motion of equation will be:
$m\frac{dv}{dt}=-kv+mg\\
\frac{dv}{dt}+\frac{kv}{m}=g\\
e^{\frac{kt}{m}}\frac{dv}{dt}+e^{\frac{kt}{m}}\frac{kv}{m}
=e^{\frac{kt}{m}}g\\
\frac{d}{dt} \left( e^{\frac{kt}{m}}v\right)=e^{\frac{kt}{m}}g\\
e^{\frac{kt}{m}}v=\int e^{\frac{kt}{m}}gdt+C\\
v=Ce^{\frac{-kt}{m}}+\frac{mg}{k}$
- 例: Typical differential equations:
$\begin{align}
y' &=k & \qquad & y=kx+C\\
y'' &=k
& & y=\frac{k}{2}x^2+Ax+B\\
y' &=ky & & y=Ce^{kx}\\
y'' &=k^2y & & y=Ae{kx}+Be{-kx}\\
y'' &=k^2y & & y=A\cos{kx}+B\sin{kx}
\end{align}$
31:
Differential equation includes some function with its derivatives (also with Nth-order having N kinds of arbitray contants): only simple differential equations are solvable by explicit formulas; includes 1) Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE), and 2) Partial Diffrential Equation (PDE).
>Top 32. 行列式 (Determinant):
- $\begin{align}
A+B&=B+A &\; \text{(交換法則 Communtative law)}\\
(A+B)+C&=A+(B+C) & \text{(結合法則 Associative law)}\\
A+O&=O+A=A & \text{(零行列 Zero matrix)}\\
k(A+B)&=kA+kB & \text{(実数倍 Scalar multiple)}\\
\end{align}
$
- 行列の実数倍 (Scalar multiplication):
$\begin{align}
k(AB)&=(kA)B=A(kB) &\; \text{(実数倍 Scalar multiple)}\\
(AB)C&=A(BC) & \text{(結合法則 Associative law)}\\
A(B+C)&=AB+AC=(A+B)C & \text{(分配法則 Distributive law)}\\
AB &\neq BA\\
\end{align}
$
- 行列の乗法 (Matrix Multiplication):
$\pmatrix{a&b\cr c&d}\pmatrix{p\cr r}=\pmatrix{ap+br\cr cp+dr}$
$\pmatrix{a&b\cr c&d}\pmatrix{p&q\cr r&s}=
\pmatrix{ap+br & aq+bs \cr cp+dr & cq+ds}$
- $A^2=\pmatrix{a&b\cr c&d}^2=\pmatrix{a&b\cr c&d}
\pmatrix{a&b\cr c&d}=\pmatrix{(a^2+bc)&b(a+d)\cr c(a+d)&bc+d^2}$
$A^n=A^{n-1}A=A^nA^{n-1} \; (n\geq 2)$
$A^mA^n=a^{m+n}$
$(A^m)^n=A^{mn}$
$(A+B)^2=A^2+AB+BA+B^2$
$(A+B)(A-B)=A^2-AB+BA-B^2$
- 逆行列 (Inverse matrix):
$A^{-1}=\frac{1}{ad-bc}\pmatrix{d&-b \cr -c&a} \; (\varDelta=ad-bc\neq 0)$
$AA^{-1}=A^{-1}A=E$
$(A^{-1})^{-1}=A$
- 逆行列計算 (Inverse matrix calculation):
- $AA^{-1}=A^{-1}A=E\\
AX=E \Rightarrow X=A^{-1}\\
(A^{-1})^{-1}=A\\
(AB)^{-1}=B^{-1}A^{-1}\\
(ABC)^{-1}=C^{-1}B^{-1}A^{-1}\\
\exists A^{-1},
AX=B \Rightarrow X=A^{-1}B\\
\exists (AB)^{-1} \Rightarrow
\exists (A)^{-1} \;\text{and}\;
\exists (B)^{-1}$
- 零因子 null factor:
$AB=O \nRightarrow A=O \; \text{or} \; B=O\\
A^2=O
\nRightarrow A=O\\
\exists A^{-1}:
AB=O \Leftrightarrow B=O$
- 対角行列 (Diagonal matrix):
$\pmatrix{\alpha&0 \cr 0&\beta}^n=\pmatrix{\alpha^n&0 \cr 0&\beta^n}$
32:
- クラメールの定理 (Cramer's rule):
$Ax=b \; (det(a)\neq 0)\\
A=\begin{pmatrix}
a_{11}&a_{12}&\dots&a_{1n}\\
a_{21}&a_{22}&\dots&a_{2n}\\
\vdots&\vdots&\ddots&\vdots\\
a_{n1}&a_{n2}&\dots&a_{nn}\\
\end{pmatrix}
, \; x=\begin{pmatrix}x_1\cr x_2\cr \vdots\cr x_n\end{pmatrix}
,
\; b=\begin{pmatrix}b_1\cr b_2\cr \vdots\cr b_n\end{pmatrix}.
x_i=\frac{det(A_i)}{det(A)}\\
A_i=\begin{pmatrix}
a_{11}&\dots&a_{1, i-1}&b_1&a_{1, i+1}\dots&a_{1n}\\
a_{21}&\dots&a_{2, i-1}&b_2&a_{2, i+1}\dots&a_{2n}\\
\vdots& &\vdots&\vdots&\vdots& &\vdots\\
a_{n1}&\dots&a_{n, i-1}&b_n&a_{n, i+1}\dots&a_{nn}\\
\end{pmatrix} $
- Example:
$82x_1+45x_2+9x_3=1
27x_1K16x_2+3x_3=1
9x_1+5x_2+x_3=0$
$(A b)=\left(
\begin{array}{@{\,}ccc|c@{\,}}
82
& 45 & 9 & 1\\
27
& 16 & 3 & 1\\
9
& 5 & 1 & 0\\
\end{array} \right)
$
$x_1=\frac{det(A_1)}{det(A)}=\frac{
\begin{vmatrix}1&45&9\\1&16&3\\0&5&1\\\end{vmatrix}}
{\begin{vmatrix}82&45&9\\27&16&3\\9&5&1\\\end{vmatrix}}=\frac{1}{1}=1\\
x_2=\frac{det(A_2)}{det(A)}=\dots=1\\
x_3=\frac{det(A_3)}{det(A)}=\dots =-14$
>Top 33. 点の移動 (Movement of Point):
- $\cases{ x'=ax+by \cr y'=cx+dy} \longrightarrow
\pmatrix{a&b \cr c&d}\pmatrix{x \cr y}\\
\pmatrix{x \cr y} \xrightarrow{f} \pmatrix{x' \cr y'}$
- Symetrical movement to X-axis:
$\pmatrix{1&0 \cr 0&-1}$
- Symetrical movement to Y-axis:
$\pmatrix{-1&0 \cr 0&1}$
- Symetrical movement to the origin:
$\pmatrix{-1&0 \cr 0&-1}$
- Symetrical movement with respect to $y=x$:
$\pmatrix{0&1 \cr 1&0}$
- Symetrical movement with respect to $y=-x$:
$\pmatrix{0&-1 \cr -1&0}$
- Rotational movement around the origin:
$f: \pmatrix{x' \cr y'}=\pmatrix{\cos{\theta}&-\sin{\theta} \cr
\sin{\theta}&\cos{\theta}}\pmatrix{x \cr y}$
- Reverse rotational movement around the origin:
$f^{-1}: \pmatrix{x' \cr y'}=\pmatrix{\cos{\theta}&\sin{\theta} \cr
-\sin{\theta}&\cos{\theta}}\pmatrix{x \cr y}$
- Synthesis of rotational movement around the origin:
$h=g\circ f: \pmatrix{\cos{\alpha+\beta}&-\sin{\alpha+\beta} \cr
+\sin{\alpha+\beta}&\cos{\alpha+\beta}}=
\pmatrix{\cos{\alpha}&-\sin{\alpha} \cr\sin{\alpha}&\cos{\alpha}}
\pmatrix{\cos{\beta}&-\sin{\beta} \cr\sin{\beta}&\cos{\beta}}$
- $g\circ f \neq f\circ g \;$ (No-communicative law is applicable)
$h\circ (g\circ f)=(h\circ g)\circ f \;$ (Associative law)
$f\circ=e\circ f=f \;$ (Identity movement)
$g\circ f=f\circ g=e \; (f^{-1}: \;$Reverse movement)
- 一次変換 (Linear transformation):
$f: \pmatrix{x' \cr y'}=\pmatrix{a&b \cr c&d}\pmatrix{x \cr y}
$
- 不動点 (Fixed point):
$\pmatrix{x \cr y}=\pmatrix{a&b \cr c&d}\pmatrix{x \cr y}
\rightarrow \; \pmatrix{a-1 & b \cr c & d-1}\pmatrix{x \cr y}=\pmatrix{0 \cr 0}$
- ケーリー・ハミルトンの定理 (Cayley-Hamilton Formula):
$A=\pmatrix{a&b \cr c&d}\Rightarrow
A^2-(a+d)A+(ad-bc)E=0$
- Other determinant:
$(E-A)(E+A+A^2+\dots +A^{n-1})=E-A^n$
- 回転行列 (Rotation determinant):
$R(\theta)=\pmatrix{\cos{\theta}&-\sin{\theta} \cr
\sin{\theta}&-\cos{\theta}}\\
R(\alpha)R(\beta)=R(\alpha+\beta)\\
\{R(\alpha)\}^2=R(2\alpha)\\
\{R(\theta)\}^{-1}=R(-\theta), \{R(\theta)\}^n=R(n\theta); \;
(
n:\; \text{integer)}$
33:
>Top 34. 行列の固有値 (Eigenvalue of matrix):
- $A\vec{p}=k\vec{p} \rightarrow (A-kE)\vec{p}=\vec{0} \; \\
\text{the condition of:}
\exists \vec{p}\neq=0, \; \varDelta(A-kE)=0$
$A=\pmatrix{a&b \cr c&d} \rightarrow A-kE=\pmatrix{a-k &b \cr c& d-k}\\
\varDelta(A-kE)=(a-k)(d-k)-bc=0\\
\therefore \; K^2-(a+d)k+(ad-bc)=0 \; \text{(Eigen equation)}
$
- 行列の対角化 (Diagonalization of matrix):
if Eugen equation $D>0:$ Eigen value is $\alpha, \beta \; (\alpha\neq\beta)$
$A\pmatrix{p \cr r}=\alpha\pmatrix{p \cr r}, \;
A\pmatrix{q \cr s}=\beta\pmatrix{q \cr s}\\
A\pmatrix{p&q \cr r&s}=\pmatrix{\alpha p&\beta q\cr \alpha r& \beta s}=
\pmatrix{p&q \cr r&s}\pmatrix{\alpha&0 \cr 0&\beta}\\
\text{where,}\; P=\pmatrix{p&q \cr r&s}: P^{-1}AP=\pmatrix{\alpha&0 \cr 0&\beta}$
34:
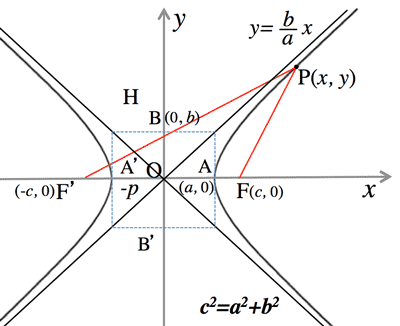
>Top 35. 二次曲線 (Quadratic curve):
- 放物線 (Parabola):
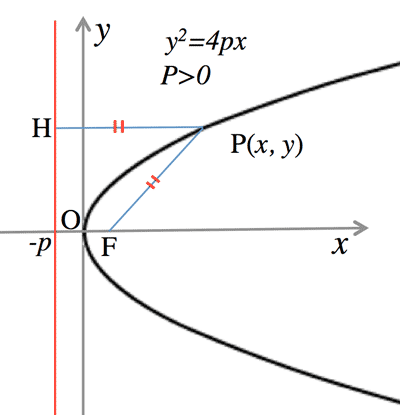
- 標準形 (Standard form):
$y^2=4px: \; \text{focus:}F(p, 0) \; \text{directrix:}\; x=-p$
$x^2=4py: \; \text{focus:}F(0, p) \; \text{directrix:}\; y=-p$
- vertex: on the point of $(m, n):$
$(y-n)^2=4p(x-m)\; \text{focus:}F(p+m, n) \; \text{directrix:}\; x=m-p$ t
- tangent line: gradient:
$y=mx+\frac{p}{m}\; \text{gradient is}\; m\\
y_1y=2p(x+x_1) \; \text{on the point of}\; P(x_1, y_1)
$
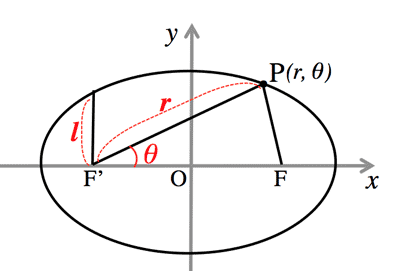
- 楕円 (Ellipse):
- 標準形 (Standard form):
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{x^2}{b^2}=1\\
F(\sqrt{a^2-b^2}, 0), \; F'(-\sqrt{a^2-b^2}, 0)
\\
PF+PF'=2a, \; PF=a-ex, \; PF'=a-ex
$
- Center $(m, n):$
$\frac{(x-m)^2}{a^2}+\frac{(y-n)^2}{b^2}=1$
- tangent line:
$y=mx\pm \sqrt{a^2m^2+b^2}\;\text{gradient is}\; m\\
\frac{x_1x}{a^2}y+\frac{y_1y}{b^2}=1 \; \text{on the point of}\; P(x_1, y_1) $
- 双曲線 (Hyperbola):
- 標準形 (Standard form):
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{x^2}{b^2}=1\\
\text{asymptote:}
\; y=\pm\frac{b}{a}x \; (\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{y^2}{b^2}=0)\\
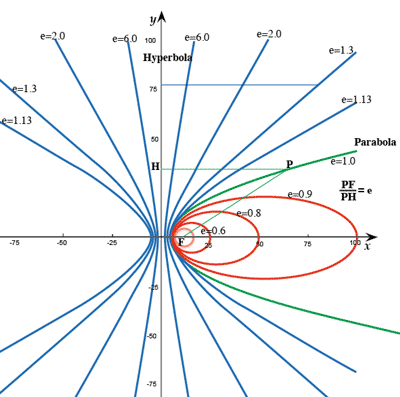
\text{excentricity:}\; e=\frac{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}{a}=\frac{OF}{OA} \; (e\gt 1)\\
F(\sqrt{a^2+b^2}, 0), F'(-sqrt{a^2+b^2}, 0)\; \left[F(ae, 0), F'(-ae, 0)\right]
\\
|PF - PF'|=2a, PF=|ex-a|, PF'=|ex+a|
- tangent line:
$y=mx\pm \sqrt{a^2m^2-b^2}\;\text{gradient is}\; m\\
\frac{x_1x}{a^2}y-\frac{y_1y}{b^2}=\pm 1 \; \text{on the point of}\; P(x_1, y_1) $$
35:
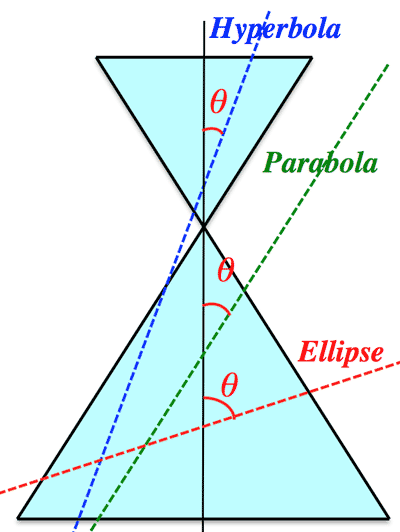
- 媒介変数表示 (Parametric representation):
- Line: $P(x_0, y_0)$, Grandient: $\alpha$
$\cases{x=x_0+t\cos\alpha \cr y=y_0+t\sin\alpha}$
- Circle:
$\cases{x=r\cos\theta \cr y=r\sin\theta}\; (x^2+y^2=r^2)
\cases{x=a+r\cos\theta \cr b+y=r\sin\theta}\; ({x-a}^2+{y-b}^2=r^2)$
- Ellipse:
$\cases{x=a\cos\theta \cr y=b\sin\theta}\; (\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{y^2}{b^2}=1)
- Hyperbola:
$\cases{x=\frac{a}{\cos\theta} \cr y=b\tan\theta} \; (\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{y^2}{b^2}=1) $
- Parabola:
$\cases{x=pt^2 \cr y=2pt}$
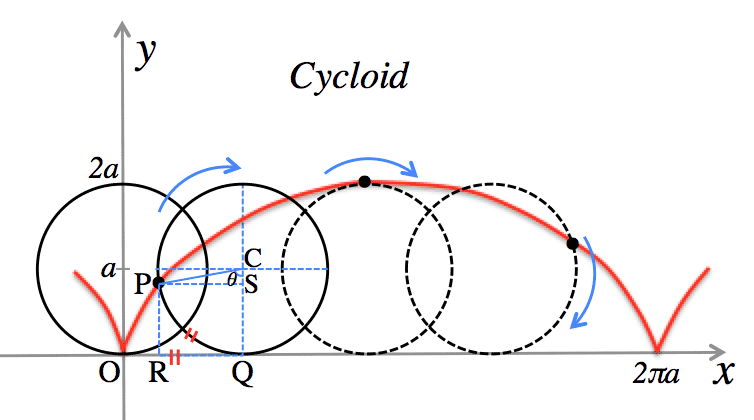
- サイクロイド (Cycloid):
$\cases{x=a(\theta-\sin\theta) \cr y=a(1-\cos\theta}$
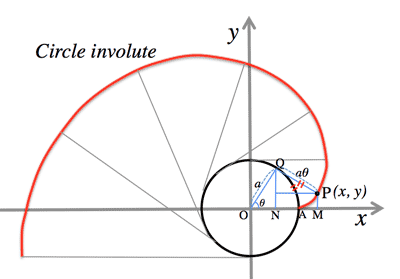
- 伸開線 (Involute):
$\cases{x=a(\cos\theta+\theta\sin\theta) \cr y=a(\sin\theta-\theta\cos\theta)}$
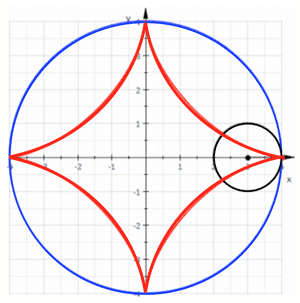
>Top 36. 極座標 (Polar coordinates):
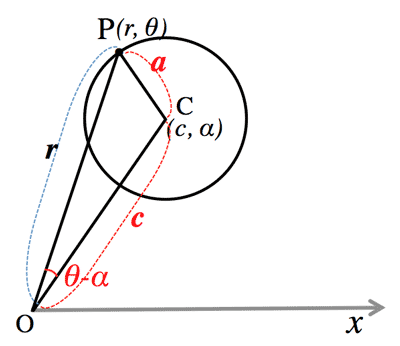
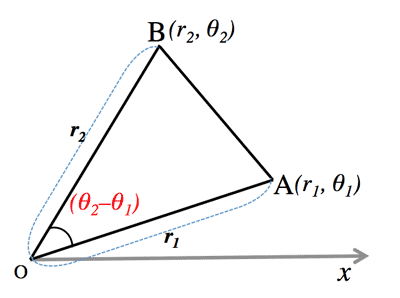
- 二点間の距離、三角形の面積 (Distance, Area of triangle):
- $AB=\sqrt{{r_1}^2+{r_2}^2-2r_1r_2\cos{(\theta_2-\theta_1)}}$
- $\triangle OAB=\frac{1}{2}r_1r_2|\sin{(\theta_2-\theta_1)}|$
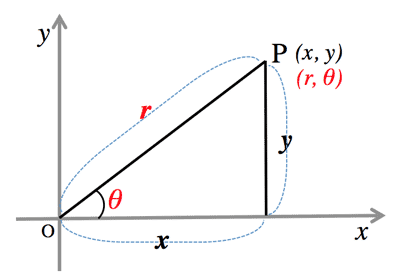
- 極座標と直交座標 (Polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates):
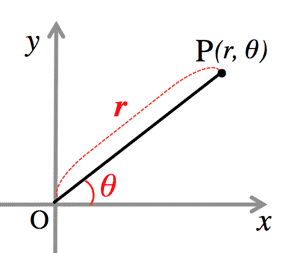
- where, $\; P(r, \theta), (x, y)\\
\cases{x=r\cos\theta \cr y=r\sin\theta} \;
\cases{r=\sqrt{x^2+y^2} \cr \tan\theta=\dfrac{y}{x}}$
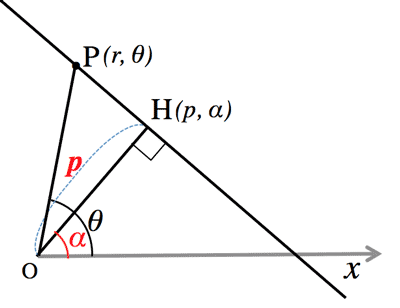
- 極方程式 (Polar equation):
- Line perpendicular to OH:
$r\cos(\theta-\alpha)=p \; (\gt 0)$
- 円の極方程式 (Polar equation of circle):
- Cener of the origin: $r=a$
- Circle on $C(a, 0): \; r=2a\cos\theta$
- Circle on $C(c, \alpha): \; r^2-2cr\cos{(\theta-\alpha)}+a^2$:
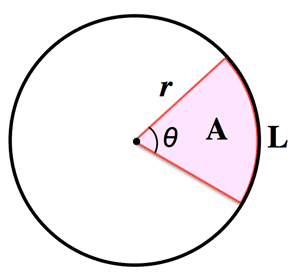
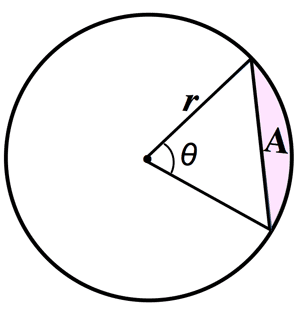
- Circle sector:
$L=\frac{\theta}{360}2\pi r=\theta r \; (\theta: \text{radian})\\
A=\frac{\theta}{360}\pi r^2=\frac{Lr}{2}=\frac{\theta r^2}{2}=\frac{Lr}{2}$
- Cicle segment:
$A=\frac{1}{2}r^2(\theta -\sin\theta)$
- 二次曲線の極方程式 (Polar equation of quadratic curve):
- Center is on the origin:
Ellipse:
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{y^2}{b^2} \Longleftrightarrow
r^2=\frac{b^2}{1-e^2\cos^2{\theta}} \;
(e=\frac{\sqrt{a^2-b^2}}{a})$
- Hyperbola:
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{y^2}{b^2} \Longleftrightarrow
r^2=\frac{b^2}{e^2 \cos^2{\theta}-1} \;
(e=\frac{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}{a})$
- Focus is on the origin:
Ellipse: $\; F'(-ae, 0)=O$
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{y^2}{b^2} \Longleftrightarrow
r=\frac{l}{1-e\cos\theta} \; (0\lt e\lt 1)$
Hyperbola: $\; F(ae, 0)=O$
$\frac{x^2}{a^2}-\frac{y^2}{b^2} \Longleftrightarrow
r=\frac{l}{1-e\cos\theta} \; (e\gt 1) $
Parabola:
$\; F(p, 0)=O$
$y^2=4px \; (p \gt 0)\Longleftrightarrow
r=\frac{l}{1-\cos\theta}$
36:

>Top 37. 複素数平面 (Complex plane):
- 極形式 (Polar coordinates):
$z=(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)$
- $z$の絶対値 (absolute value):
$r=|z|=|x+yi|=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}$
$z$の偏角(declination): $\theta=arg z$
where $z=x+yi \; (x, y)$ is real number.
$x=r\cos\theta, \; y=r\sin\theta$
- 共役複素数 (Conjugate complex):
$z=a+bi, \; \bar{z}=a-bi\\
z+\bar{z}=2a, \; z\bar{z}=a^2+b^2$
- 基本的性質 (basic property):
- $\overline{\alpha\pm\beta}=\bar{\alpha}\pm\bar{\beta}$
- $\overline{\alpha\beta}=\bar{\alpha}\bar{\beta}$
- $\overline{\left( \frac{\alpha}{\beta} \right)}=\frac{\bar{\alpha}}{\bar{\beta}}$
- $\overline{(\bar{\alpha})}=\alpha$
- where $R(\alpha)$ is real part, and $I(\alpha)$ is imaginary part:
- $R(\alpha)=a=\frac{1}{2}(\alpha+\bar{\alpha})\\
I(\alpha)=b=\frac{1}{2i}(\alpha+\bar{\alpha})
$
- 複素数の絶対値 (absolute value of complex number):
- $|\alpha|=|\bar{\alpha}|$
- $|\alpha|^2=\alpha\bar{\alpha}$
- $|\alpha|=1 \Longleftrightarrow |\alpha|^2=1 \Longleftrightarrow \alpha\bar{\alpha}=1$
- $|\alpha\beta|=|\alpha||\beta|$
- $\bigl| \frac{\alpha}{\beta} \bigr| =\frac{|\alpha|}{|\beta|} \; (\beta\neq 0)$
- 和 (Addition):
$\vec{OP_1}+\vec{OP_2}=\vec{OP}$ \rightarrow \; P(z_1+z_2)$
- 差 (Subtraction):
$\vec{OP_1}-\vec{OP_2}=\vec{P2P1}=\vec{OP}$ \rightarrow \; P(z_1-z_2)$
- 内分・外分点 (internally/externally dividing point)
- $\frac{nz_1+mz_2}{m+n} \; (mn>0: \text{Internal DP}, mn<0 \text{External DP})$
- $G=\frac{z_1+z_2+z_3}{3}\; $ \text{G: gravity}
- 三角不等式 (triangle inequality):
- $\bigl| |z_1|-|z_2|\bigr|\leqq |z_1+z_2|\leqq |z_1|+|z_2|$
- $\bigl| |z_1|-|z_2|\bigr|\leqq |z_1-z_2|\leqq |z_1|+|z_2|$
- De Moivre's theorem:
- $(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)^n=\cos{n\theta}+i\sin{n\theta}$
- N-th root:
$z^n=r(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)\\
\rightarrow \; \sqrt[n]{r}(\cos{\frac{\theta+2\pi k}{n}}+i\sin{\frac{\theta+2\pi k}{n}}), \; (k=0, 1, 2, \dots, n-1)
$
- Roots of unity: 1 of N-th root:
$\omega=\cos{\frac{2\pi}{n}}+i\sin{\frac{2\pi}{n}}$
- $1, \omega, \omega^2, \dots, \omega^{n-1}$
- $\cases{\omega^n=1 \cr 1+\omega+\omega^2+\dots +\omega^{n-1}}$
37:
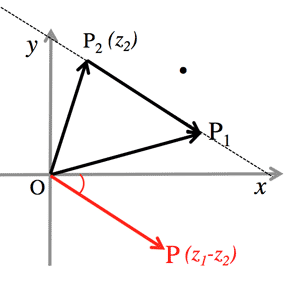
>Top 38. 確率分布 (Probability distribution):
- 条件付き確率の乗法定理 (Multiplation theorem of conditional probability):
- $P(A\cap B)=P(A)P(B|A)\\
P(A\cap B\cap C)=P(A)P(B|A)P(C|A\cap B)\\
P(B|A)=\frac{P(A\cap B)}{P(A)} \; (P(A)\neq 0)$
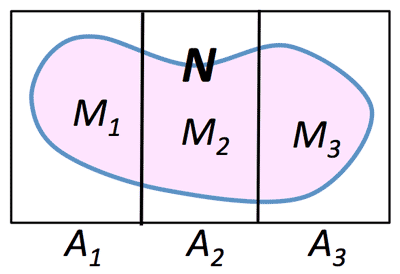
- Mutually exclusive events: $A_1, A_2, A_3$
$P_n(A_1)=\frac{p(A_1\cap N}{P(N)}=
\frac{P(A_1)P(N|A_1)}{P(A_1)P(N|A_1)+P(A_2)P(N|A_2)+P(A_3)P(N|A_3)}$
- 樹形図 (Decision tree):
- A=$\begin{cases}
B & P(A \cap B)=P(A)P(B|A)\\
B^C & P(A \cap B^C)=P(A)P(B^C|A)
\end{cases}
$
- A^C=$\begin{cases}
B & P(A^C \cap B)=P(A^C)P(B|A^C)\\
B^C & P(A^C \cap B^C)=P(A^C)P(B^C|A^C)
\end{cases}
$
$\therefore P(B)=P(A\cap B)+P(A^C\cap B)=
P(A)P(B|A)+P(A^C)P(B|A^C)
$
- $A_1 \cup A_2 \cup A_3=U$ (whole event)
$A_1, A_2, A_3$ are mutually exclusive
$P(B)=P(A_1 \cap B)+P(A_2 \cap B)+P(A_3 \cap B)=\\
P(A_1)P(B|A_1)+P(A_2)P(B|A_2)+P(A_3)P(B|A_3)$
- 独立事象 (Independent event): either of follows consists:
- $\begin{cases}
P(B|A)=P(B)\\
P(A|B)=P(A)
\\
P(A\cap B)=P(A)P(B)
\end{cases}
$
- 乗法定理: (A, B, C are independent events)
$P(A\cap B)=P(A)P(B)\\
P(A\cap B\cap C)=P(A)P(B)P(C)$
- 独立反復試行 (Independent repeated trials): (Poberbility=p; trials=n)
- $P_r=_nC_rp^rq^{n-r} \; (p+q=1)$
Maximum of $P_r$:
- $p_{k-1}\gtreqqless P_k \Longleftrightarrow \frac{P_k}{p_{k-1}}=
\frac{(n-k+1)p}{k(1-p)}\gtreqqless
1 \\
\Longleftrightarrow (n+1)p \gtreqqless k \; \text{(double sign corresponds)}$
- 確率分布 (Probablility distribution):
- 平均値/期待値 (Mean/Expectation):
$E(X)=m=\sum_{i=1}^n x_ip_i \; (E(x) $ or m: Average or expectation)
- 分散 (Variance):
$V(X)=\sigma^2=\sum_{i=1}^n p_i{(x_i-m)}^2=\sum_{i=1}^n p_i{x_i}^2-m^2$
- 標準偏差 (Standard deviation, SD):
$V(X)=E(X^2)-\{E(X)\}^2, \; D(X)=\sigma=\sqrt{V(X)}\\
E(ax+b)=aE(X)+b, \; V(aX+b)=a^2V(X)\\
E(aX+b)=aE(X)+bE(Y)\\
V(aX+bY)=a^2V(X)+b^2V(Y) \; \text{(X, Y: mutually independent)}\\
E(XY)=E(X)E(Y)
$
- 二項分布 (Binomial distribution):
- Event A: occuring probability(p) , not-occuring (q):
$p_r=P(X=r)= _nC_rp^rq^{n-r} \; (p+q=1)$
- Mean ($m$) and SD ($\sigma$):
$m=np, \; \sigma=\sqrt{npq}\; (p+q=1)$
- 大数の法則 (Law of large number):
- Poisson distribution:
$P(X=k)=\frac{m^ke^{-m}}{k!} \; (k=0, 1, 2, \dots)$
- 確率変数 (Random variable):
平均値 (Mean):
$E(X)=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}xf(x)dx$
分散 (Distribution):
$V(X)=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}(x-m)^2f(x)dx=\\
\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}x^2f(x)dx-m^2=E(X^2)-\{E(X)\}^2$
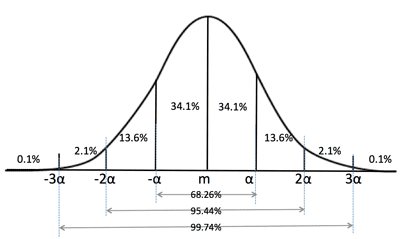
- 正規分布 (Normal distribution) ガウス分布 (Gaussian)
($N(m, \sigma^2$):
$f(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma}e^{-\frac{(x-m)^2}{2e^2}}$
- 正規分布表 (Normal distribution table):
$\varphi(z)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}\int_0^ze^{-\frac{z^2}{2}}dz$
38:
樹形図:
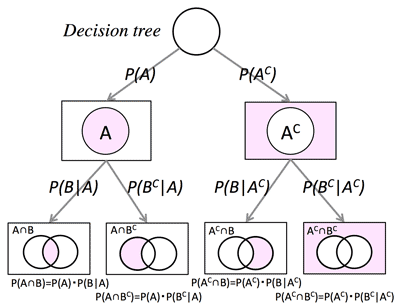
条件付き確率:
>Top 39. 複素数と図形 (Complex number & Shapes)
- $z+\bar{z},\;\;z\bar{z}=$ real number
- $\bar{\bar{z}}=z$
- $\overline{\alpha+\beta}=\bar{\alpha}+\bar{\beta},\;\;\overline{\alpha\beta}=\bar{\alpha}\bar{\beta}$
- $\overline{\frac{\alpha}{\beta}}=\frac{\bar{\alpha}}{\bar{\beta}}$
- $\overline{\alpha^n}=(\bar{\alpha})^n$
- $|z|^2=z\bar{z},\;\;n|\alpha\beta|=|\alpha||\beta|,\;\;|\frac{\alpha}{\beta}|=\frac{|\alpha|}{|\beta|}$
- Distance between 2 points: $|\overline{AB}|=|\overline{OB}-\overline{OA}|=|\beta-\alpha|$
- Imaginary Roots & Coefficients:
- $\alpha+\beta=\alpha+\bar{\alpha}=-\frac{b}{a}$
- $\alpha\beta=\alpha\bar{\alpha}=|\alpha|^2=\frac{c}{a}$
- Polar format:
- $z=r(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta,\;\; r>0$
- $r=|z|=\sqrt{a^2+b^2},\;\; \theta+2n\pi=$arg $z$
- Product & quotient of complex numbers:
- $|z_1z_2|=|z_1||z_2|,\;\; \rm{arg}(z_1z_2)=\theta_1+\theta_2=\rm{arg}\;z_1+\rm{arg}\;z_2$
- $|\frac{z_1}{z_2}|=\frac{|z_1|}{|z_2|},\;\;\rm{arg}\frac{z_1}{z_2}=\rm{arg}\;z_1-\rm{arg}\;z_2$
- where $z=r_0(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta),\;\;w=r(\cos\alpha+i\sin\alpha$
→$zw=r_0r{\cos(\theta+\alpha)+i\sin(\theta+\alpha)}$ [$\alpha$ rotation ccw]
→$\frac{z}{w}=\frac{r_0}{r}{\cos(\theta-\alpha)+i\sin(\theta-\alpha)}$ [$\alpha$ rotation clockwise]
- De Moivre's theorem: $(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)^n=\cos n\theta+i\sin n\theta$
- Triple angle formula: $\cos 3\theta+i\sin 3\theta$
$=(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)^3=\cos^3\theta+3\cos^2\theta i\sin\theta+3\cos\theta i^2\sin^2\theta+i^3\sin^3\theta$
$=(4\cos^3\theta-3\cos\theta)+i(-4\sin^3\theta+3\sin\theta)$
- Angle between two lines:
- where $C(\gamma) is the point rotated the angle of $\theta$ ccw of $B(\beta)$ around $A(\alpha)$:
→$\gamma=(\cos\thea+i\sin\theta)(\beta-\alpha)+\alpha$
- $\frac{\gamma-\alpha}{\beta-\alpha}=\cos\theta+i\sin\theta,\;\;\theta=\rm{arg}\frac{\gamma-\alpha}{\beta-\alpha}$
- Vertical condition: $\cos\theta=0\;→\frac{\gamma-\alpha}{\beta-\alpha}=r(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)
=r\sin\theta ・i=
$ pure imaginary number
- $\bar{AC}=\bar{AB}$ magnified by $r$ times, and rotated by ang $\theta$:
- $\frac{\gamma-\alpha}{\beta-\alpha}=r(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)$
$→(\gamma-\alpha)=r(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)(\beta-\alpha)$
- Equation of a line passing through point A($\alpha$) and point B($\beta$):
- $\frac{z-\alpha}{\beta-\alpha}=\overline{\frac{z-\alpha}{\beta-\alpha}}\;\;$=real number
- $\theta=\rm{arg} \frac{z-\alpha}{\beta-\alpha}=0, \; \pi$
- Equation of a line passing through point A($\alpha$) and perpendicular to $\overline{O\beta}$
- $\frac{z-\alpha}{\beta}=-overline{(\frac{z-\alpha}{\beta})}\;\;$=0 or pure imaginary number
- $\overline{O\beta}\perp\overline{\alpha z}\leftrightarrow \rm{arg}\frac{z-\alpha}{\beta}
=\pm\frac{\pi}{2}\leftrightarrow \frac{z-\alpha}{\beta}\;\;
$= pure imaginary number; $z=-\bar{z}$
- Equation of a line pependicular bisector of the line segment connecting two points of A($\alpha$) and B(\beta):
- $|z-\alpha|=|z-\beta|$
- Root of unity, 冪根:
- $z^n={r(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)}^n=r^n(\cos n\theta+i\sin n\theta)=1$
$→\;r^n=1,\; n\theta=2\pi k\;\; (k=0,1,\dots,n-1)$
$→\;r=1,\; \theta=\frac{2\pi}{n}$
$→\;z=\cos\frac{2\pi}{n}k+i\sin\frac{2\pi}{n}k\;\; (k=0,1,\dots,n-1)\;亜sxz$■
39:
- abosolute value: modulus, magnitude
$r=|z|=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}$
- argument: 偏角
- 四則演算
- (a+bi)±(c+di)=(a±c)+(bc+ad)i
- (a+bi)(c+di)=(ac-bd)+(bc+ad)i
- $\frac{a+bi}{c+di}$
$=\frac{ac+bd}{c^2+d^2}$
$+\frac{bc-ad}{c^2+d^2}i$
- $(z^n)z^m=z^{n+m}$
- $(z^n)^m=z^{nm}$
- $(zw)^n=z^nz^n$
- 共役(共軛)conjugate:
- $\overline{z±w}
$
$=\bar{z}±\bar{w}$
- $\overline{zw}
$
$=\bar{z}\bar{w}$
- $\overline{\frac{z}{w}}
$
$=\frac{\bar{z}}{\bar{w}}$
- $\overline{z^n}
$
$=(\bar{z})^n$
- 対合 involution:
$\bar{\bar{z}}=z$
- $|z|=\bar{|z|}=r$
$(z=r(\cos\theta
+i\sin\theta)
$
$z=re^{i\phi}$
- $|z|^2=z\bar{z}
=x^2+y^2
$
- $\frac{1}{z}
=\frac{\bar{z}}{|z|^2}
;\ (z\ne 0)$
- $|z|=0\Leftrightarrow z=0$
- $|zw|=|z||w|$
- $|z+w|\le|z|+|w|$
- $z_1z_2=r_1r_2$
$((\cos(\phi_1+\phi_2)$
$+i
(\sin(\phi_1+\phi_2))$
- $\frac{z_1}{z_2}
=\frac{r_1}{r_2}$
$((\cos(\phi_1-\phi_2)$
$+i
(\sin(\phi_1-\phi_2))$
- $(\cos\theta+i\sin\theta)^n$
$=(\cos n\theta+i\sin n\theta)$
- $(e^{i\theta})^n$
$
=e^{in\theta}$
>Top 40. Jacobian:
- One variable ($x→t$):
- $\int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx=\int_{\alpha}^{\beta}f(g(t))g'(t)dt\;\;\rm{where} [x|a→b; t|\alpha→\beta]$
- Jacobian: $(x,y)→(u,v)$
- $\iint_{D}f(x,y)dxdy,\; x(u,v),\;y(u,v)$
- $J=\pmatrix{\frac{\partial x}{\partial u}&\frac{\partial x}{\partial v}\\
\frac{\partial y}{\partial u}&\frac{\partial y}{\partial v}}$
- $det(J)=\begin{vmatrix}\frac{\partial x}{\partial u}&\frac{\partial x}{\partial v}\\
\frac{\partial y}{\partial u}&\frac{\partial y}{\partial v}\end{vmatrix}$
- Polar coordinates: $x=r\cos\theta,\; y=r\sin\theta$
- $\frac{\partial x}{\partial r}=\cos\theta;\;\frac{\partial x}{\partial\theta}=-r\sin\theta;$
$\frac{\partial y}{\partial r}=\sin\theta;\;\frac{\partial y}{\partial\theta}=r\cos\theta;$
- $det(J)=\begin{vmatrix}\cos\theta&-r\sin\theta\\
\sin\theta&r\cos\theta\end{vmatrix}=r\cos^2\theta+r\sin^2\theta=r$
- $→\; \iint_{D}f(x,y)dxdy=\iint_{E}f(x(r,\theta),\;y(r,\theta))・r・drd\theta$
- Normal vector:
- $\bar{r}=x(u,v)\bar{i}+y(u,v)\bar{j}+z(u,v)\bar{k}$
- $→\; \bar{n}=\frac{\frac{\partial r}{\partial u}\times\frac{\partial r}{\partial v}}
{\|\frac{\partial r}{\partial u}\times\frac{\partial r}{\partial v}\|}$
4:
- 法線ベクトル
- \frac{\partial }{\partial }
>Top 41.
4:
Comment
- In order to express mathematical formula in full expression, we need to learn LaTex and Bézier Curve.
- 数式を正しく表現するには、LaTexとペジェ曲線を学ぶ必要がある。
Title |
Mathematical Formulas |
数学公式 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Index |
|
|
||
Why? |
|
|
||
Resume |
Remarks |
Remarks |
>Top 1. 数と式 (Numbers and equation)
|
1. 数と式:
|
>Top 2. 方程式 (Equation):
|
2. 方程式: |
>Top 2b. ラジアン (Radian):
|
2b: ラジアン
|
>Top 2c. 一次変換 (Linear Transformation):
|
39: 一次変換
|
>Top 3. 三角函数 (Trigonometric function):
|
3. 三角函数:1. 正弦定理:
7. 加法定理:
8/9. 積和/和積公式:
11.三倍角公式:
|
||
正弦定理 |
余弦定理 |
三角形の面積 |
二等分線の長さ |
|
単振動
|
||
円と比例 (Circle and Proportion):
|
方冪の定理 |
||
>Top 4. 集合 (Set):
|
4. 集合:ドモルガンの定理 |
>Top 5. 論理 (Logic):
|
5. 論理:
Truth table:
|
>Top 6. 群 (Group):
|
6. 群:
|
>Top 7. 順列と組合せ (Permutation and Combination):
|
7. 順列と組合せ: |
>Top 8. 二項定理 (Binomial theorem):
|
8. 二項定理: |
>Top 9. 確率論 (Probability theory):
|
9. 確率:
|
>Top 10. 平面図形 (Plane figure):
|
10. 平面図形:中点連絡定理
|
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
|
>Top 11. ベクトル (Vector):
|
11. ベクトル:6. 直線上の点
19. 三角形の面積
|
>Top 12. ベクトル方程式 (Vector equation):
|
12. ベクトル方程式:平行直線 (Parallel line): 法線 (Normal line): |
||
3. Bisector vector: |
4. Circular equation: |
5. Set of point P: |
|
>Top 13. 空間ベクトル (Spatial vector):
|
13. 空間ベクトル:
|
|
2. Line equation: |
3. Line passes points A & B:
|
|
>Top 14. 球の方程式 (Equation of a sphere):
|
14. 球の方程式:
|
>Top 15. 平面の方程式 (Equation of a plane):
|
15. 平面の方程式:点Aを通り,$\overrightarrow{n}$ に垂直な面  |
>Top 16. 接平面 (Tangent plane)
|
16. 球と直線: |
>Top 17. 統計 (Statistics):
|
18. 統計:
|
>Top 18. 方程式の近似解 (Approximate solution):
|
18. :
|
|
Newton's method: |
Newton's method2:
|
Simpson's formula |
>Top 19. 分数函数 (Fractional function):
|
19. :Hyperbola:
|
||
Parabola: |
Circular: |
Ellipse: |
|
>Top 20. 数列 (Sequence or Progression):
|
20: |
21. >Top 無限級数 (Infinite series)
|
21: |
22. >Top 指数と対数 (Exponential and logarithm):
|
22. :
|
>Top 23. 微分法 (Differentiation):
|
23: |
|
平均値の定理
|
>Top 24. 接線の方程式等 (Equation of tangent line, etc.):
|
24: |
>Top 25. 近似式 (Approximate eqution):
|
25: |
>Top 26. 不定積分 (Indefinite integral):
|
26: |
|
|
|
Eg: $\int \ln xdx= \\ \frac{1}{3}\ln x -\int \frac{x^3}{3}\frac{1}{x}dx= \\ \frac{x^3\ln x}{3}-\frac{x^3}{9}=\\ \frac{x^3}{9}(3\ln x-1) $ |
>Top 27. 定積分 (Definite integral):
|
28: |
|
|
|
9. 積分の平均値の定理
|
>Top 28. 定積分の応用 (Application of definite integral):
|
28:3. 閉曲線の囲む面積
|
>Top 29. 体積 (Volume):
|
29:9. 側圧
|
>Top 30. 数列 (Progression):
|
30: |
>Top 31. 微分方程式 (Differential equation):
|
31:Differential equation includes some function with its derivatives (also with Nth-order having N kinds of arbitray contants): only simple differential equations are solvable by explicit formulas; includes 1) Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE), and 2) Partial Diffrential Equation (PDE). |
>Top 32. 行列式 (Determinant):
|
32: |
|
>Top 33. 点の移動 (Movement of Point):
|
33: |
>Top 34. 行列の固有値 (Eigenvalue of matrix):
|
34: |
>Top 35. 二次曲線 (Quadratic curve):
|
35:
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
>Top 36. 極座標 (Polar coordinates):
|
36:
|
|
 |
 |
 |
>Top 37. 複素数平面 (Complex plane):
|
37:
|
>Top 38. 確率分布 (Probability distribution):
|
38:樹形図:
条件付き確率:
|
>Top 39. 複素数と図形 (Complex number & Shapes)
|
39:
|
>Top 40. Jacobian:
|
4:
|
>Top 41. |
4: |
Comment |
|
|